Abstract
Glycation of human erythrocyte membrane proteins was induced by incubation in vitro with high concentrations (80 mM or 200 mM) of D-glucose for 3 or 6 days. The extent of glycation was quantified from the covalent incorporation of 3H by reduction of the glucose glycation products with NaB3H4. For membranes incubated for 3 days with 80 mM-D-glucose, glycation in vitro of Band 4.5 (containing the glucose transporter) was equivalent to 0.11 mol of glucose/mol of glucose transporter, compared with 3H labelling in 3-day-incubated control membranes of 0.055 mol of glucose/mol of glucose transporter. In membranes incubated for 6 days with 200 mM-D-glucose, glycation increased to 0.21 mol of glucose/mol of glucose transporter, whereas the controls without glucose had 0.11 mol of glucose/mol of glucose transporter. Glycation in vitro was accompanied by a fall in the Bmax of binding of [3H]cytochalasin B (a competitive inhibitor of glucose transport), without any change in the binding affinity. The data suggest that glycated glucose transporters have decreased ability to bind cytochalasin B. It is proposed that glycation can alter glucose transporter activity.
Full text
PDF



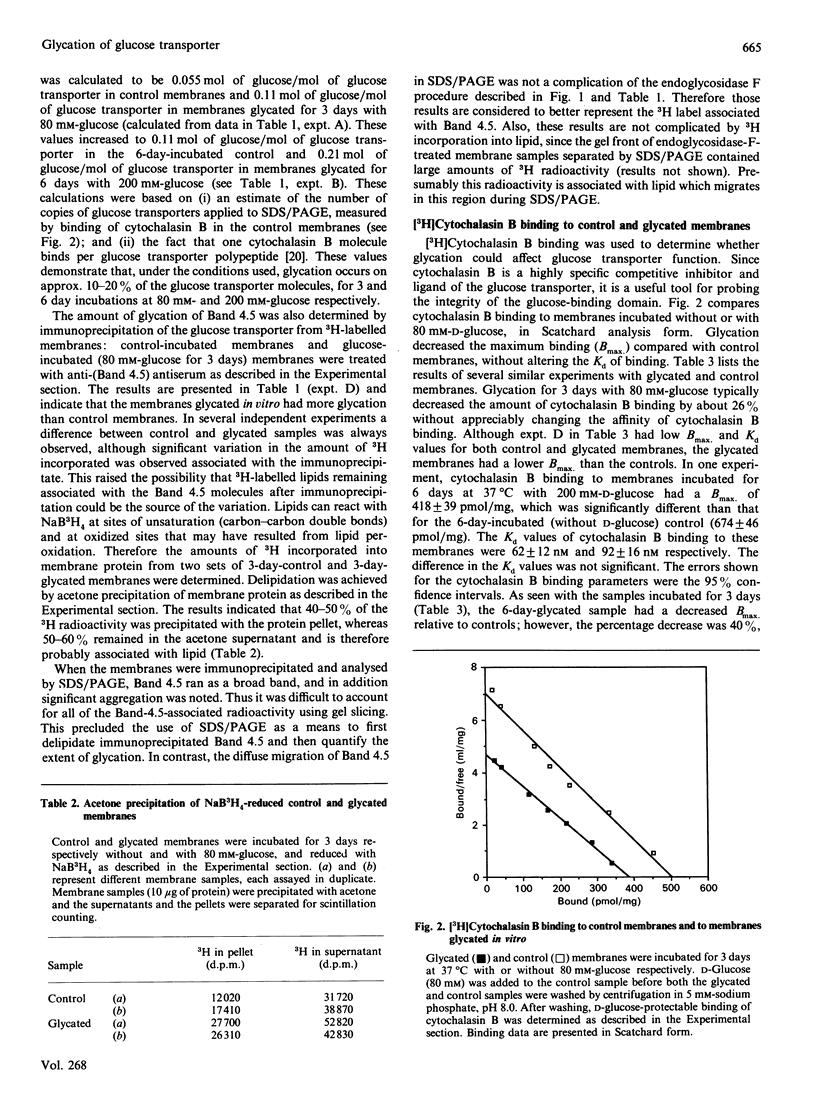
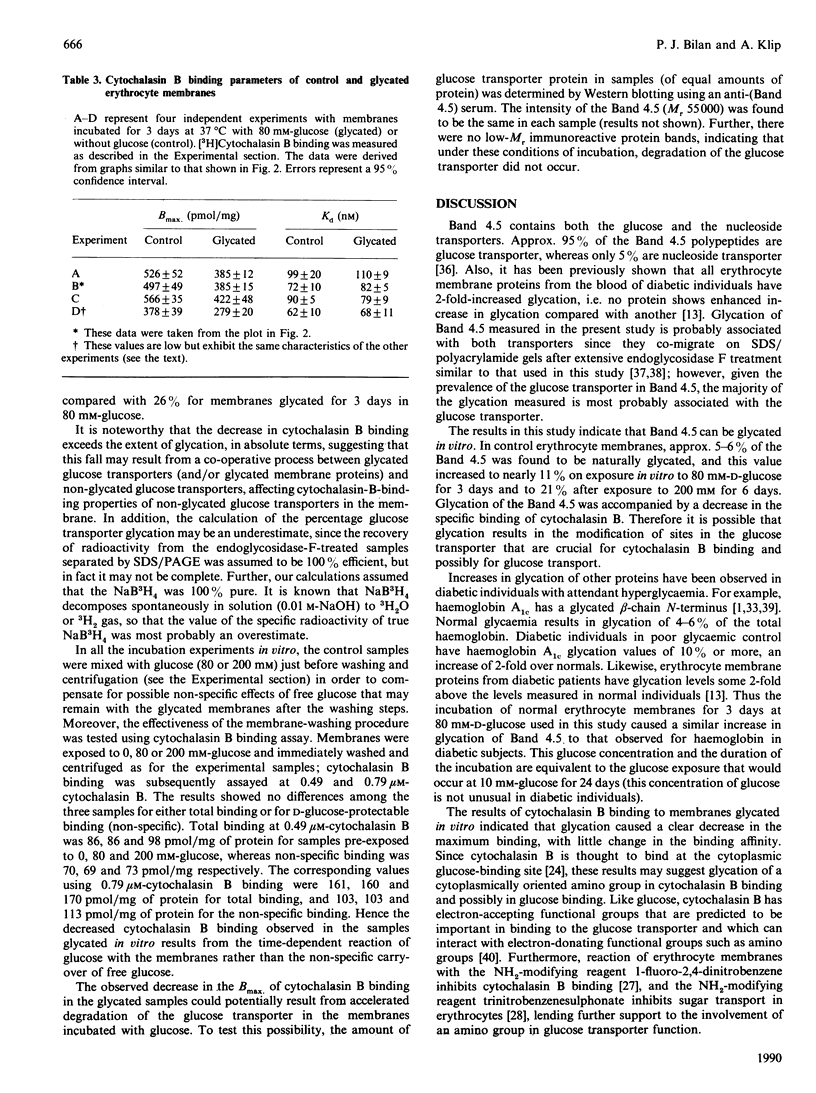

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin S. A., Baldwin J. M., Lienhard G. E. Monosaccharide transporter of the human erythrocyte. Characterization of an improved preparation. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 3;21(16):3836–3842. doi: 10.1021/bi00259a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin S. A., Lienhard G. E. Immunological identification of the human erythrocyte monosaccharide transporter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jun 30;94(4):1401–1408. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90575-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookchin R. M., Gallop P. M. Structure of hemoglobin AIc: nature of the N-terminal beta chain blocking group. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jul 11;32(1):86–93. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee M., Cerami A. The biochemistry of the complications of diabetes mellitus. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:385–432. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn H. F., Gabbay K. H., Gallop P. M. The glycosylation of hemoglobin: relevance to diabetes mellitus. Science. 1978 Apr 7;200(4337):21–27. doi: 10.1126/science.635569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn H. F., Haney D. N., Gabbay K. H., Gallop P. M. Further identification of the nature and linkage of the carbohydrate in hemoglobin A1c. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):103–109. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90289-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn H. F., Shapiro R., McManus M., Garrick L., McDonald M. J., Gallop P. M., Gabbay K. H. Structural heterogeneity of human hemoglobin A due to nonenzymatic glycosylation. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3892–3898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerami A., Stevens V. J., Monnier V. M. Role of nonenzymatic glycosylation in the development of the sequelae of diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 1979 Apr;28(4 Suppl 1):431–437. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon H. B. A reaction of glucose with peptides. