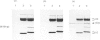Abstract
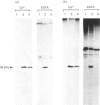
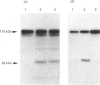
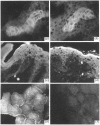
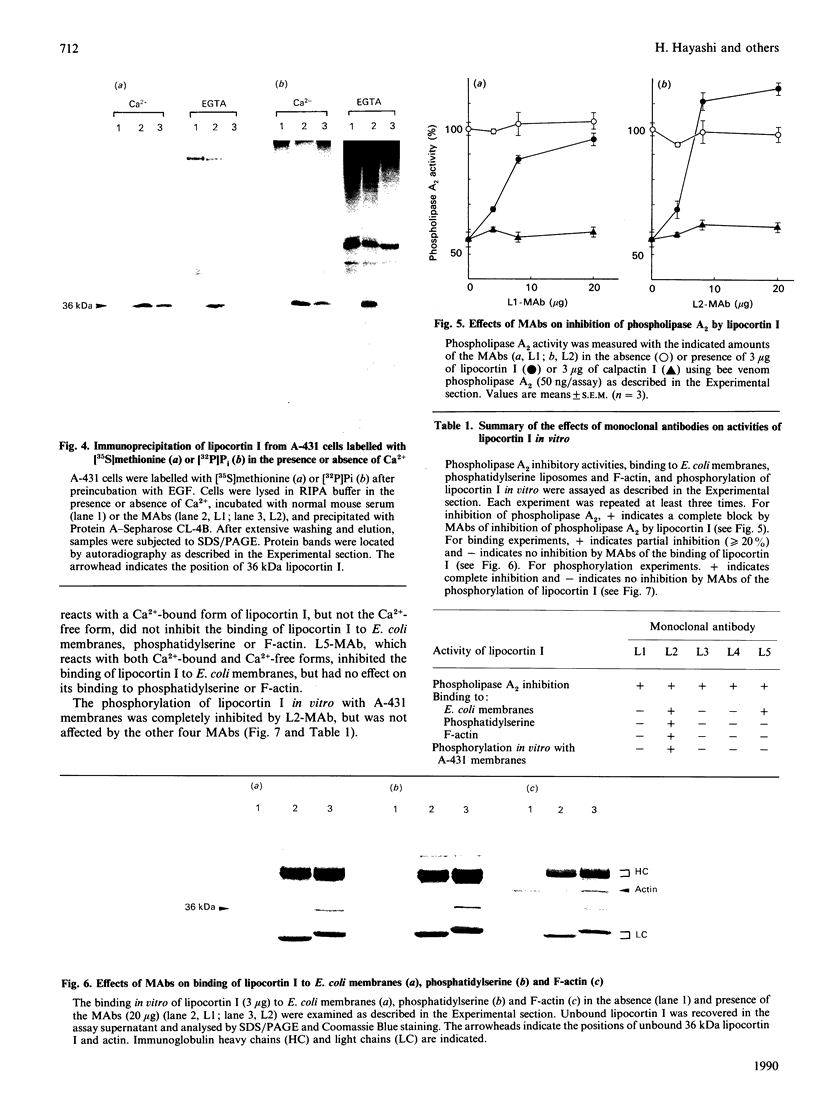
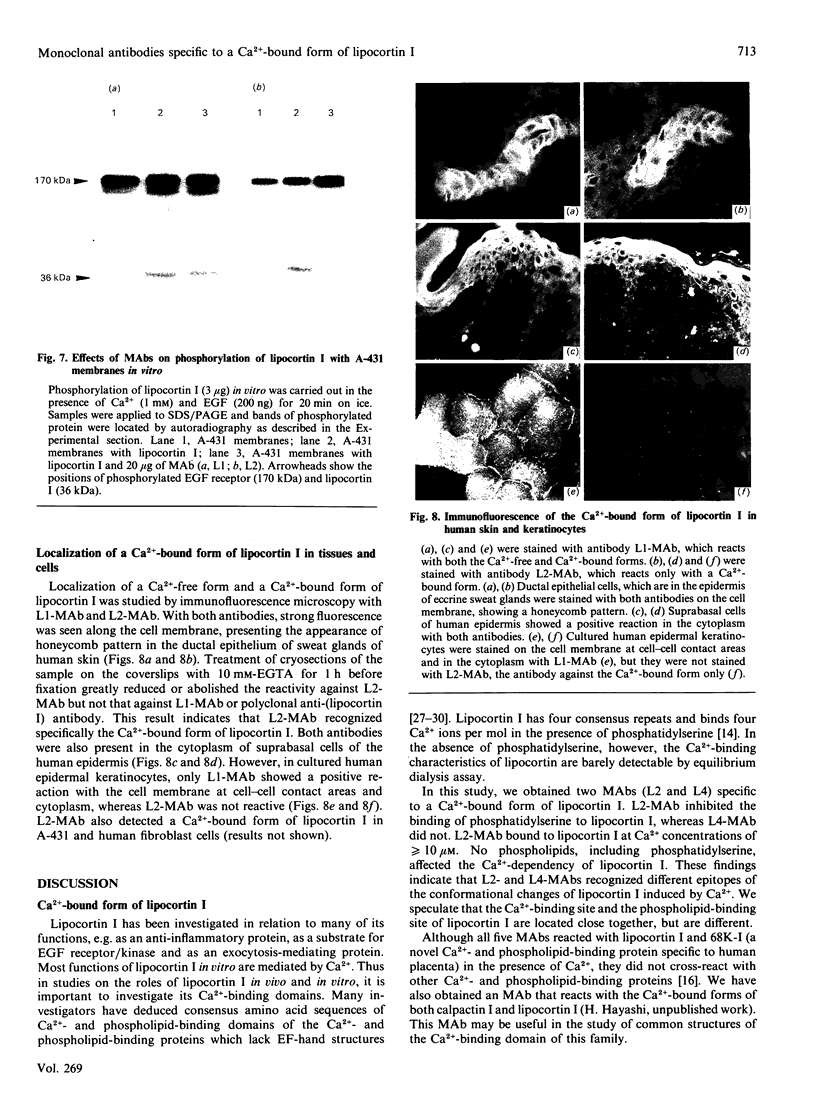
Lipocortin I, a Ca2(+)-and phospholipid-binding protein without EF-hand structures, has many biological effects in vitro. Its actual role in vivo, however is unknown. We obtained and characterized five monoclonal antibodies to lipocortin I. Two of these monoclonal antibodies (L2 and L4-MAbs) reacted with the Ca(+)-bound form of lipocortin I, but not with the Ca2(+)-free form, both in vivo and in vitro. Lipocortin I required greater than or equal to 10 microM-Ca2+ to bind the two antibodies, and this Ca2+ requirement was not affected by phosphatidylserine. L2-MAb abolished the phospholipase A2 inhibitory activity of lipocortin I and inhibited its binding to Escherichia coli membranes and to phosphatidylserine in vitro. L4-MAb abolished the phospholipase A2 inhibitory activity of lipocortin I, but did not affect its binding to E. coli membranes or to phosphatidylserine. These findings indicated that the inhibition of phospholipase A2 by lipocortin I was not simply due to removal or capping of the substrates in E. coli membranes. Furthermore, an immunofluorescence study using L2-MAb showed the actual existence of Ca2(+)-bound form of lipocortin I in vivo.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando Y., Imamura S., Hong Y. M., Owada M. K., Kakunaga T., Kannagi R. Enhancement of calcium sensitivity of lipocortin I in phospholipid binding induced by limited proteolysis and phosphorylation at the amino terminus as analyzed by phospholipid affinity column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6948–6955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D. Calpactin in exocytosis. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):20–20. doi: 10.1038/331020a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirino G., Flower R. J., Browning J. L., Sinclair L. K., Pepinsky R. B. Recombinant human lipocortin 1 inhibits thromboxane release from guinea-pig isolated perfused lung. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):270–272. doi: 10.1038/328270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutz C. E., Dowling L. G., Sando J. J., Villar-Palasi C., Whipple J. H., Zaks W. J. Characterization of the chromobindins. Soluble proteins that bind to the chromaffin granule membrane in the presence of Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14664–14674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crompton M. R., Moss S. E., Crumpton M. J. Diversity in the lipocortin/calpactin family. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crompton M. R., Owens R. J., Totty N. F., Moss S. E., Waterfield M. D., Crumpton M. J. Primary structure of the human, membrane-associated Ca2+-binding protein p68 a novel member of a protein family. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):21–27. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02779.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson F. F., Dennis E. A., Powell M., Glenney J. R., Jr Inhibition of phospholipase A2 by "lipocortins" and calpactins. An effect of binding to substrate phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1698–1705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De B. K., Misono K. S., Lukas T. J., Mroczkowski B., Cohen S. A calcium-dependent 35-kilodalton substrate for epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase isolated from normal tissue. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13784–13792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drust D. S., Creutz C. E. Aggregation of chromaffin granules by calpactin at micromolar levels of calcium. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):88–91. doi: 10.1038/331088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duhamel R. C., Meezan E., Brendel K. The addition of SDS to the Bradford dye-binding protein assay, a modification with increased sensitivity to collagen. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1981 Aug;5(2):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(81)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fava R. A., Cohen S. Isolation of a calcium-dependent 35-kilodalton substrate for the epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase from A-431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2636–2645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisow M. J. Common domain structure of Ca2+ and lipid-binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 14;203(1):99–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81445-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisow M. J., Fritsche U., Hexham J. M., Dash B., Johnson T. A consensus amino-acid sequence repeat in Torpedo and mammalian Ca2+-dependent membrane-binding proteins. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):636–638. doi: 10.1038/320636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Tack B., Powell M. A. Calpactins: two distinct Ca++-regulated phospholipid- and actin-binding proteins isolated from lung and placenta. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):503–511. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. Two related but distinct forms of the Mr 36,000 tyrosine kinase substrate (calpactin) that interact with phospholipid and actin in a Ca2+-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4258–4262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J., Zokas L. Antibodies to the N-terminus of calpactin II (p35) affect Ca2+ binding and phosphorylation by the epidermal growth factor receptor in vitro. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):2069–2076. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundmann U., Abel K. J., Bohn H., Löbermann H., Lottspeich F., Küpper H. Characterization of cDNA encoding human placental anticoagulant protein (PP4): homology with the lipocortin family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3708–3712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., Schlaepfer D. D., Burgess W. H. Characterization of lipocortin I and an immunologically unrelated 33-kDa protein as epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase substrates and phospholipase A2 inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6921–6930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi H., Owada M. K., Sonobe S., Kakunaga T. Characterizations of two distinct Ca2+-dependent phospholipid-binding proteins of 68-kDa isolated from human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17222–17230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellewell S. B., Taylor D. L. The contractile basis of ameboid movement. VI. The solation-contraction coupling hypothesis. J Cell Biol. 1979 Dec;83(3):633–648. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Matsuda K., Notsu Y., Hattori T., del Carmine R. Phosphorylation at a tyrosine residue of lipomodulin in mitogen-stimulated murine thymocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4717–4721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Schiffmann E., Venkatasubramanian K., Salomon D., Axelrod J. A phospholipase A2 inhibitory protein in rabbit neutrophils induced by glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2533–2536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F. The regulation of lipomodulin, a phospholipase inhibitory protein, in rabbit neutrophils by phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7730–7733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., McGray