Abstract
The role of Ins(1,4,5)P3 in receptor-induced Ca2+ mobilization in pituitary cells was studied at the single-cell level. Experimental strategies were developed which allowed a comparative analysis of the effects of Ins(1,4,5)P3 with those of receptor activation under identical conditions. These include microfluorimetry as well as a novel technique which permits the controlled and rapid application of intracellular messenger molecules to individual cells. This latter approach is based on the tight-seal whole-cell recording (WCR) technique, and utilizes two patch-clamp micropipettes, one for electrical recording and the second for the controlled pressure injection. Ins(1,4,5)P3, when applied with this dual-WCR (DWCR) technique, leads rapidly to a marked rise in cytosolic free Ca2+ [( Ca2+]i) and a concomitant stimulation of Ca2(+)-activated K+ current; Ins(1,4,5)P3 can thus mimic the effects of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) in the same cells under identical conditions. In cells dialysed intracellularly with heparin, a potent antagonist of Ins(1,4,5)P3 action, the rapid response to extracellular stimulation with TRH was abolished, as were the effects of intracellular application of Ins(1,4,5)P3. Heparin, which abolished Ins(1,4,5)P3 action completely, blocked responses to TRH in some cells only partially, revealing that Ca2+ mobilization response to TRH is in part slower in onset than the response to Ins(1,4,5)P3. It is concluded (1) that Ins(1,4,5)P3 is an essential element for the action of TRH, providing a rapid mechanism for Ca2+ mobilization induced by the releasing hormone and (2) that TRH action in mobilizing intracellular Ca2+ is sustained by a slower mechanism which is independent of Ins(1,4,5)P3.
Full text
PDF
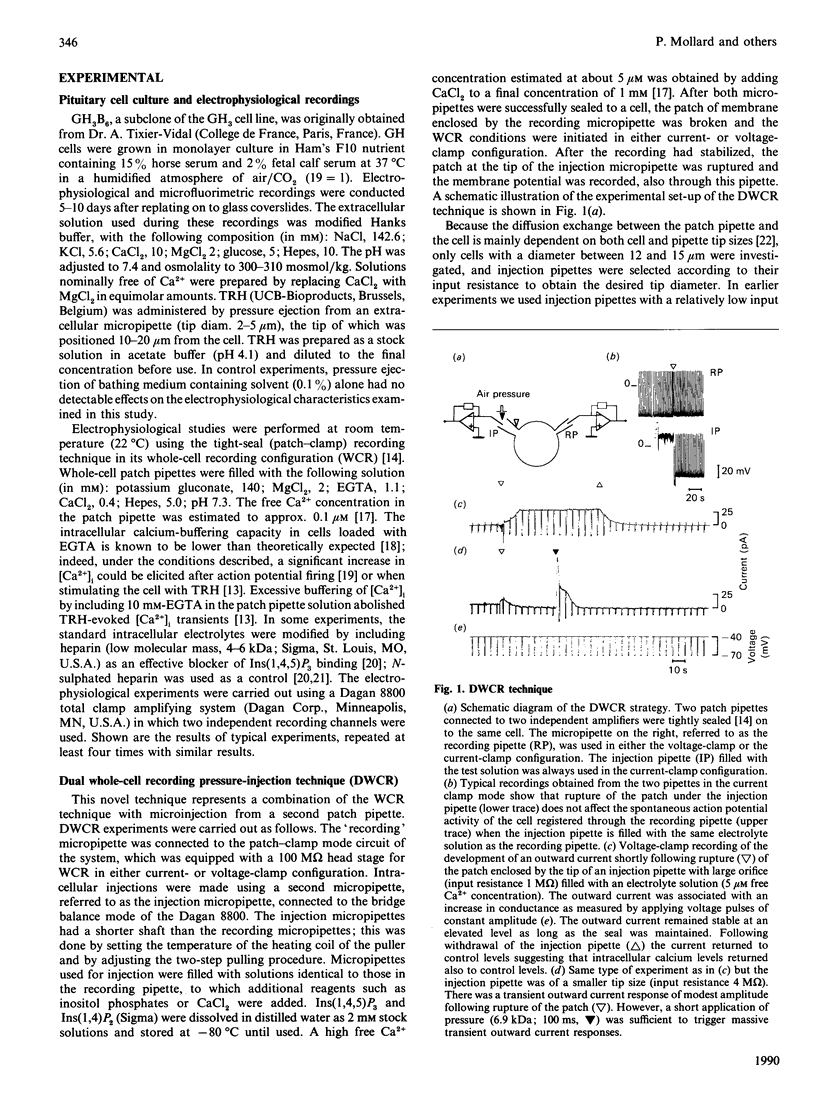
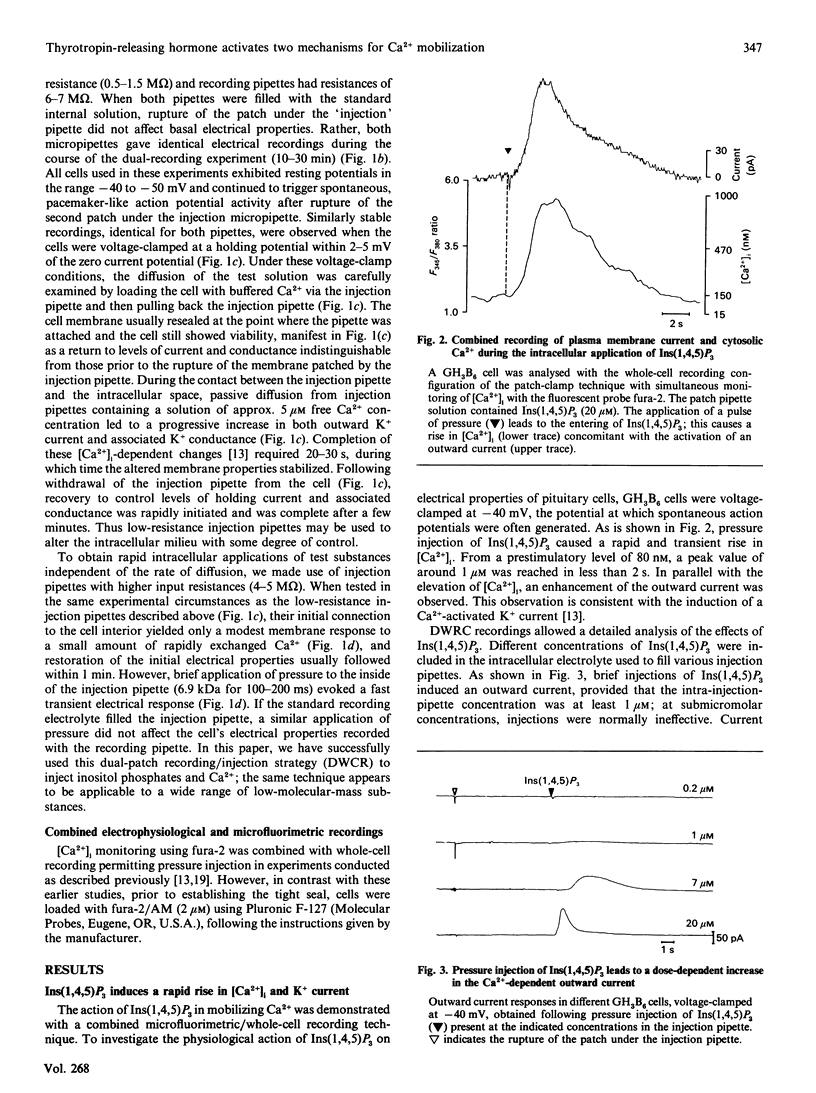





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abercrombie R. F., Masukawa L. M., Sjodin R. A., Livengood D. Uptake and release of 45Ca by Myxicola axoplasm. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Oct;78(4):413–429. doi: 10.1085/jgp.78.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aizawa T., Hinkle P. M. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rapidly stimulates a biphasic secretion of prolactin and growth hormone in GH4C1 rat pituitary tumor cells. Endocrinology. 1985 Jan;116(1):73–82. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert P. R., Tashjian A. H., Jr Thyrotropin-releasing hormone-induced spike and plateau in cytosolic free Ca2+ concentrations in pituitary cells. Relation to prolactin release. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5827–5832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Neher E. The Ca signal from fura-2 loaded mast cells depends strongly on the method of dye-loading. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. L., Dufy B., Harrington J. W., Harrison N. L., MacDermott A. B., MacDonald J. F., Owen D. G., Vicini S. Signals transduced by gamma-aminobutyric acid in cultured central nervous system neurons and thyrotropin releasing hormone in clonal pituitary cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;494:1–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb29477.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate-induced membrane potential oscillations in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1988 Sep;403:589–599. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biden T. J., Wollheim C. B., Schlegel W. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis in clonal pituitary cells (GH3). Translocation of Ca2+ into mitochondria from a functionally discrete portion of the nonmitochondrial store. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7223–7229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changya L., Gallacher D. V., Irvine R. F., Petersen O. H. Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate act by different mechanisms when controlling Ca2+ in mouse lacrimal acinar cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81425-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chueh S. H., Mullaney J. M., Ghosh T. K., Zachary A. L., Gill D. L. GTP- and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-activated intracellular calcium movements in neuronal and smooth muscle cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13857–13864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich B. E., Watras J. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate activates a channel from smooth muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):583–586. doi: 10.1038/336583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. G., Marty A. Calcium-dependent chloride currents in isolated cells from rat lacrimal glands. J Physiol. 1986 Sep;378:437–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershengorn M. C., Geras E., Purrello V. S., Rebecchi M. J. Inositol trisphosphate mediates thyrotropin-releasing hormone mobilization of nonmitochondrial calcium in rat mammotropic pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10675–10681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershengorn M. C. Mechanism of thyrotropin releasing hormone stimulation of pituitary hormone secretion. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:515–526. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.002503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershengorn M. C. Mechanism of thyrotropin releasing hormone stimulation of pituitary hormone secretion. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:515–526. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.002503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershengorn M. C., Thaw C. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) stimulates biphasic elevation of cytoplasmic free calcium in GH3 cells. Further evidence that TRH mobilizes cellular and extracellular Ca2+. Endocrinology. 1985 Feb;116(2):591–596. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-2-591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh T. K., Eis P. S., Mullaney J. M., Ebert C. L., Gill D. L. Competitive, reversible, and potent antagonism of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-activated calcium release by heparin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11075–11079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh T. K., Mullaney J. M., Tarazi F. I., Gill D. L. GTP-activated communication between distinct inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive and -insensitive calcium pools. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):236–239. doi: 10.1038/340236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. L., Ueda T., Chueh S. H., Noel M. W. Ca2+ release from endoplasmic reticulum is mediated by a guanine nucleotide regulatory mechanism. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):461–464. doi: 10.1038/320461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemette G., Balla T., Baukal A. J., Catt K. J. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate binds to a specific receptor and releases microsomal calcium in the anterior pituitary gland. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8195–8199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao J. P., Harootunian A. T., Tsien R. Y. Photochemically generated cytosolic calcium pulses and their detection by fluo-3. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8179–8184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V. Guanine nucleotide- and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced calcium release in rabbit main pulmonary artery. J Physiol. 1988 Sep;403:601–619. