Abstract
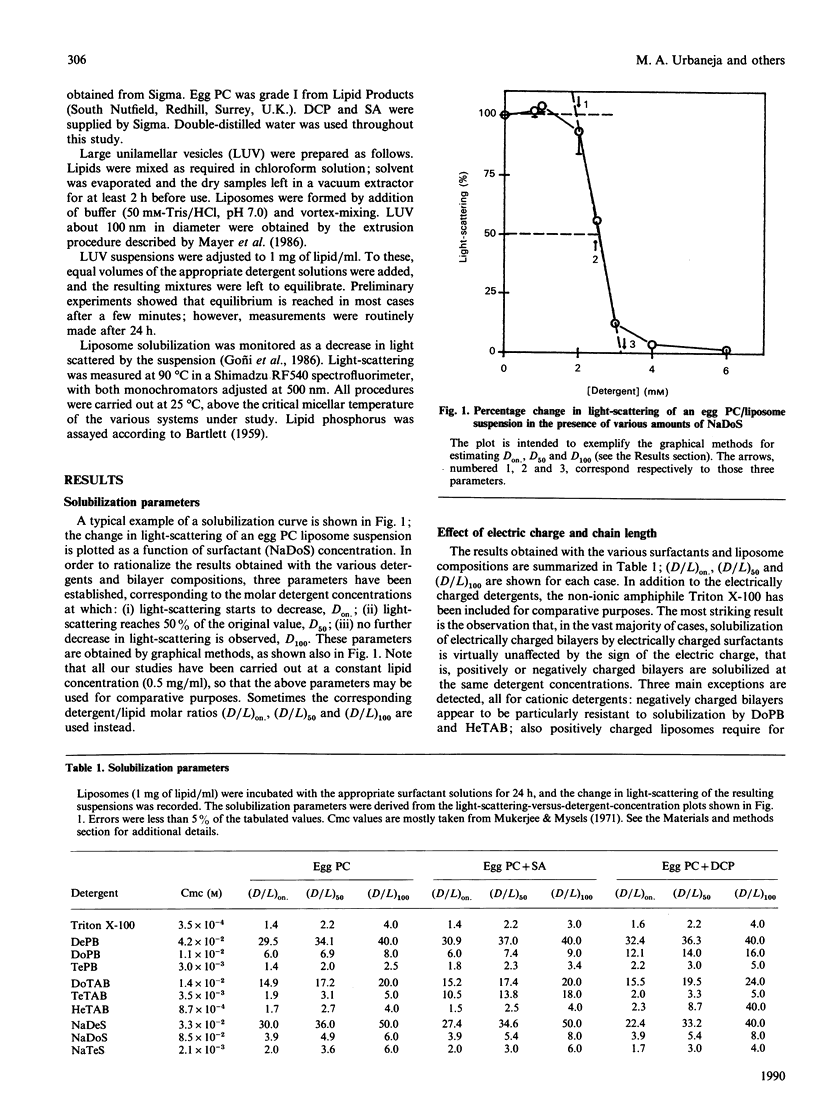
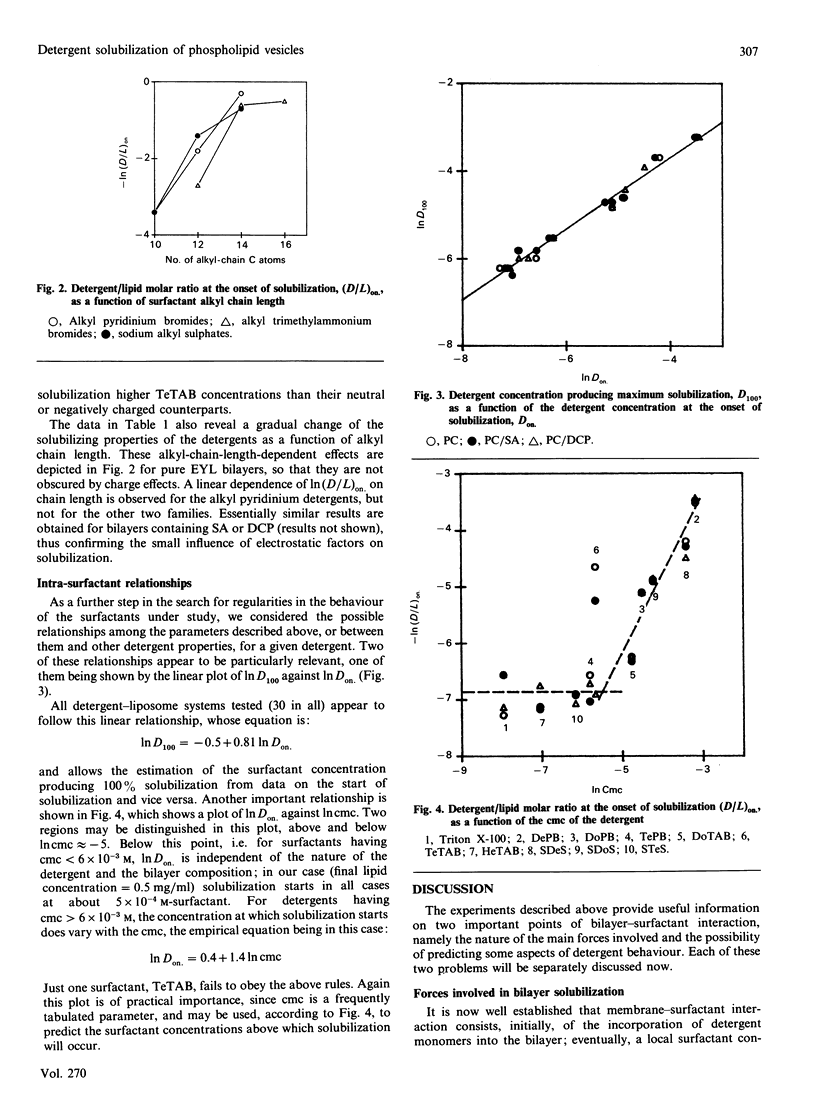
In order to explore the effect of electric charge on detergent solubilization of phospholipid bilayers, the interaction of nine electrically charged surfactants with neutral or electrically charged liposomes has been examined. The detergents belonged to the alkyl pyridinium, alkyl trimethylammonium or alkyl sulphate families. Large unilamellar liposomes formed by egg phosphatidylcholine plus or minus stearylamine or dicetyl phosphate were used. Solubilization was assessed as a decrease in light-scattering of the liposome suspensions. The results suggest that electrostatic forces do not play a significant role in the formation of mixed micelles and that hydrophobic interactions are by far the main forces involved in solubilization. In addition, from the study of thirty different liposome-surfactant systems, we have derived a series of empirical rules that may be useful in predicting the behaviour of untested surfactants: (i) the detergent concentration producing the onset of solubilization (Don) decreases as the alkyl chain length increases; the decrease follows a semi-logarithmic pattern in the case of alkyl pyridinium compounds; (ii) for surfactants with critical micellar concentrations (cmc) less than 6 x 10(-3) M, Don. is independent of the nature of the detergent and the bilayer composition; for detergents having cmc greater than 6 x 10(-3) M, Don. increases linearly with the cmc; and (iii) Don. varies linearly with the surfactant concentration that produces maximum solubilization.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goñi F. M., Urbaneja M. A., Arrondo J. L., Alonso A., Durrani A. A., Chapman D. The interaction of phosphatidylcholine bilayers with Triton X-100. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 3;160(3):659–665. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., McCaslin D. R., Fries E., Tanford C. Properties of detergents. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:734–749. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Solubilization of membranes by detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):29–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Miyakawa K., Shimozawa R. Interaction of surfactants with vesicle membrane of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine. Effect on gel-to-liquid-crystalline phase transition of lipid bilayer. Chem Phys Lipids. 