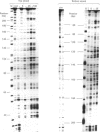
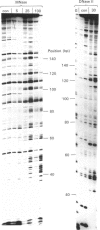
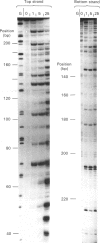
Abstract
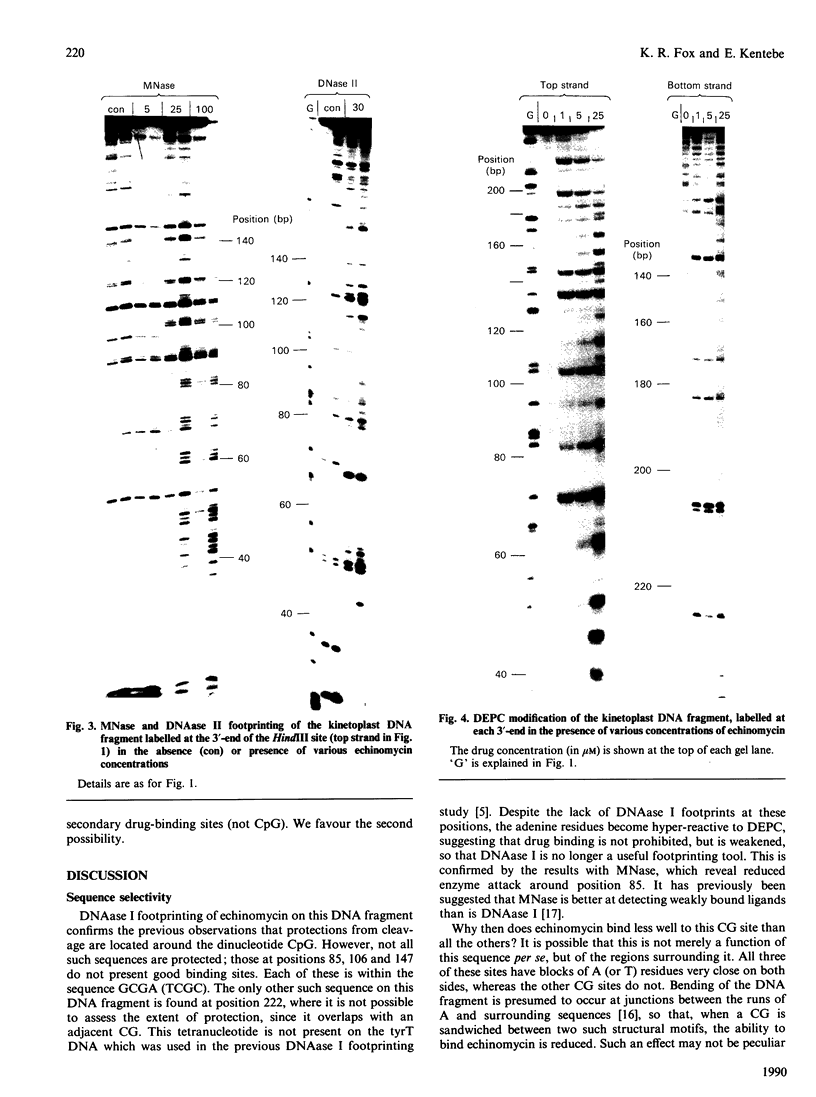
The interaction of echinomycin with a kinetoplast DNA fragment which contains phased runs of adenine residues has been examined by various footprinting techniques. DNAase I footprinting confirms that all drug-binding sites contain the dinucleotide CpG. However, not all such sequences are protected. Three sites, each of which is located between two adenine tracks in the sequence GCGA, are not protected from DNAase I attack. Enhanced cleavage by DNAase I, DNAase II and micrococcal nuclease is observed in regions surrounding drug-binding sites. The results suggest that echinomycin alters the conformation of the AT tracks, making them more like an average DNA structure. Echinomycin renders adenine residues in the sequence CGA hyper-reactive to diethyl pyrocarbonate.