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolesnick R. N., Musacchio I., Thaw C., Gershengorn M. C. Arachidonic acid mobilizes calcium and stimulates prolactin secretion from GH3 cells. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 1):E458–E462. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.246.5.E458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Gardner P. Ion channels activated by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in plasma membrane of human T-lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):301–304. doi: 10.1038/326301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llano I., Marty A., Tanguy J. Dependence of intracellular effects of GTP gamma S and inositoltrisphosphate on cell membrane potential and on external Ca ions. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Aug;409(4-5):499–506. doi: 10.1007/BF00583807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macphee C. H., Drummond A. H. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone stimulates rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate in GH3 pituitary tumor cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;25(2):193–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rapidly activates the phosphodiester hydrolysis of polyphosphoinositides in GH3 pituitary cells. Evidence for the role of a polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C in hormone action. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14816–14822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Holowka D., Stryer L. Highly cooperative opening of calcium channels by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):653–656. doi: 10.1126/science.2452482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollard P., Vacher P., Dufy B., Winiger B. P., Schlegel W. Inhibitors of 1,2-diacylglycerol kinase potentiate the TRH-induced stimulation of Ca2+-activated K+ current. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Mar 7;172(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(89)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollard P., Vacher P., Dufy B., Winiger B. P., Schlegel W. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone-induced rise in cytosolic calcium and activation of outward K+ current monitored simultaneously in individual GH3B6 pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19570–19576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. P., Gallacher D. V., Irvine R. F., Petersen O. H. Synergism of inositol trisphosphate and tetrakisphosphate in activating Ca2+-dependent K+ channels. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):653–655. doi: 10.1038/330653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muallem S., Pandol S. J., Beeker T. G. Hormone-evoked calcium release from intracellular stores is a quantal process. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):205–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muallem S., Pandol S. J., Beeker T. G. Two components of hormone-evoked calcium release from intracellular stores of pancreatic acinar cells. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):301–307. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullaney J. M., Yu M., Ghosh T. K., Gill D. L. Calcium entry into the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-releasable calcium pool is mediated by a GTP-regulatory mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2499–2503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R., Matthews G., Neher E. Regulation of calcium influx by second messengers in rat mast cells. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):499–504. doi: 10.1038/334499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusch M., Neher E. Rates of diffusional exchange between small cells and a measuring patch pipette. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Feb;411(2):204–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00582316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel W., Roduit C., Zahnd G. R. Polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis by phospholipase C is accelerated by thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) in clonal rat pituitary cells (GH3 cells). FEBS Lett. 1984 Mar 12;168(1):54–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel W., Winiger B. P., Mollard P., Vacher P., Wuarin F., Zahnd G. R., Wollheim C. B., Dufy B. Oscillations of cytosolic Ca2+ in pituitary cells due to action potentials. Nature. 1987 Oct 22;329(6141):719–721. doi: 10.1038/329719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel W., Wollheim C. B. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone increases cytosolic free Ca2+ in clonal pituitary cells (GH3 cells): direct evidence for the mobilization of cellular calcium. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):83–87. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soejima M., Noma A. Mode of regulation of the ACh-sensitive K-channel by the muscarinic receptor in rabbit atrial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Apr;400(4):424–431. doi: 10.1007/BF00587544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supattapone S., Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Snyder S. H. Solubilization, purification, and characterization of an inositol trisphosphate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1530–1534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Heslop J. P., Berridge M. J. Subsecond and second changes in inositol polyphosphates in GH4C1 cells induced by thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 1;243(1):305–308. doi: 10.1042/bj2430305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tones M. A., Bootman M. D., Higgins B. F., Lane D. A., Pay G. F., Lindahl U. The effect of heparin on the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor in rat liver microsomes. Dependence on sulphate content and chain length. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 31;252(1-2):105–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80898-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacher P., McKenzie J., Dufy B. Arachidonic acid affects membrane ionic conductances of GH3 pituitary cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 1):E203–E211. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.257.2.E203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe P., Krause K. H., Hashimoto S., Zorzato F., Pozzan T., Meldolesi J., Lew D. P. "Calciosome," a cytoplasmic organelle: the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ store of nonmuscle cells? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1091–1095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. W., Somlyo A. V., Goldman Y. E., Somlyo A. P., Trentham D. R. Kinetics of smooth and skeletal muscle activation by laser pulse photolysis of caged inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1987 May 21;327(6119):249–252. doi: 10.1038/327249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winiger B. P., Schlegel W. Rapid transient elevations of cytosolic calcium triggered by thyrotropin releasing hormone in individual cells of the pituitary line GH3B6. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):161–167. doi: 10.1042/bj2550161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. A., Florholmen J., Colca J. R., McDaniel M. L. GTP mobilization of Ca2+ from the endoplasmic reticulum of islets. Comparison with myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 15;242(1):137–141. doi: 10.1042/bj2420137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Supattapone S., Wilson V. S., Snyder S. H. Characterization of inositol trisphosphate receptor binding in brain. Regulation by pH and calcium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12132–12136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



