Abstract
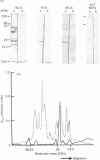
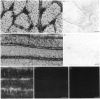
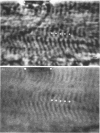
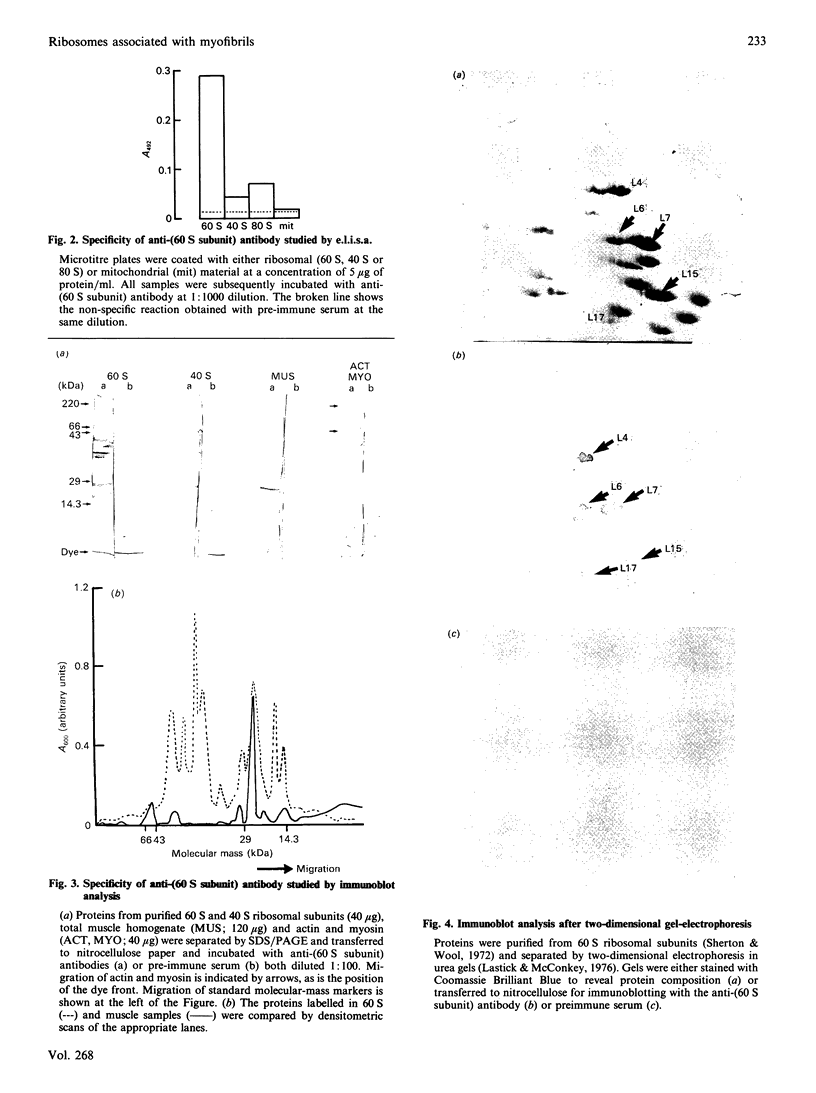
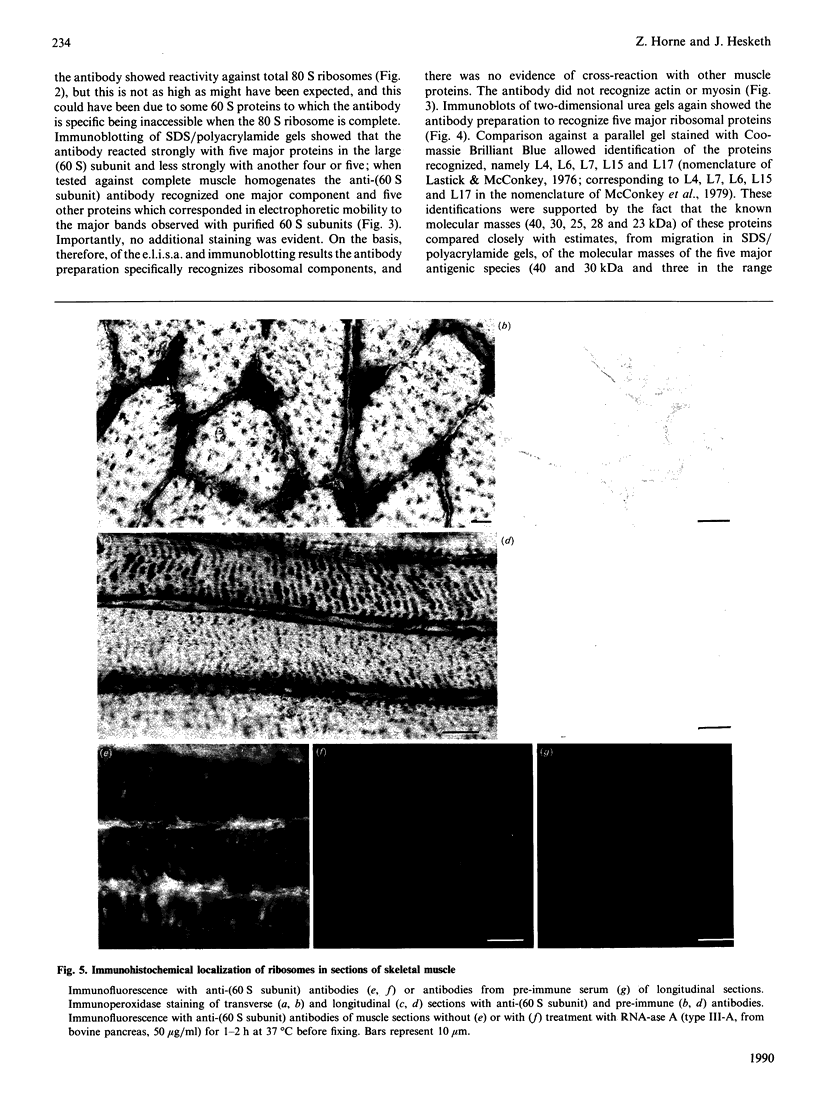
Ribosome distribution in skeletal-muscle fibres was investigated immunohistochemically by using polyclonal antibodies raised against large-ribosomal-subunit proteins isolated from rat liver. Immunoblot analysis showed the antibodies to recognize five major proteins of the large subunit; these were identified as L4, L6, L7, L15 and L17 by two-dimensional electrophoresis. Immunohistochemistry of frozen rat skeletal-muscle sections showed staining of both the subsarcolemmal and intermyofibrillar cytoplasm. A distinct banding pattern was observed, and when peroxidase and phase-contrast images of the same field were compared by image analysis the anti-ribosome staining was found to correspond to the A-bands. These results suggest that a proportion of muscle ribosomes are present in the myofibrillar cytoplasm in a regular fashion, possibly associated with myosin. Densitometric analysis of the peroxidase immunostaining showed that the ratio of myofibrillar to sub-sarcolemmal ribosomal material was lower in muscle from 51-day-old rats compared with those from 14-day-old animals.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell D. A., du Bois R. M., Butcher R. G., Poulter L. W. The density of HLA-DR antigen expression on alveolar macrophages is increased in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Jul;65(1):165–171. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galavazi G. Identification of helical polyribosomes in sections of mature skeletal muscle fibers. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1971;121(4):531–547. doi: 10.1007/BF00560158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galavazi G., Szirmai J. A. The influence of age and testosterone on the ribosomal population in the m. levator ani and a thigh muscle of the rat. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1971;121(4):548–560. doi: 10.1007/BF00560159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier G. F., Dunn R. A. Ultrastructural and cytochemical features of mammalian skeletal muscle fibres following denervation. J Cell Sci. 1973 Mar;12(2):525–547. doi: 10.1242/jcs.12.2.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier G. F., Schaeffer S. F. Ultrastructural and cytochemical manifestations of protein synthesis in the peripheral sarcoplasm of denervated and newborn skeletal muscle fibres. J Cell Sci. 1974 Jan;14(1):113–137. doi: 10.1242/jcs.14.1.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh J. E., Pryme I. F. Evidence that insulin increases the proportion of polysomes that are bound to the cytoskeleton in 3T3 fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 11;231(1):62–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80703-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heywood S. M., Dowben R. M., Rich A. A study of muscle polyribosomes and the coprecipitation of polyribosomes with myosin. Biochemistry. 1968 Sep;7(9):3289–3296. doi: 10.1021/bi00849a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyhse-Andersen J. Electroblotting of multiple gels: a simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide to nitrocellulose. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 Dec;10(3-4):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson P. F., Hudgson P., Walton J. N. Morphological relationship of polyribosomes and myosin filaments in deeloping and regenerating skeletal muscle. Nature. 