Abstract
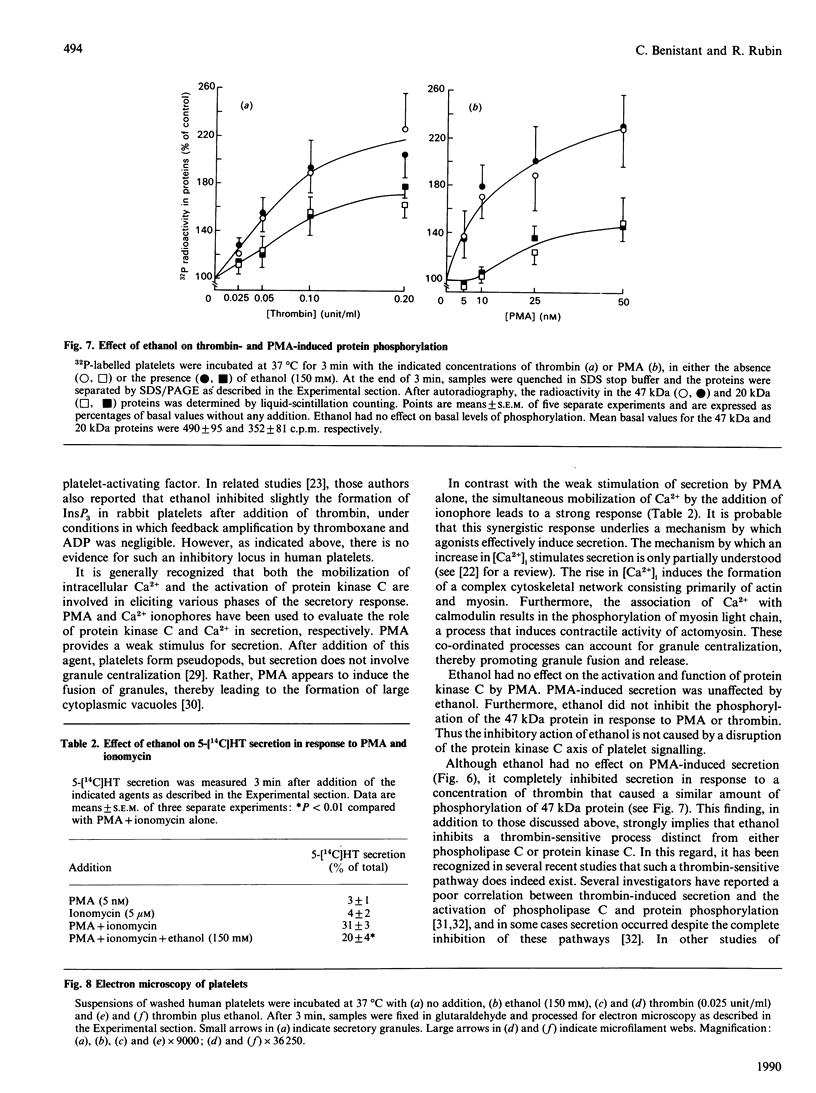
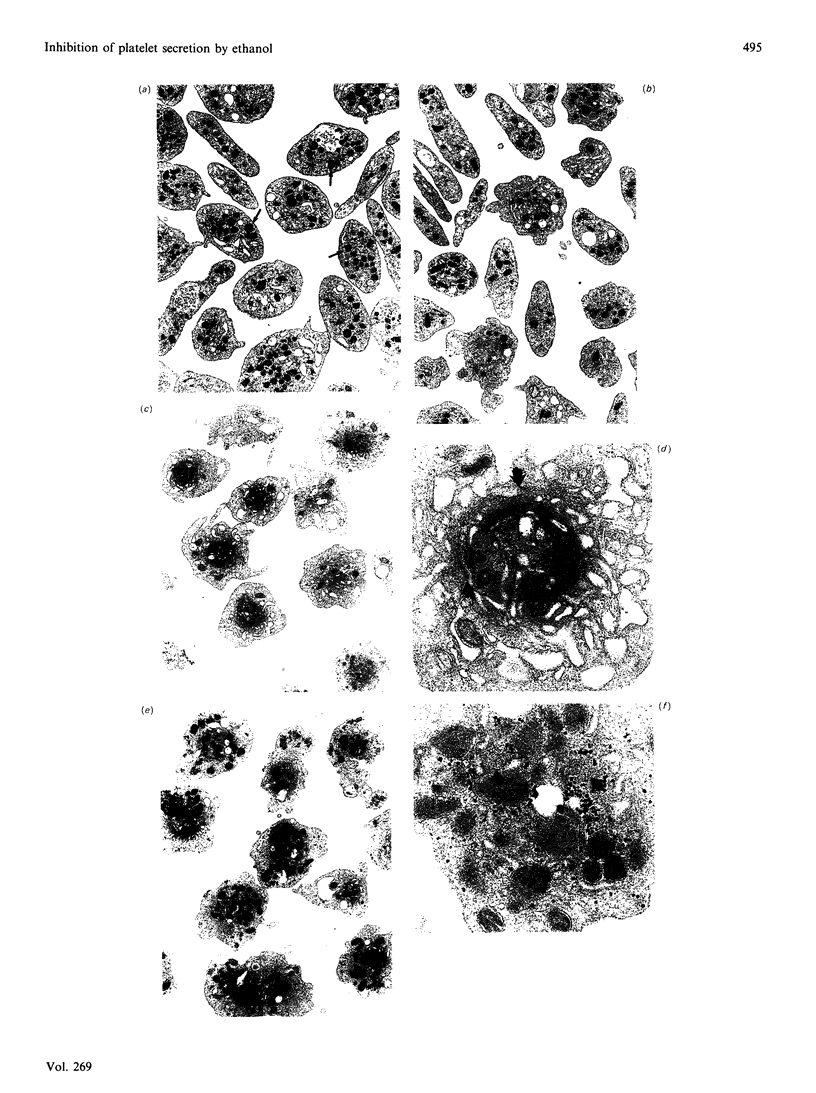
Ethanol is known to inhibit the activation of platelets in response to several physiological agonists, but the mechanism of this action is unclear. The addition of physiologically relevant concentrations of ethanol (25-150 mM) to suspensions of washed human platelets resulted in the inhibition of thrombin-induced secretion of 5-hydroxy[14C]tryptamine. Indomethacin was included in the incubation buffer to prevent feedback amplification by arachidonic acid metabolites. Ethanol had no effect on the activation of phospholipase C by thrombin, as determined by the formation of inositol phosphates and the mobilization of intracellular Ca2+. Moreover, ethanol did not interfere with the thrombin-induced formation of diacylglycerol or phosphatidic acid. Stimulation of platelets with phorbol ester (5-50 nM) resulted in 5-hydroxy[14C]tryptamine release comparable with those with threshold doses of thrombin. However, ethanol did not inhibit phorbol-ester-induced secretion. Ethanol also did not interfere with thrombin- or phorbol-ester-induced phosphorylation of myosin light chain (20 kDa) or a 47 kDa protein, a known substrate for protein kinase C. By electron microscopy, ethanol had no effect on thrombin-induced shape change and pseudopod formation, but prevented granule centralization and fusion. The results indicate that ethanol does not inhibit platelet secretion by interfering with the activation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C or protein kinase C by thrombin. Rather, the data demonstrate an inhibition of a Ca2(+)-mediated event such as granule centralization.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brass L. F., Laposata M., Banga H. S., Rittenhouse S. E. Regulation of the phosphoinositide hydrolysis pathway in thrombin-stimulated platelets by a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide-binding protein. Evaluation of its contribution to platelet activation and comparisons with the adenylate cyclase inhibitory protein, Gi. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16838–16847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R. C., Butler R. G., Morris P. A., Gerrard J. M. Separable assembly of platelet pseudopodal and contractile cytoskeletons. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):385–393. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90236-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan D. H. Effect of alcoholism on hemostasis. Semin Hematol. 1980 Apr;17(2):137–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai K., Owen J. S., Wilson D. T., Hutton R. A. Platelet aggregation and plasma lipoproteins in alcoholics during alcohol withdrawal. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Apr 30;55(2):173–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorio R. J., Hoek J. B., Rubin E. Ethanol treatment selectively decreases neutral amino acid transport in cultured hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11430–11435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmér O., Göransson G., Zoucas E. Impairment of primary hemostasis and platelet function after alcohol ingestion in man. Haemostasis. 1984;14(2):223–228. doi: 10.1159/000215060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenn C. G., Littleton J. M. Inhibition of platelet aggregation by ethanol in vitro shows specificity for aggregating agent used and is influenced by platelet lipid composition. