Abstract
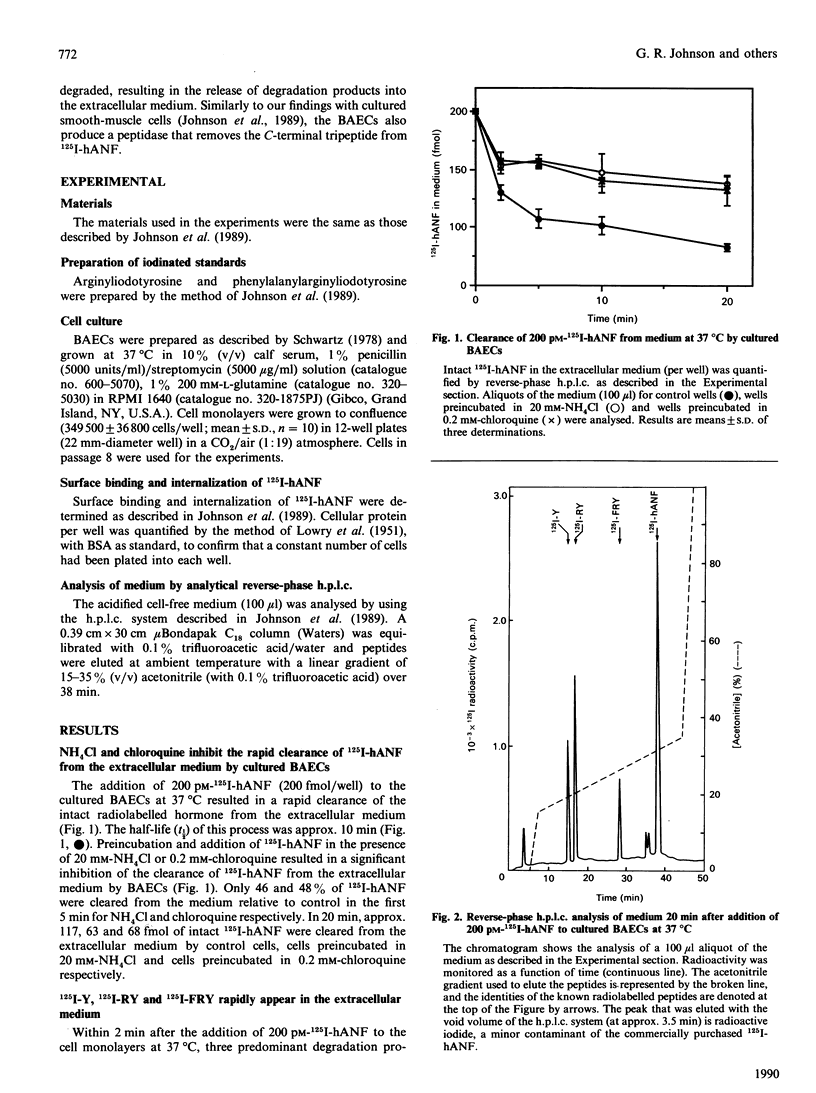
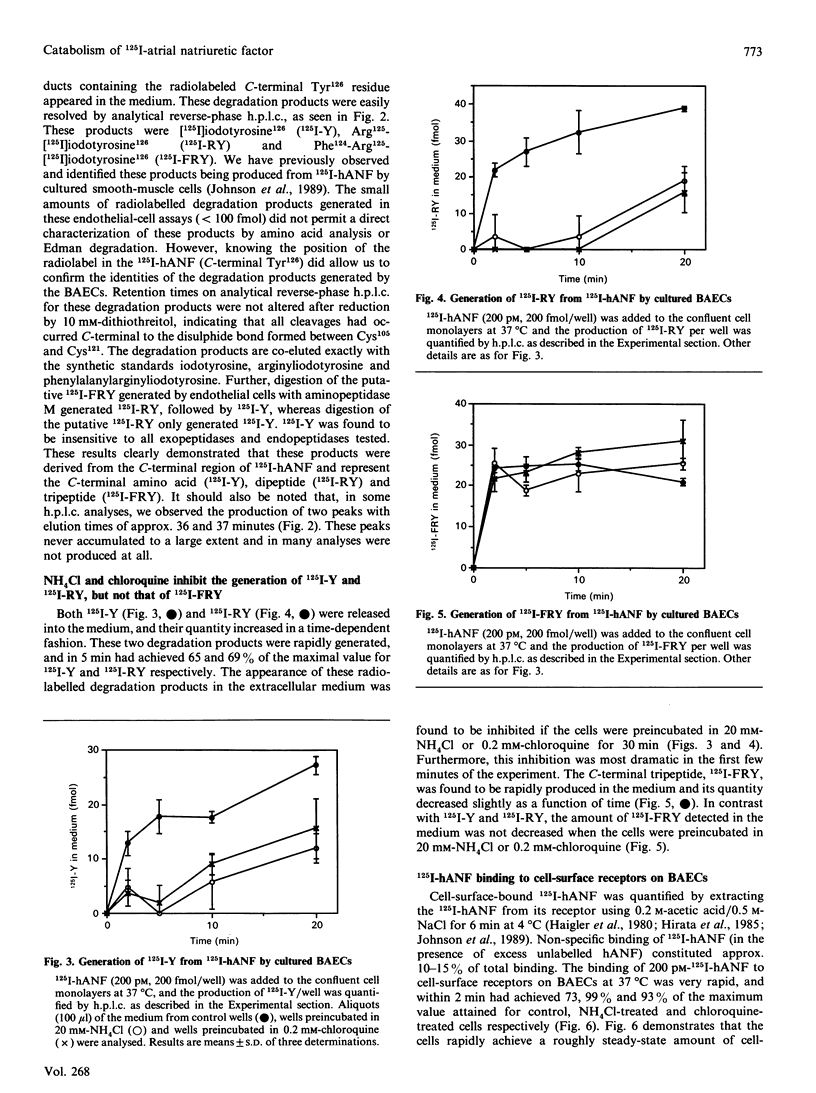
The binding, internalization and degradation of 200 pM monoiodinated human atrial natriuretic factor-(99-126) (125I-hANF) by cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells (BAECs) were studied at 37 degrees C. 125I-hANF was rapidly cleared from the extracellular medium (t1/2 approximately 10 min), whereas preincubation of the cells in the presence of 20 mM-NH4Cl or 0.2 mM-chloroquine resulted in a significant inhibition of this process. The BAECs rapidly produce three major degradation products of 125I-hANF, namely [125I]iodotyrosine 126 (125I-Y), Arg125-[125I]iodotyrosine126 (125I-RY) and Phe124-Arg125-[125I]iodotyrosine126(125I-FRY), which were detected in the extracellular medium. NH4Cl and chloroquine acted to inhibit the generation of 125I-Y and 125I-RY, but not that of 125I-FRY. Furthermore, excess unlabelled hANF (300 nM) completely blocked the rapid production of 125I-Y and 125I-RY in the first 5 min, but only partially (49%) inhibited the generation of 125I-FRY. Thus, in contrast with our previous findings with cultured smooth-muscle cells [Johnson, Arik & Foster (1989) J. Biol. Chem. 264, 11637-11642], BAECs bind, internalize and rapidly degrade 125I-hANF, resulting in the release of 125I-Y and 125I-RY into the extracellular medium. Similarly to smooth-muscle cells, the BAECs generate 125I-FRY from 125I-hANF via an extracellular proteolytic event. The rapidity of the receptor-mediated process and its sensitivity to NH4Cl and chloroquine suggest that the 125I-hANF is proteolytically processed in the endosomes of BAECs and that its receptors cycle between the cell surface and intracellular stores.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballerman B. J., Brenner B. M. Biologically active atrial peptides. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2041–2048. doi: 10.1172/JCI112206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantin M., Genest J. The heart and the atrial natriuretic factor. Endocr Rev. 1985 Spring;6(2):107–127. doi: 10.1210/edrv-6-2-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A., Schwartz A. L., Dautry-Varsat A., Lodish H. F. Kinetics of internalization and recycling of transferrin and the transferrin receptor in a human hepatoma cell line. Effect of lysosomotropic agents. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9681–9689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Léan A., Gutkowska J., McNicoll N., Schiller P. W., Cantin M., Genest J. Characterization of specific receptors for atrial natriuretic factor in bovine adrenal zona glomerulosa. Life Sci. 1984 Dec 3;35(23):2311–2318. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90522-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean R. T., Jessup W., Roberts C. R. Effects of exogenous amines on mammalian cells, with particular reference to membrane flow. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 1;217(1):27–40. doi: 10.1042/bj2170027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn W. A., Connolly T. P., Hubbard A. L. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of epidermal growth factor by rat hepatocytes: receptor pathway. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):24–36. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., Maxfield F. R., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Dansylcadaverine inhibits internalization of 125I-epidermal growth factor in BALB 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1239–1241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamet P., Tremblay J., Pang S. C., Garcia R., Thibault G., Gutkowska J., Cantin M., Genest J. Effect of native and synthetic atrial natriuretic factor on cyclic GMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 17;123(2):515–527. