Abstract
The target of most of the autoantibodies against the acetylcholine receptor (AChR) in myasthenic sera is the main immunogenic region (MIR) on the extracellular side of the AChR alpha-subunit. Binding of anti-MIR monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) has been recently localized between residues alpha 67 and alpha 76 of Torpedo californica electric organ (WNPADYGGIK) and human muscle (WNPDDYGGVK) AChR. In order to evaluate the contribution of each residue to the antigenicity of the MIR, we synthesized peptides corresponding to residues alpha 67-76 from Torpedo and human AChRs, together with 13 peptide analogues. Nine of these analogues had one residue of the Torpedo decapeptide replaced by L-alanine, three had a structure which was intermediate between those of the Torpedo and human alpha 67-76 decapeptides, and one had D-alanine in position 73. Binding studies employing six anti-MIR mAbs and all 15 peptides revealed that some residues (Asn68 and Asp71) are indispensable for binding by all mAbs tested, whereas others are important only for binding by some mAbs. Antibody binding was mainly restricted to residues alpha 68-74, the most critical sequence being alpha 68-71. Fish electric organ and human MIR form two distinct groups of strongly overlapping epitopes. Some peptide analogues enhanced mAb binding compared with Torpedo and human peptides, suggesting that the construction of a very antigenic MIR is feasible.
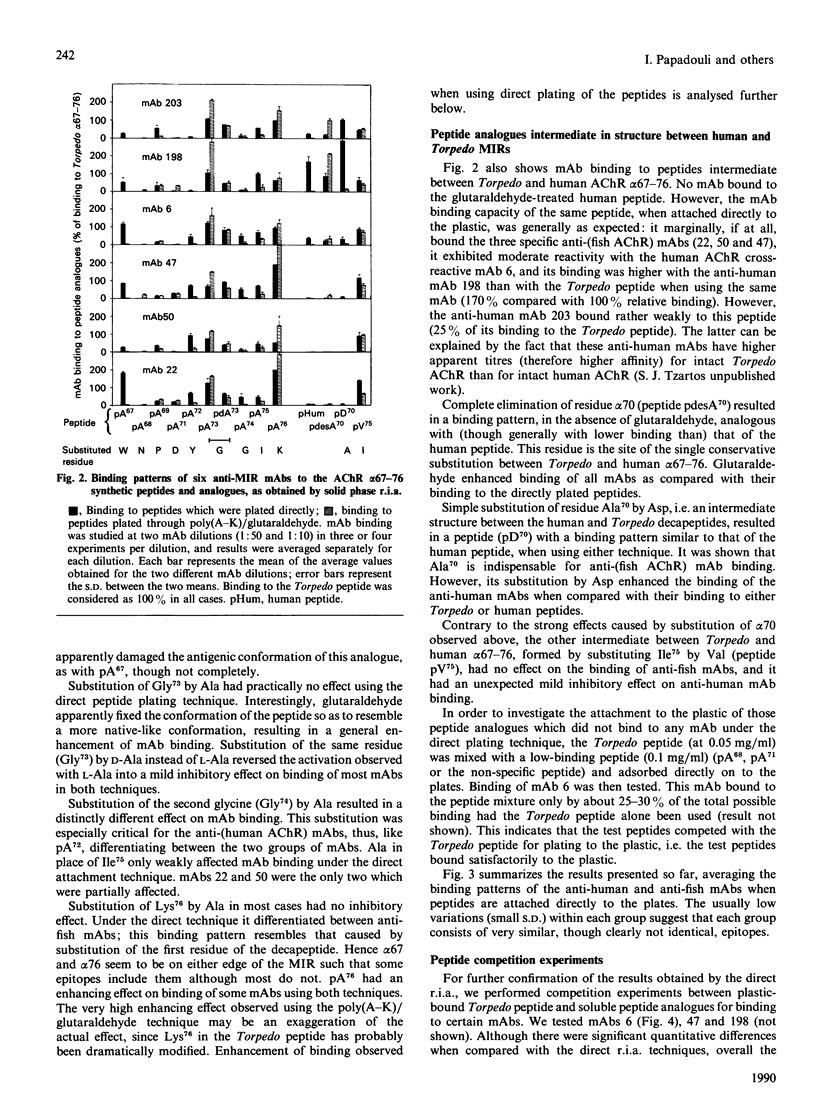
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin T. J., Yoshihara C. M., Blackmer K., Kintner C. R., Burden S. J. Regulation of acetylcholine receptor transcript expression during development in Xenopus laevis. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):469–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkas T., Gabriel J. M., Juillerat M., Kokla A., Tzartos S. J. Localisation of the main immunogenic region of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. FEBS Lett. 1986 Feb 17;196(2):237–241. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80254-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkas T., Gabriel J. M., Mauron A., Hughes G. J., Roth B., Alliod C., Tzartos S. J., Ballivet M. Monoclonal antibodies to the main immunogenic region of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor bind to residues 61-76 of the alpha subunit. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5916–5920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkas T., Mauron A., Roth B., Alliod C., Tzartos S. J., Ballivet M. Mapping the main immunogenic region and toxin-binding site of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):77–80. doi: 10.1126/science.2432658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinchetru M. A., Marquez J., Garcia-Borron J. C., Richman D. P., Martinez-Carrion M. Interaction of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor with two monoclonal antibodies recognizing different epitopes. Biochemistry. 1989 May 16;28(10):4222–4229. doi: 10.1021/bi00436a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cung M. T., Marraud M., Hadjidakis I., Bairaktari E., Sakarellos C., Kokla A., Tzartos S. Two-dimensional 1H-NMR study of synthetic peptides containing the main immunogenic region of the Torpedo acetylcholine receptor. Biopolymers. 1989 Jan;28(1):465–478. doi: 10.1002/bip.360280141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs S., Neumann D., Safran A., Souroujon M., Barchan D., Fridkin M., Gershoni J. M., Mantegazza R., Pizzighella S. Synthetic peptides and their antibodies in the analysis of the acetylcholine receptor. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;505:256–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb51295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich F., Vincent A., Roberts A., Newsom-Davis J. Epitopes on human acetylcholine receptor defined by monoclonal antibodies and myasthenia gravis sera. Autoimmunity. 1988;1(4):285–297. doi: 10.3109/08916938809010682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges R. S., Heaton R. J., Parker J. M., Molday L., Molday R. S. Antigen-antibody interaction. Synthetic peptides define linear antigenic determinants recognized by monoclonal antibodies directed to the cytoplasmic carboxyl terminus of rhodopsin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11768–11775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordossi A. A., Tzartos S. J. Conformation of cytoplasmic segments of acetylcholine receptor alpha- and beta-subunits probed by monoclonal antibodies: sensitivity of the antibody competition approach. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1605–1610. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02407.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordossi A. A., Tzartos S. J. Monoclonal antibodies against the main immunogenic region of the acetylcholine receptor. Mapping on the intact molecule. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Jun;23(1):35–40. