Abstract
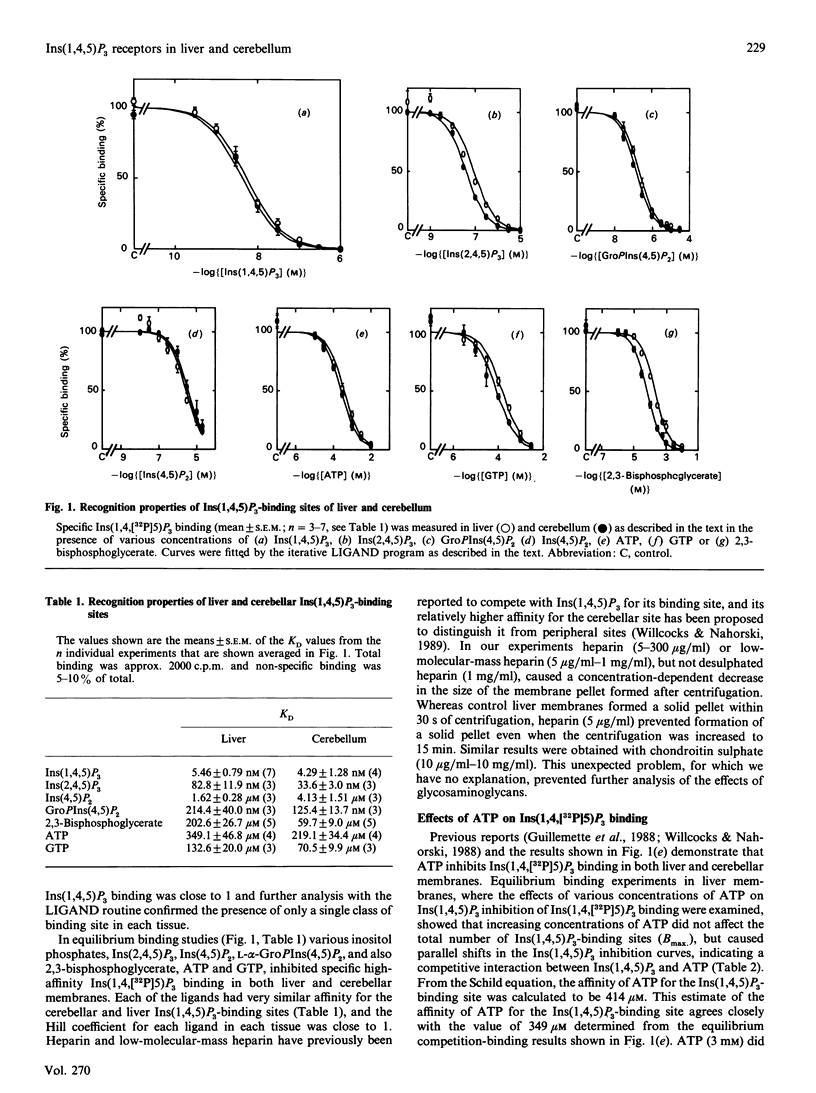
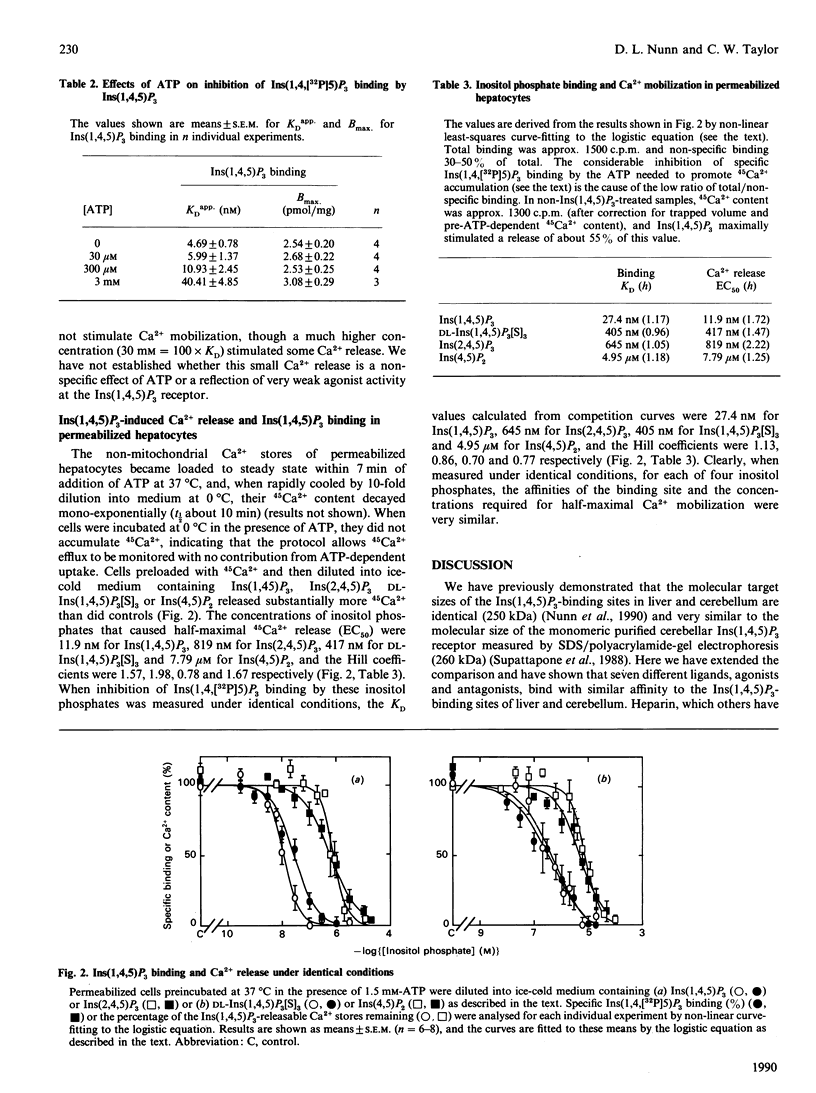
Ins(1,4,5)P3 is the intracellular messenger that in many cells mediates the effects of Ca2(+)-mobilizing receptors on intracellular Ca2+ stores. An Ins(1,4,5)P3 receptor from cerebellum has been purified and functionally reconstituted, but the relationship between this protein and the high-affinity Ins(1,4,5)P3-binding sites of peripheral tissues is unclear. We compared the Ins(1,4,5)P3-binding sites of liver and cerebellum by measuring inhibition of specific Ins(1,4,[32P]5)P3 binding by various ligands under equilibrium conditions, and find that each ligand binds with similar affinity in the two tissues. Earlier studies in which Ins(1,4,5)P3 binding and Ca2+ mobilization were measured under different conditions demonstrated large differences between KD values for binding and EC50 values (concn. giving half-maximal effect) for Ca2+ release. We show here that, when measured under identical conditions, KD and EC50 values for four agonists are similar. Schild analysis of inhibition of Ins(1,4,5)P3 binding by ATP demonstrates a competitive interaction between the two at the liver Ins(1,4,5)P3-binding site, and this partly accounts for earlier discrepancies in binding and Ca2(+)-release data. We conclude that the high-affinity Ins(1,4,5)P3-binding site of hepatocytes is likely to be the receptor that mediates Ca2+ mobilization, and that this receptor is at present indistinguishable from that in cerebellum.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champeil P., Combettes L., Berthon B., Doucet E., Orlowski S., Claret M. Fast kinetics of calcium release induced by myo-inositol trisphosphate in permeabilized rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17665–17673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris C. D., Huganir R. L., Supattapone S., Snyder S. H. Purified inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor mediates calcium flux in reconstituted lipid vesicles. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):87–89. doi: 10.1038/342087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi T., Yoshikawa S., Miyawaki A., Wada K., Maeda N., Mikoshiba K. Primary structure and functional expression of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-binding protein P400. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):32–38. doi: 10.1038/342032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh T. K., Eis P. S., Mullaney J. M., Ebert C. L., Gill D. L. Competitive, reversible, and potent antagonism of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-activated calcium release by heparin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11075–11079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh T. K., Mullaney J. M., Tarazi F. I., Gill D. L. GTP-activated communication between distinct inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive and -insensitive calcium pools. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):236–239. doi: 10.1038/340236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemette G., Balla T., Baukal A. J., Catt K. J. Characterization of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors and calcium mobilization in a hepatic plasma membrane fraction. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4541–4548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemette G., Balla T., Baukal A. J., Spät A., Catt K. J. Intracellular receptors for inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in angiotensin II target tissues. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1010–1015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horstman D. A., Takemura H., Putney J. W., Jr Formation and metabolism of [3H]inositol phosphates in AR42J pancreatoma cells. Substance P-induced Ca2+ mobilization in the apparent absence of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15297–15303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Rice H. L. The relationship between inositol trisphosphate receptor density and calcium release in brain microsomes. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Mar;35(3):355–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauger J. P., Claret M., Pietri F., Hilly M. Hormonal regulation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8821–8826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. A practical computer-based approach to the analysis of radioligand binding experiments. Comput Programs Biomed. 1983 Aug-Oct;17(1-2):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(83)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Holowka D., Stryer L. Highly cooperative opening of calcium channels by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):653–656. doi: 10.1126/science.2452482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muallem S., Schoeffield M., Pandol S., Sachs G. Inositol trisphosphate modification of ion transport in rough endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4433–4437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahorski S. R., Potter B. V. Molecular recognition of inositol polyphosphates by intracellular receptors and metabolic enzymes. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Apr;10(4):139–144. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn D. L., Potter B. V., Taylor C. W. Molecular target sizes of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors in liver and cerebellum. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):393–398. doi: 10.1042/bj2650393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prpić V., Green K. C., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Vasopressin-, angiotensin II-, and alpha 1-adrenergic-induced inhibition of Ca2+ transport by rat liver plasma membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1382–1385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spät A., Bradford P. G., McKinney J. S., Rubin R. P., Putney J. W., Jr A saturable receptor for 32P-inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate in hepatocytes and neutrophils. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):514–516. doi: 10.1038/319514a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supattapone S., Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Snyder S. H. Solubilization, purification, and characterization of an inositol trisphosphate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1530–1534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W., Berridge M. J., Cooke A. M., Potter B. V. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphorothioate, a stable analogue of inositol trisphosphate which mobilizes intracellular calcium. Biochem J. 1989 May 1;259(3):645–650. doi: 10.1042/bj2590645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willcocks A. L., Nahorski S. R. ATP and the binding of [3H]inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate to its receptor. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 1;255(3):1061–1061. doi: 10.1042/bj2551061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Supattapone S., Wilson V. S., Snyder S. H. Characterization of inositol trisphosphate receptor binding in brain. Regulation by pH and calcium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12132–12136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