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;129(1):203–208. doi: 10.1042/bj1290203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick R. L., Mazer J. S. The principal site of nonenzymatic glycosylation of human serum albumin in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6142–6146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonen B., Baenziger J., Schonfeld G., Jacobson D., Farrar P. Nonenzymatic glycosylation of low density lipoproteins in vitro. Effects on cell-interactive properties. Diabetes. 1981 Oct;30(10):875–878. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.10.875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. F., Rampal A. L., Jung C. Y. Inhibition of glucose transport in human erythrocytes by cytochalasins: A model based on diffraction studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3759–3763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundberg C. M., Anderson M., Dickson I., Gallop P. M. "Glycated" osteocalcin in human and bovine bone. The effect of age. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14557–14561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman G. D., Rees W. D. Photolabelling of the hexose transporter at external and internal sites: fragmentation patterns and evidence for a conformational change. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Mar 12;897(3):395–405. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90437-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist W. R., Schroeder W. A. A new N-terminal blocking group involving a Schiff base in hemoglobin AIc. Biochemistry. 1966 Aug;5(8):2489–2503. doi: 10.1021/bi00872a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara M., Hinkle P. C. Reconstitution and purification of the D-glucose transporter from human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7384–7390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Deziel M., Walkert D. Chemical identity of the glucose transporter with the [3H]cytochalasin B-photolabelled component of human erythrocyte membranes. Equal sensitivity to trypsin and endoglycosidase F. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):218–224. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90462-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Walker D., Cohen A., Leung C. Y. Chemical and genetic comparison of the glucose and nucleoside transporters. Biochem Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;64(11):1170–1180. doi: 10.1139/o86-154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig R. J., Peterson C. M., Jones R. L., Saudek C., Lehrman M., Cerami A. Correlation of glucose regulation and hemoglobin AIc in diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1976 Aug 19;295(8):417–420. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197608192950804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupka R. M., Devés R. Asymmetric binding of steroids to internal and external sites in the glucose carrier of erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 8;598(1):134–144. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90271-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong F. Y., Baldwin S. A., Scudder P. R., Jarvis S. M., Choy M. Y., Young J. D. Erythrocyte nucleoside and sugar transport. Endo-beta-galactosidase and endoglycosidase-F digestion of partially purified human and pig transporter proteins. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):349–356. doi: 10.1042/bj2400349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong F. Y., Davies A., Tse C. M., Young J. D., Henderson P. J., Baldwin S. A. Purification of the human erythrocyte nucleoside transporter by immunoaffinity chromatography. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):243–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lienhard G. E., Crabb J. H., Ransome K. J. Endoglycosidase f cleaves the oligosaccharides from the glucose transporter of the human erythrocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 25;769(2):404–410. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90324-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lienhard G. E., Gorga F. R., Orasky J. E., Jr, Zoccoli M. A. Monosaccharide transport system of the human erythrocyte. Identification of the cytochalasin B binding component. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 1;16(22):4921–4926. doi: 10.1021/bi00641a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald M. J., Bleichman M., Bunn H. F., Noble R. W. Functional properties of the glycosylated minor components of human adult hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):702–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. A., Gravallese E., Bunn H. F. Nonenzymatic glycosylation of erythrocyte membrane proteins. Relevance to diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Apr;65(4):896–901. doi: 10.1172/JCI109743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M., Caruso C., Baldwin S. A., Panico M., Blench I., Morris H. R., Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E., Lodish H. F. Sequence and structure of a human glucose transporter. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):941–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3839598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampal A. L., Jung C. Y. Substrate-induced conformational change of human erythrocyte glucose transporter: inactivation by alkylating reagents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jan 26;896(2):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90189-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins S. P., Bailey A. J. Age-related changes in collagen: the identification of reducible lysine-carbohydrate condensation products. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 11;48(1):76–84. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90346-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogozinski S., Blumenfeld O. O., Seifter S. The nonenzymatic glycosylation of collagen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Mar;221(2):428–437. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90161-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Kant J. A. Preparation of impermeable ghosts and inside-out vesicles from human erythrocyte membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:172–180. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens V. J., Rouzer C. A., Monnier V. M., Cerami A. Diabetic cataract formation: potential role of glycosylation of lens crystallins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2918–2922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlassara H., Brownlee M., Cerami A. Excessive nonenzymatic glycosylation of peripheral and central nervous system myelin components in diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1983 Jul;32(7):670–674. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.7.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins N. G., Thorpe S. R., Baynes J. W. Glycation of amino groups in protein. Studies on the specificity of modification of RNase by glucose. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10629–10636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoccoli M. A., Baldwin S. A., Lienhard G. E. The monosaccharide transport system of the human erythrocyte. Solubilization and characterization on the basis of cytochalasin B binding. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6923–6930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