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubalek E., Ralston S., Lindstrom J., Unwin N. Location of subunits within the acetylcholine receptor by electron image analysis of tubular crystals from Torpedo marmorata. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):9–18. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon V. A., Griesmann G. E. Evidence against acetylcholine receptor having a main immunogenic region as target for autoantibodies in myasthenia gravis. Neurology. 1989 Aug;39(8):1069–1076. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.8.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Shelton D., Fujii Y. Myasthenia gravis. Adv Immunol. 1988;42:233–284. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60847-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maelicke A., Plümer-Wilk R., Fels G., Spencer S. R., Engelhard M., Veltel D., Conti-Tronconi B. M. Epitope mapping employing antibodies raised against short synthetic peptides: a study of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):1396–1405. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Smith M. M. Synthesis and assembly of acetylcholine receptor, a multisubunit membrane glycoprotein. J Membr Biol. 1986;91(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01870209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnam M., Sargent P. B., Sarin V., Fox J. L., Nguyen D. L., Rivier J., Criado M., Lindstrom J. Location of antigenic determinants on primary sequences of subunits of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by peptide mapping. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2621–2632. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent P. B., Hedges B. E., Tsavaler L., Clemmons L., Tzartos S., Lindstrom J. M. Structure and transmembrane nature of the acetylcholine receptor in amphibian skeletal muscle as revealed by cross-reacting monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):609–618. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sophianos D., Tzartos S. J. Fab fragments of monoclonal antibodies protect the human acetylcholine receptor against antigenic modulation caused by myasthenic sera. J Autoimmun. 1989 Dec;2(6):777–789. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(89)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroud R. M. An archetypal molecular transducer of the nervous system: the acetylcholine receptor. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1987;65:51–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Kokla A., Walgrave S. L., Conti-Tronconi B. M. Localization of the main immunogenic region of human muscle acetylcholine receptor to residues 67-76 of the alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2899–2903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Lindstrom J. M. Monoclonal antibodies used to probe acetylcholine receptor structure: localization of the main immunogenic region and detection of similarities between subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Loutrari H. V., Tang F., Kokla A., Walgrave S. L., Milius R. P., Conti-Tronconi B. M. Main immunogenic region of Torpedo electroplax and human muscle acetylcholine receptor: localization and microheterogeneity revealed by the use of synthetic peptides. J Neurochem. 1990 Jan;54(1):51–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb13282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Rand D. E., Einarson B. L., Lindstrom J. M. Mapping of surface structures of electrophorus acetylcholine receptor using monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8635–8645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Seybold M. E., Lindstrom J. M. Specificities of antibodies to acetylcholine receptors in sera from myasthenia gravis patients measured by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):188–192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Sophianos D., Efthimiadis A. Role of the main immunogenic region of acetylcholine receptor in myasthenia gravis. An Fab monoclonal antibody protects against antigenic modulation by human sera. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2343–2349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S., Hochschwender S., Vasquez P., Lindstrom J. Passive transfer of experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis by monoclonal antibodies to the main immunogenic region of the acetylcholine receptor. J Neuroimmunol. 1987 Jun;15(2):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(87)90092-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S., Langeberg L., Hochschwender S., Lindstrom J. Demonstration of a main immunogenic region on acetylcholine receptors from human muscle using monoclonal antibodies to human receptor. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jul 11;158(1):116–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80688-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worobec E. A., Paranchych W., Parker J. M., Taneja A. K., Hodges R. S. Antigen-antibody interaction. The immunodominant region of EDP208 pili. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):938–943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