1969 Jun 21;222(5199):1168–1169. doi: 10.1038/2221168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lastick S. M., McConkey E. H. Exchange and stability of HeLa ribosomal proteins in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 25;251(10):2867–2875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leader D. P., Rankine A. D., Coia A. A. The phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in baby hamster kidney fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 23;71(4):966–974. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90749-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. E., Kelly F. J., Goldspink D. F. Pre- and post-natal growth and protein turnover in smooth muscle, heart and slow- and fast-twitch skeletal muscles of the rat. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 15;217(2):517–526. doi: 10.1042/bj2170517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIHALYI E., LAKI K., KNOLLER M. I. Nucleic acid and nucleotide content of myosin preparations. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 May;68(1):130–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90333-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion M. J., Marion C. Localization of ribosomal proteins on the surface of mammalian 60S ribosomal subunits by means of immobilized enzymes. Correlation with chemical cross-linking data. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 31;149(3):1077–1083. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90518-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey E. H., Bielka H., Gordon J., Lastick S. M., Lin A., Ogata K., Reboud J. P., Traugh J. A., Traut R. R., Warner J. R. Proposed uniform nomenclature for mammalian ribosomal proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 16;169(1):1–6. doi: 10.1007/BF00267538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metlas R., Popić S., Kanazir D. Preparation of ribosomal subunits from rat liver postmitochondrial supernatant. Anal Biochem. 1973 Oct;55(2):539–543. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90142-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P., Goelz S., Trachsel H. The role of the cytoskeleton in eukaryotic protein synthesis. (A minireview). Cell Biol Int Rep. 1983 Apr;7(4):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(83)90057-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY S. V. The adenosinetriphosphatase activity of lipoprotein granules isolated from skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1952;8(5):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(52)90081-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY S. V. The chromatography of L-myosin on diethylaminoethylcellulose. Biochem J. 1960 Jan;74:94–101. doi: 10.1042/bj0740094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padykula H. A., Gauthier G. F. The ultrastructure of the neuromuscular junctions of mammalian red, white, and intermediate skeletal muscle fibers. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jul;46(1):27–41. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaekers F. C., Benedetti E. L., Dunia I., Vorstenbosch P., Bloemendal H. Polyribosomes associated with microfilaments in cultured lens cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 9;740(4):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherton C. C., Wool I. G. Determination of the number of proteins in liver ribosomes and ribosomal subunits by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4460–4467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zak R., Rabinowitz M., Platt C. Ribonucleic acids associated with myofibrils. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2493–2499. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]