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90260-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamet P., Tremblay J., Pang S. C., Skuherska R., Schiffrin E. L., Garcia R., Cantin M., Genest J., Palmour R., Ervin F. R. Cyclic GMP as mediator and biological marker of atrial natriuretic factor. J Hypertens Suppl. 1986 Jun;4(2):S49–S56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. B., Wilson I. B. Atrial tissue contains a metallo dipeptidyl carboxyhydrolase not present in ventricular tissue: partial purification and characterization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Sep;233(2):667–675. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90493-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslanger M. F., Sybertz E. J., Neustadt B. R., Smith E. M., Nechuta T. L., Berger J. Carboxyalkyl dipeptides with atrial natriuretic factor potentiating and antihypertensive activity. J Med Chem. 1989 Apr;32(4):737–739. doi: 10.1021/jm00124a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata Y., Takata S., Tomita M., Takaichi S. Binding, internalization, and degradation of atrial natriuretic peptide in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells of rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Nov 15;132(3):976–984. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91903-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori R., Inui K., Saito H., Matsukawa Y., Okumura K., Nakao K., Morii N., Imura H. Specific receptors for atrial natriuretic polypeptide on basolateral membranes isolated from rat renal cortex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jun 28;129(3):773–779. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91959-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagami T. Atrial natriuretic factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3043–3046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. R., Arik L., Foster C. J. Metabolism of 125I-atrial natriuretic factor by vascular smooth muscle cells. Evidence for a peptidase that specifically removes the COOH-terminal tripeptide. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11637–11642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangawa K., Tawaragi Y., Oikawa S., Mizuno A., Sakuragawa Y., Nakazato H., Fukuda A., Minamino N., Matsuo H. Identification of rat gamma atrial natriuretic polypeptide and characterization of the cDNA encoding its precursor. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):152–155. doi: 10.1038/312152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Stephenson S. L. Role of endopeptidase-24.11 in the inactivation of atrial natriuretic peptide. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 9;232(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80375-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Van Renswoude J., Ashwell G., Kempf C., Schechter A. N., Dean A., Bridges K. R. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin in K562 cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4715–4724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehn J. A., Norman J. A., Jones B. N., LeSueur L., Sakane Y., Ghai R. D. Degradation of atrial natriuretic factor by kidney cortex membranes. Isolation and characterization of the primary proteolytic product. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11623–11627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitman D. C., Andresen J. W., Kuno T., Kamisaki Y., Chang J. K., Murad F. Identification of multiple binding sites for atrial natriuretic factor by affinity cross-linking in cultured endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11650–11655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitman D. C., Murad F. Comparison of binding and cyclic GMP accumulation by atrial natriuretic peptides in endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 23;885(1):74–79. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Lang R. E., Aronoff G. R., Ruskoaho H., Toth M., Ganten D., Sterzel R. B., Unger T. Atriopeptin III kinetics and pharmacodynamics in normal and anephric rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Feb;236(2):416–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maack T., Suzuki M., Almeida F. A., Nussenzveig D., Scarborough R. M., McEnroe G. A., Lewicki J. A. Physiological role of silent receptors of atrial natriuretic factor. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):675–678. doi: 10.1126/science.2823385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy K. K., Thibault G., Garcia R., Gutkowska J., Genest J., Cantin M. Degradation of atrial natriuretic factor in the rat. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):461–469. doi: 10.1042/bj2400461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy K. K., Thibault G., Schiffrin E. L., Garcia R., Chartier L., Gutkowska J., Genest J., Cantin M. Disappearance of atrial natriuretic factor from circulation in the rat. Peptides. 1986 Mar-Apr;7(2):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90220-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napier M. A., Arcuri K. E., Vandlen R. L. Binding and internalization of atrial natriuretic factor by high-affinity receptors in A10 smooth muscle cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Aug 1;248(2):516–522. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90504-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napier M. A., Vandlen R. L., Albers-Schönberg G., Nutt R. F., Brady S., Lyle T., Winquist R., Faison E. P., Heinel L. A., Blaine E. H. Specific membrane receptors for atrial natriuretic factor in renal and vascular tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5946–5950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins G. M., Spear K. L., Siegel N. R., Zurcher-Neely H. A. Inactivation of atrial natriuretic factor by the renal brush border. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 10;901(1):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90260-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said S. I. Metabolic functions of the pulmonary circulation. Circ Res. 1982 Mar;50(3):325–333. doi: 10.1161/01.res.50.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough R. M., Schenk D. B., McEnroe G. A., Arfsten A., Kang L. L., Schwartz K., Lewicki J. A. Truncated atrial natriuretic peptide analogs. Comparison between receptor binding and stimulation of cyclic GMP accumulation in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):12960–12964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenk D. B., Johnson L. K., Schwartz K., Sista H., Scarborough R. M., Lewicki J. A. Distinct atrial natriuretic factor receptor sites on cultured bovine aortic smooth muscle and endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Mar 15;127(2):433–442. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80179-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D., Geller D. M., Manning P. T., Siegel N. R., Fok K. F., Smith C. E., Needleman P. Ser-Leu-Arg-Arg-atriopeptin III: the major circulating form of atrial peptide. Science. 1985 Jul 26;229(4711):397–400. doi: 10.1126/science.3160114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. M. Selection and characterization of bovine aortic endothelial cells. In Vitro. 1978 Dec;14(12):966–980. doi: 10.1007/BF02616210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soler D. F., Harris R. B. Atrial dipeptidyl carboxyhydrolase is a zinc-metallo proteinase which possesses tripeptidyl carboxyhydrolase activity. Peptides. 1989 Jan-Feb;10(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90077-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg J. L., Sakane Y., Jeng A. Y., Koehn J. A., Ansell J. A., Wennogle L. P., Ghai R. D. Identification of protease 3.4.24.11 as the major atrial natriuretic factor degrading enzyme in the rat kidney. Peptides. 