Abstract
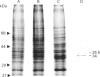
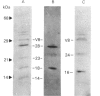
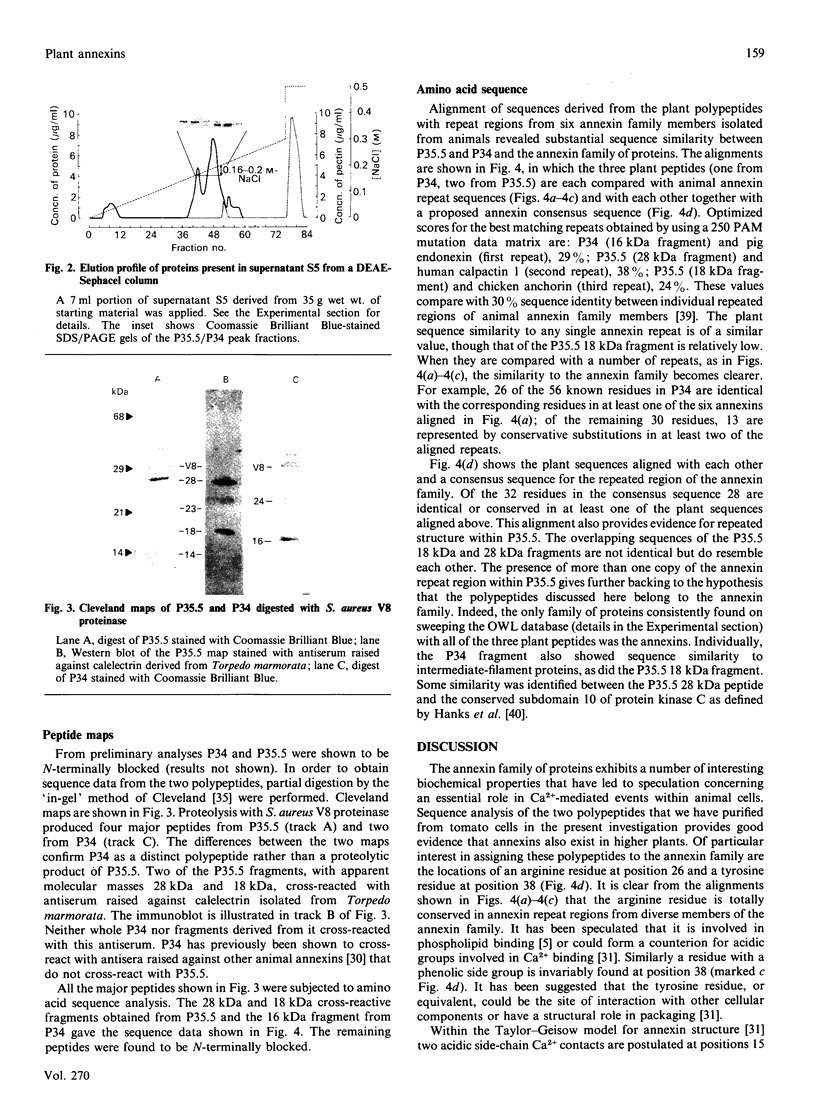
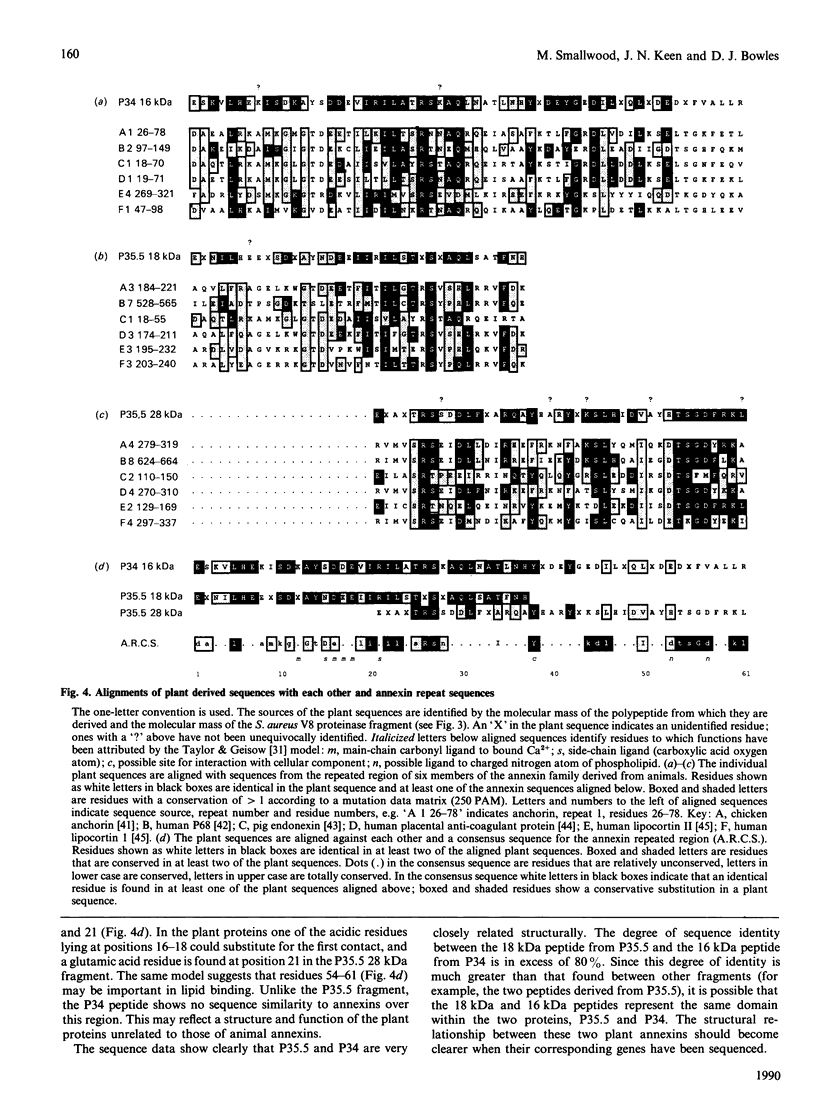
A fractionation procedure for annexins involving Ca2(+)-dependent binding to exogenous phospholipid was applied to tomato suspension culture cells. Two polypeptides (34 kDa and 35.5 kDa) were purified and separated from each other and from contaminant pectic polysaccharide by ion-exchange chromatography. After proteolytic digestion of SDS/PAGE-purified products, N-terminal sequencing of the peptide fragments revealed substantial similarity to sequences of known members of the annexin family characterized from a range of animal tissues. In particular, sequence similarity to the 70-amino acid-residue repeat region found in all annexins sequenced to date was present in both of the plant proteins. The data are discussed within the context of annexin involvement in Ca2(+)-mediated events in higher plants.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali S. M., Geisow M. J., Burgoyne R. D. A role for calpactin in calcium-dependent exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1989 Jul 27;340(6231):313–315. doi: 10.1038/340313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando Y., Imamura S., Hong Y. M., Owada M. K., Kakunaga T., Kannagi R. Enhancement of calcium sensitivity of lipocortin I in phospholipid binding induced by limited proteolysis and phosphorylation at the amino terminus as analyzed by phospholipid affinity column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6948–6955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blay J., Valentine-Braun K. A., Northup J. K., Hollenberg M. D. Epidermal-growth-factor-stimulated phosphorylation of calpactin II in membrane vesicles shed from cultured A-431 cells. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 15;259(2):577–583. doi: 10.1042/bj2590577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenkrantz N., Asboe-Hansen G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):484–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90377-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowles D. J., Marcus S. E., Pappin D. J., Findlay J. B., Eliopoulos E., Maycox P. R., Burgess J. Posttranslational processing of concanavalin A precursors in jackbean cotyledons. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1284–1297. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W. Peptide mapping in one dimension by limited proteolysis of sodium dodecyl sulfate-solubilized proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:222–229. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crompton M. R., Moss S. E., Crumpton M. J. Diversity in the lipocortin/calpactin family. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crompton M. R., Owens R. J., Totty N. F., Moss S. E., Waterfield M. D., Crumpton M. J. Primary structure of the human, membrane-associated Ca2+-binding protein p68 a novel member of a protein family. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):21–27. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02779.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson F. F., Dennis E. A., Powell M., Glenney J. R., Jr Inhibition of phospholipase A2 by "lipocortins" and calpactins. An effect of binding to substrate phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1698–1705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De B. K., Misono K. S., Lukas T. J., Mroczkowski B., Cohen S. A calcium-dependent 35-kilodalton substrate for epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase isolated from normal tissue. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13784–13792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drust D. S., Creutz C. E. Aggregation of chromaffin granules by calpactin at micromolar levels of calcium. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):88–91. doi: 10.1038/331088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Identification of a cellular protein substrate phosphorylated by the avian sarcoma virus-transforming gene product. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90446-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fava R. A., Cohen S. Isolation of a calcium-dependent 35-kilodalton substrate for the epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase from A-431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2636–2645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisow M. J., Walker J. H., Boustead C., Taylor W. Annexins--new family of Ca2+-regulated-phospholipid binding protein. Biosci Rep. 1987 Apr;7(4):289–298. doi: 10.1007/BF01121450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Glenney P. Comparison of Ca++-regulated events in the intestinal brush border. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):754–763. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Tack B., Powell M. A. Calpactins: two distinct Ca++-regulated phospholipid- and actin-binding proteins isolated from lung and placenta. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):503–511. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. Two related but distinct forms of the Mr 36,000 tyrosine kinase substrate (calpactin) that interact with phospholipid and actin in a Ca2+-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4258–4262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Woodgett J. R., Isacke C. M., Hunter T. The protein-tyrosine kinase substrate p36 is also a substrate for protein kinase C in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2738–2744. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundmann U., Abel K. J., Bohn H., Löbermann H., Lottspeich F., Küpper H. Characterization of cDNA encoding human placental anticoagulant protein (PP4): homology with the lipocortin family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3708–3712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., Schlaepfer D. D., Burgess W. H. Characterization of lipocortin I and an immunologically unrelated 33-kDa protein as epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase substrates and phospholipase A2 inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6921–6930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., McGray P., Mattaliano R. J., Burne C., Chow E. P., Sinclair L. K., Pepinsky R. B. Purification and characterization of proteolytic fragments of lipocortin I that inhibit phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7639–7645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., Wallner B. P., Mattaliano R. J., Tizard R., Burne C., Frey A., Hession C., McGray P., Sinclair L. K., Chow E. P. Two human 35 kd inhibitors of phospholipase A2 are related to substrates of pp60v-src and of the epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90736-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson N., Nguyen Van P., Söling H. D., Weber K. Functionally distinct serine phosphorylation sites of p36, the cellular substrate of retroviral protein kinase; differential inhibition of reassociation with p11. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3455–3460. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04669.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasik A., Pepinsky R. B., Shoelson S. E., Kahn C. R. Lipocortins 1 and 2 as substrates for the insulin receptor kinase in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11862–11867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miele L., Cordella-Miele E., Facchiano A., Mukherjee A. B. Novel anti-inflammatory peptides from the region of highest similarity between uteroglobin and lipocortin I. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):726–730. doi: 10.1038/335726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B., Sinclair L. K. Epidermal growth factor-dependent phosphorylation of lipocortin. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):81–84. doi: 10.1038/321081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B., Tizard R., Mattaliano R. J., Sinclair L. K., Miller G. T., Browning J. L., Chow E. P., Burne C., Huang K. S., Pratt D. Five distinct calcium and phospholipid binding proteins share homology with lipocortin I. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10799–10811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilar Fernandez M., Selmin O., Martin G. R., Yamada Y., Pfäffle M., Deutzmann R., Mollenhauer J., von der Mark K. The structure of anchorin CII, a collagen binding protein isolated from chondrocyte membrane. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5921–5925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poovaiah B. W., Reddy A. S. Calcium messenger system in plants. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci. 1987;6(1):47–103. doi: 10.1080/07352688709382247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell M. A., Glenney J. R. Regulation of calpactin I phospholipid binding by calpactin I light-chain binding and phosphorylation by p60v-src. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 15;247(2):321–328. doi: 10.1042/bj2470321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux S. J., Serlin B. S. Cellular mechanisms controlling light-stimulated gravitropism: role of calcium. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci. 1987;5(3):205–236. doi: 10.1080/07352688709382240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saris C. J., Tack B. F., Kristensen T., Glenney J. R., Jr, Hunter T. The cDNA sequence for the protein-tyrosine kinase substrate p36 (calpactin I heavy chain) reveals a multidomain protein with internal repeats. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90737-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G. F., André B. A rapid response to a plant hormone: auxin stimulates phospholipase A2 in vivo and in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 30;163(1):111–117. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer D. D., Haigler H. T. Characterization of Ca2+-dependent phospholipid binding and phosphorylation of lipocortin I. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6931–6937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedmak J. J., Grossberg S. E. A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):544–552. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets E. E., Giugni T. D., Coates G. G., Schlaepfer D. D., Haigler H. T. Epidermal growth factor dependent phosphorylation of a 35-kilodalton protein in placental membranes. Biochemistry. 1987 Feb 24;26(4):1164–1172. doi: 10.1021/bi00378a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Slaughter C. A., Leznicki I., Barjon P., Reynolds G. A. Human 67-kDa calelectrin contains a duplication of four repeats found in 35-kDa lipocortins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):664–668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. R., Geisow M. J. Predicted structure for the calcium-dependent membrane-binding proteins p35, p36, and p32. Protein Eng. 1987 Jun;1(3):183–187. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.3.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Johnsson N., Plessmann U., Van P. N., Söling H. D., Ampe C., Vandekerckhove J. The amino acid sequence of protein II and its phosphorylation site for protein kinase C; the domain structure Ca2+-modulated lipid binding proteins. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1599–1604. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02406.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]