P., Mattaliano R. J., Burne C., Chow E. P., Sinclair L. K., Pepinsky R. B. Purification and characterization of proteolytic fragments of lipocortin I that inhibit phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7639–7645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., Wallner B. P., Mattaliano R. J., Tizard R., Burne C., Frey A., Hession C., McGray P., Sinclair L. K., Chow E. P. Two human 35 kd inhibitors of phospholipase A2 are related to substrates of pp60v-src and of the epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90736-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H., Creutz C. E. Cell biology. Consensus in exocytosis. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):573–573. doi: 10.1038/320573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen T., Saris C. J., Hunter T., Hicks L. J., Noonan D. J., Glenney J. R., Jr, Tack B. F. Primary structure of bovine calpactin I heavy chain (p36), a major cellular substrate for retroviral protein-tyrosine kinases: homology with the human phospholipase A2 inhibitor lipocortin. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 12;25(16):4497–4503. doi: 10.1021/bi00364a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miele L., Cordella-Miele E., Facchiano A., Mukherjee A. B. Novel anti-inflammatory peptides from the region of highest similarity between uteroglobin and lipocortin I. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):726–730. doi: 10.1038/335726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owada M. K., Hakura A., Iida K., Yahara I., Sobue K., Kakiuchi S. Occurrence of caldesmon (a calmodulin-binding protein) in cultured cells: comparison of normal and transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3133–3137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saris C. J., Tack B. F., Kristensen T., Glenney J. R., Jr, Hunter T. The cDNA sequence for the protein-tyrosine kinase substrate p36 (calpactin I heavy chain) reveals a multidomain protein with internal repeats. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90737-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer D. D., Haigler H. T. Characterization of Ca2+-dependent phospholipid binding and phosphorylation of lipocortin I. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6931–6937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer D. D., Mehlman T., Burgess W. H., Haigler H. T. Structural and functional characterization of endonexin II, a calcium- and phospholipid-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6078–6082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki J., Owada M. K., Sakato N., Fujio H. Direct identification of phosphotyrosine-containing proteins in some retrovirus-transformed cells by use of anti-phosphotyrosine antibody. Cancer Res. 1986 Feb;46(2):907–916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Slaughter C. A., Leznicki I., Barjon P., Reynolds G. A. Human 67-kDa calelectrin contains a duplication of four repeats found in 35-kDa lipocortins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):664–668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touqui L., Rothhut B., Shaw A. M., Fradin A., Vargaftig B. B., Russo-Marie F. Platelet activation--a role for a 40K anti-phospholipase A2 protein indistinguishable from lipocortin. Nature. 1986 May 8;321(6066):177–180. doi: 10.1038/321177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Johnsson N., Plessmann U., Van P. N., Söling H. D., Ampe C., Vandekerckhove J. The amino acid sequence of protein II and its phosphorylation site for protein kinase C; the domain structure Ca2+-modulated lipid binding proteins. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1599–1604. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02406.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]