1986 Dec 31;42(4):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(86)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isomaa B. Interactions of surface-active alkyltrimethylammonium salts with the erythrocyte membrane. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Apr 1;28(7):975–980. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90289-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israelachvili J. N., Marcelja S., Horn R. G. Physical principles of membrane organization. Q Rev Biophys. 1980 May;13(2):121–200. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. L., Schmidt C. F., Lichtenberg D., Litman B. J., Albert A. D. Solubilization of phosphatidylcholine bilayers by octyl glucoside. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 14;21(19):4576–4582. doi: 10.1021/bi00262a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenberg D. Characterization of the solubilization of lipid bilayers by surfactants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 19;821(3):470–478. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenberg D., Robson R. J., Dennis E. A. Solubilization of phospholipids by detergents. Structural and kinetic aspects. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 24;737(2):285–304. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L. D., Hope M. J., Cullis P. R. Vesicles of variable sizes produced by a rapid extrusion procedure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 13;858(1):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90302-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer P. G., Seelig J. Electric charge effects on phospholipid headgroups. Phosphatidylcholine in mixtures with cationic and anionic amphiphiles. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7720–7728. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbaneja M. A., Goñi F. M., Alonso A. Structural changes induced by Triton X-100 on sonicated phosphatidylcholine liposomes. Eur J Biochem. 1988 May 2;173(3):585–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


