Abstract
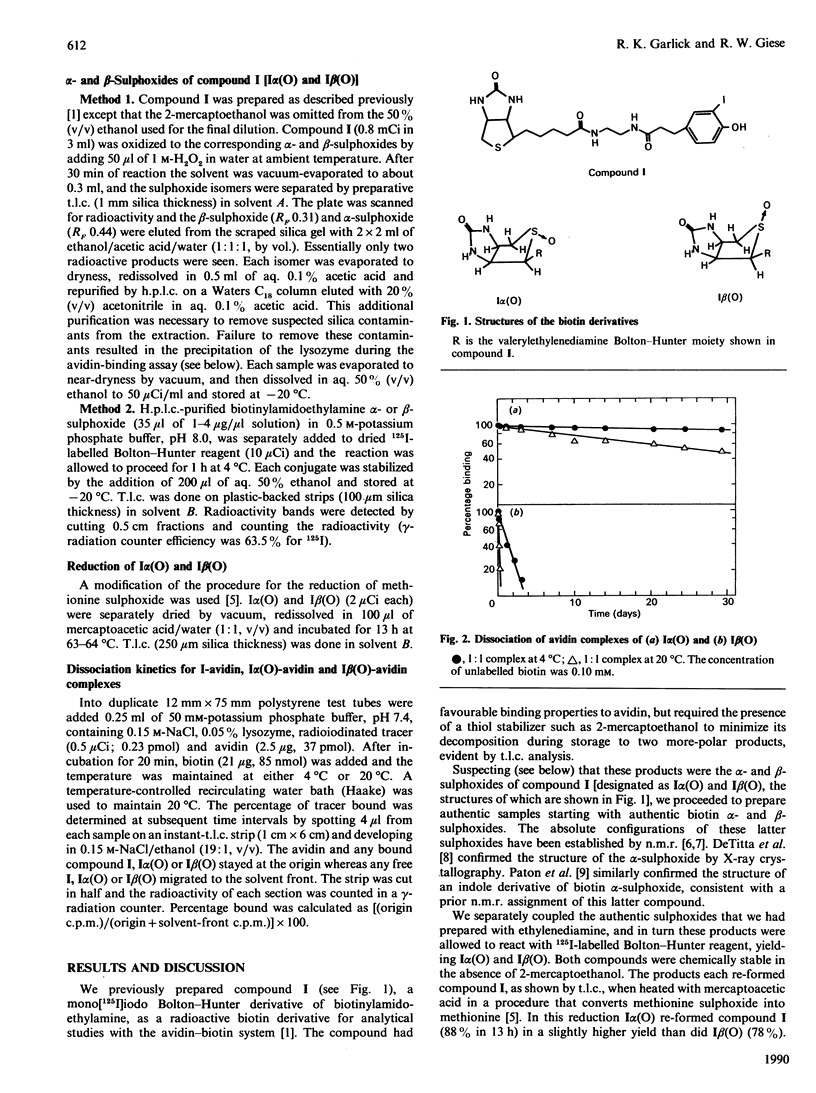
Previously we reported the dissociative binding of biotinylamidoethyl-3-(4-hydroxy-3-[125I]iodophenyl)propionamide to avidin [Garlick & Giese (1988) J. Biol. Chem. 263, 210-215]. In the present paper we report the corresponding binding of the alpha- and beta-sulphoxides of this parent compound to avidin. The 1:1 complex (obtained with avidin in excess) of the alpha-sulphoxide derivative with avidin has a dissociation half-life (t1/2) of 25 days, only 1.6 times as fast as the parent compound (t1/2 41 days). However, the corresponding beta-sulphoxide dissociates 446 times faster (t1/2 0.092 day) than the parent compound, this apparently being due to a steric effect. The alpha-sulphoxide is attractive as a tracer reagent to facilitate studies and applications of the avidin-biotin system.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argaraña C. E., Kuntz I. D., Birken S., Axel R., Cantor C. R. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the streptavidin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1871–1882. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeTitta G. T., Parthasarathy R., Blessing R. H., Stallings W. Carboxybiotin translocation mechanisms suggested by diffraction studies of biotin and its vitamers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):333–337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick R. K., Giese R. W. Avidin binding of radiolabeled biotin derivatives. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):210–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A., Li C. H. Reduction of sulfoxides in peptides and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:549–559. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELVILLE D. B. Biotin sulfoxide. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jun;208(2):495–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick D. B., Roth J. A. Specificity, stereochemistry, and mechanism of the color reaction between p-dimethylaminocinnamalhyde and biotin analogs. Anal Biochem. 1970 Mar;34:226–236. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90102-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P. C., Ohlendorf D. H., Wendoloski J. J., Salemme F. R. Structural origins of high-affinity biotin binding to streptavidin. Science. 1989 Jan 6;243(4887):85–88. doi: 10.1126/science.2911722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