Full text
PDF
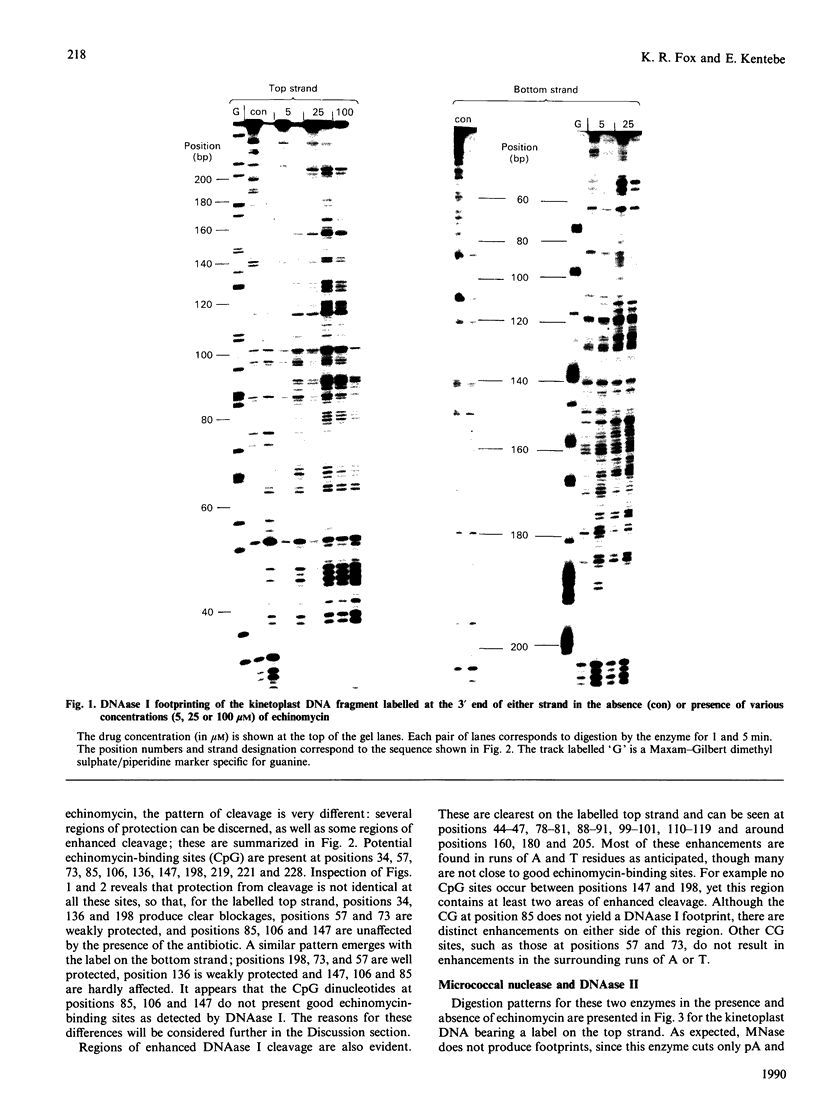


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burkhoff A. M., Tullius T. D. The unusual conformation adopted by the adenine tracts in kinetoplast DNA. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):935–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90702-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA structural variations in the E. coli tyrT promoter. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J. DNA structural variations produced by actinomycin and distamycin as revealed by DNAase I footprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9271–9285. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J. The use of micrococcal nuclease as a probe for drug-binding sites on DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 14;909(2):145–155. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao X. L., Patel D. J. NMR studies of echinomycin bisintercalation complexes with d(A1-C2-G3-T4) and d(T1-C2-G3-A4) duplexes in aqueous solution: sequence-dependent formation of Hoogsteen A1.T4 and Watson--Crick T1.A4 base pairs flanking the bisintercalation site. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 8;27(5):1744–1751. doi: 10.1021/bi00405a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. E., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Feigon J. Unstable Hoogsteen base pairs adjacent to echinomycin binding sites within a DNA duplex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3006–3010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeppesen C., Nielsen P. E. Detection of intercalation-induced changes in DNA structure by reaction with diethyl pyrocarbonate or potassium permanganate. Evidence against the induction of Hoogsteen base pairing by echinomycin. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 11;231(1):172–176. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80725-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchin P. A., Klein V. A., Ryan K. A., Gann K. L., Rauch C. A., Kang D. S., Wells R. D., Englund P. T. A highly bent fragment of Crithidia fasciculata kinetoplast DNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11302–11309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low C. M., Drew H. R., Waring M. J. Sequence-specific binding of echinomycin to DNA: evidence for conformational changes affecting flanking sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):4865–4879. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.4865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean M. J., Waring M. J. Chemical probes reveal no evidence of Hoogsteen base pairing in complexes formed between echinomycin and DNA in solution. J Mol Recognit. 1988 Jun;1(3):138–151. doi: 10.1002/jmr.300010307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel D., Dervan P. B. Hoogsteen base pairs proximal and distal to echinomycin binding sites on DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):910–914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson H. C., Finch J. T., Luisi B. F., Klug A. The structure of an oligo(dA).oligo(dT) tract and its biological implications. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):221–226. doi: 10.1038/330221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portugal J., Fox K. R., McLean M. J., Richenberg J. L., Waring M. J. Diethyl pyrocarbonate can detect a modified DNA structure induced by the binding of quinoxaline antibiotics. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):3655–3670. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.3655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley M., Maling B. Physical and chemical characterization of two- and three-stranded adenine-thymine and adenine-uracil homopolymer complexes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(2):359–389. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ughetto G., Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Rich A. A comparison of the structure of echinomycin and triostin A complexed to a DNA fragment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2305–2323. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. M., Dervan P. B. Echinomycin binding sites on DNA. Science. 1984 Sep 14;225(4667):1122–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.6089341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelin S. P., Waring M. J. The binding of echinomycin to deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):721–740. doi: 10.1042/bj1570721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Ughetto G., Quigley G. J., Rich A. Interactions of quinoxaline antibiotic and DNA: the molecular structure of a triostin A-d(GCGTACGC) complex. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Dec;4(3):319–342. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10506353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. J., Wakelin L. P. Echinomycin: a bifunctional intercalating antibiotic. Nature. 1974 Dec 20;252(5485):653–657. doi: 10.1038/252653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]