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Aug 24;48(1):49–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenn C. G., Littleton J. M. Interactions between ethanol and dietary fat in determining human platelet function. Thromb Haemost. 1984 Feb 28;51(1):50–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenn C. G., Littleton J. M. The human blood platelet as a model for studying interactions of ethanol with membrane lipids. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1983 Winter;7(1):59–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1983.tb05412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenn G. C., Caberos L. P., Littleton J. M. Effect of ethanol on thrombin-induced platelet phospholipid breakdown and release of [3H]-5-hydroxytryptamine. Alcohol. 1985 Jan-Feb;2(1):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0741-8329(85)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., Beattie L. L., Park J., Israels S. J., McNicol A., Lint D., Cragoe E. J., Jr A role for protein kinase C in the membrane fusion necessary for platelet granule secretion. Blood. 1989 Nov 15;74(7):2405–2413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Davidson M. M. Potentiation by thrombin of the secretion of serotonin from permeabilized platelets equilibrated with Ca2+ buffers. Relationship to protein phosphorylation and diacylglycerol formation. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 1;222(2):351–361. doi: 10.1042/bj2220351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennekens C. H., Willett W., Rosner B., Cole D. S., Mayrent S. L. Effects of beer, wine, and liquor in coronary deaths. JAMA. 1979 Nov 2;242(18):1973–1974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoek J. B., Taraschi T. F., Rubin E. Functional implications of the interaction of ethanol with biologic membranes: actions of ethanol on hormonal signal transduction systems. Semin Liver Dis. 1988 Feb;8(1):36–46. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoek J. B., Thomas A. P., Rubin R., Rubin E. Ethanol-induced mobilization of calcium by activation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C in intact hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):682–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Siegel F. L. Shape change induced in human platelets by platelet-activating factor. Correlation with the formation of phosphatidic acid and phosphorylation of a 40,000-dalton protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7241–7244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikhailidis D. P., Jenkins W. J., Barradas M. A., Jeremy J. Y., Dandona P. Platelet function defects in chronic alcoholism. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Sep 20;293(6549):715–718. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6549.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. C., Figures W. R., Scearce L. M., Stewart G. J., Colman R. F., Colman R. W. Two mechanisms for inhibition of ADP-induced platelet shape change by 5'-p-fluorosulfonylbenzoyladenosine. Conversion to adenosine, and covalent modification at an ADP binding site distinct from that which inhibits adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8078–8083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponnappa B. C., Waring A. J., Hoek J. B., Rottenberg H., Rubin E. Chronic ethanol ingestion increases calcium uptake and resistance to molecular disordering by ethanol in liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10141–10146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puskin S., Rubin E. Effects of ADP, ethanol and acetaldehyde on the relaxing complex of human muscle and its adsorption by polystyrene particles. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Dec;177(2):574–584. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90469-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puszkin S., Rubin E. Adenosine diphosphate effect on contractility of human muscle actomyosin: inhibition by ethanol and acetaldehyde. Science. 1975 Jun 27;188(4195):1319–1320. doi: 10.1126/science.124949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand M. L., Packham M. A., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Fraser Mustard J. Effects of ethanol on pathways of platelet aggregation in vitro. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Jun 16;59(3):383–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand M. L., Vickers J. D., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Packham M. A., Mustard J. F. Thrombin-induced inositol trisphosphate production by rabbit platelets is inhibited by ethanol. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 1;251(1):279–284. doi: 10.1042/bj2510279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse S. E. Activation of human platelet phospholipase C by ionophore A23187 is totally dependent upon cyclo-oxygenase products and ADP. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 15;222(1):103–110. doi: 10.1042/bj2220103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. Ethanol interferes with collagen-induced platelet activation by inhibition of arachidonic acid mobilization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Apr;270(1):99–113. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R., Hoek J. B. Alcohol-induced stimulation of phospholipase C in human platelets requires G-protein activation. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 15;254(1):147–153. doi: 10.1042/bj2540147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R., Ponnappa B. C., Thomas A. P., Hoek J. B. Ethanol stimulates shape change in human platelets by activation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jan;260(1):480–492. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90472-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W. Molecular mechanisms of platelet activation. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jan;69(1):58–178. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzdak P. D., Schwartz R. D., Skolnick P., Paul S. M. Ethanol stimulates gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor-mediated chloride transport in rat brain synaptoneurosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4071–4075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabakoff B., Hoffman P. L., McLaughlin A. Is ethanol a discriminating substance? Semin Liver Dis. 1988 Feb;8(1):26–35. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraschi T. F., Rubin E. Effects of ethanol on the chemical and structural properties of biologic membranes. Lab Invest. 1985 Feb;52(2):120–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuma D. J., Sorrell M. F. Effects of ethanol on protein trafficking in the liver. Semin Liver Dis. 1988 Feb;8(1):69–80. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Hambleton S. Phosphorylation-dependent and -independent pathways of platelet aggregation. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 1;258(2):479–485. doi: 10.1042/bj2580479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]