1988 Jan-Feb;9(1):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(88)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson S. L., Kenny A. J. The hydrolysis of alpha-human atrial natriuretic peptide by pig kidney microvillar membranes is initiated by endopeptidase-24.11. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 1;243(1):183–187. doi: 10.1042/bj2430183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayanagi R., Snajdar R. M., Imada T., Tamura M., Pandey K. N., Misono K. S., Inagami T. Purification and characterization of two types of atrial natriuretic factor receptors from bovine adrenal cortex: guanylate cyclase-linked and cyclase-free receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 14;144(1):244–250. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80502-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang J., Webber R. J., Chang D., Chang J. K., Kiang J., Wei E. T. Depressor and natriuretic activities of several atrial peptides. Regul Pept. 1984 Sep;9(1-2):53–59. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(84)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibault G., Garcia R., Gutkowska J., Bilodeau J., Lazure C., Seidah N. G., Chrétien M., Genest J., Cantin M. The propeptide Asn1-Tyr126 is the storage form of rat atrial natriuretic factor. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):265–272. doi: 10.1042/bj2410265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibault G., Lazure C., Schiffrin E. L., Gutkowska J., Chartier L., Garcia R., Seidah N. G., Chrétien M., Genest J., Cantin M. Identification of a biologically active circulating form of rat atrial natriuretic factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 15;130(3):981–986. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91711-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend R. R., Wall D. A., Hubbard A. L., Lee Y. C. Rapid release of galactose-terminated ligands after endocytosis by hepatic parenchymal cells: evidence for a role of carbohydrate structure in the release of internalized ligand from receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):466–470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Atrial natriuretic factor selectively activates particulate guanylate cyclase and elevates cyclic GMP in rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14332–14334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall D. A., Hubbard A. L. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of asialoglycoproteins by rat liver hepatocytes: biochemical characterization of the endosomal compartments. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2104–2112. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wileman T., Harding C., Stahl P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):1–14. doi: 10.1042/bj2320001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolkoff A. W., Klausner R. D., Ashwell G., Harford J. Intracellular segregation of asialoglycoproteins and their receptor: a prelysosomal event subsequent to dissociation of the ligand-receptor complex. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):375–381. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yandle T. G., Richards A. M., Nicholls M. G., Cuneo R., Espiner E. A., Livesey J. H. Metabolic clearance rate and plasma half life of alpha-human atrial natriuretic peptide in man. Life Sci. 1986 May 19;38(20):1827–1833. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90137-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bold A. J., Borenstein H. B., Veress A. T., Sonnenberg H. A rapid and potent natriuretic response to intravenous injection of atrial myocardial extract in rats. Life Sci. 1981 Jan 5;28(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90370-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


