Abstract
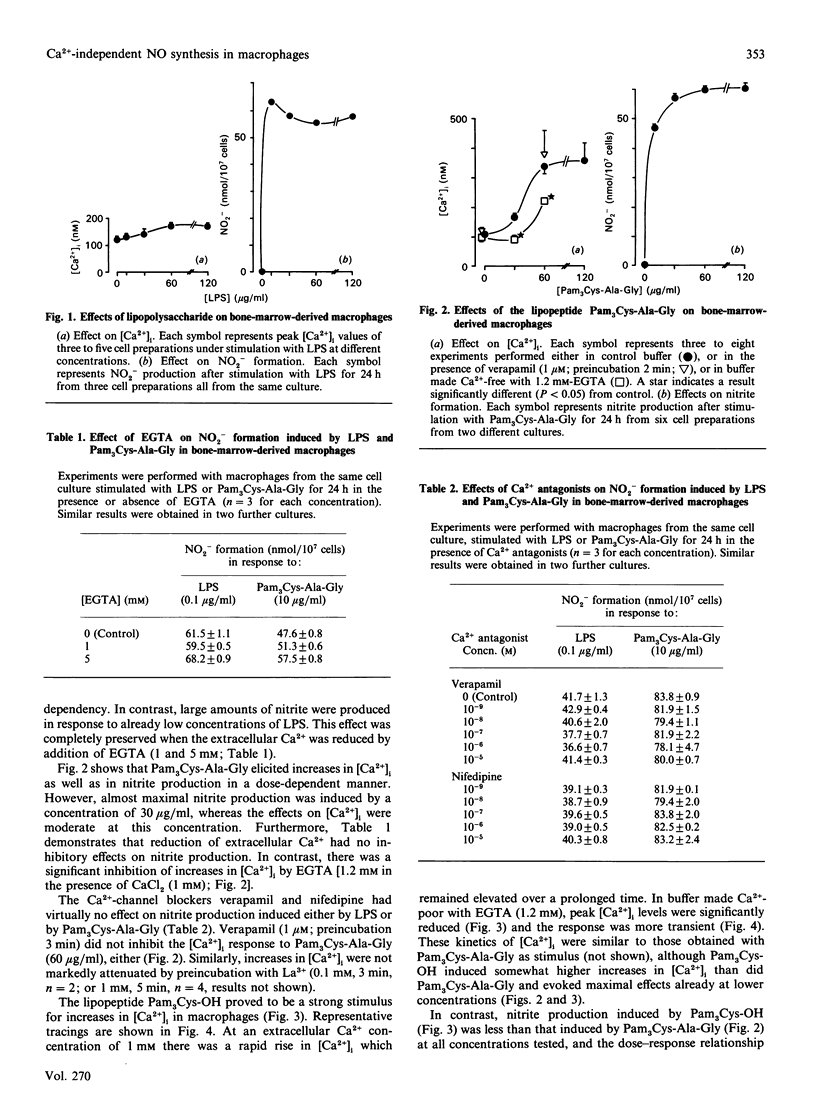
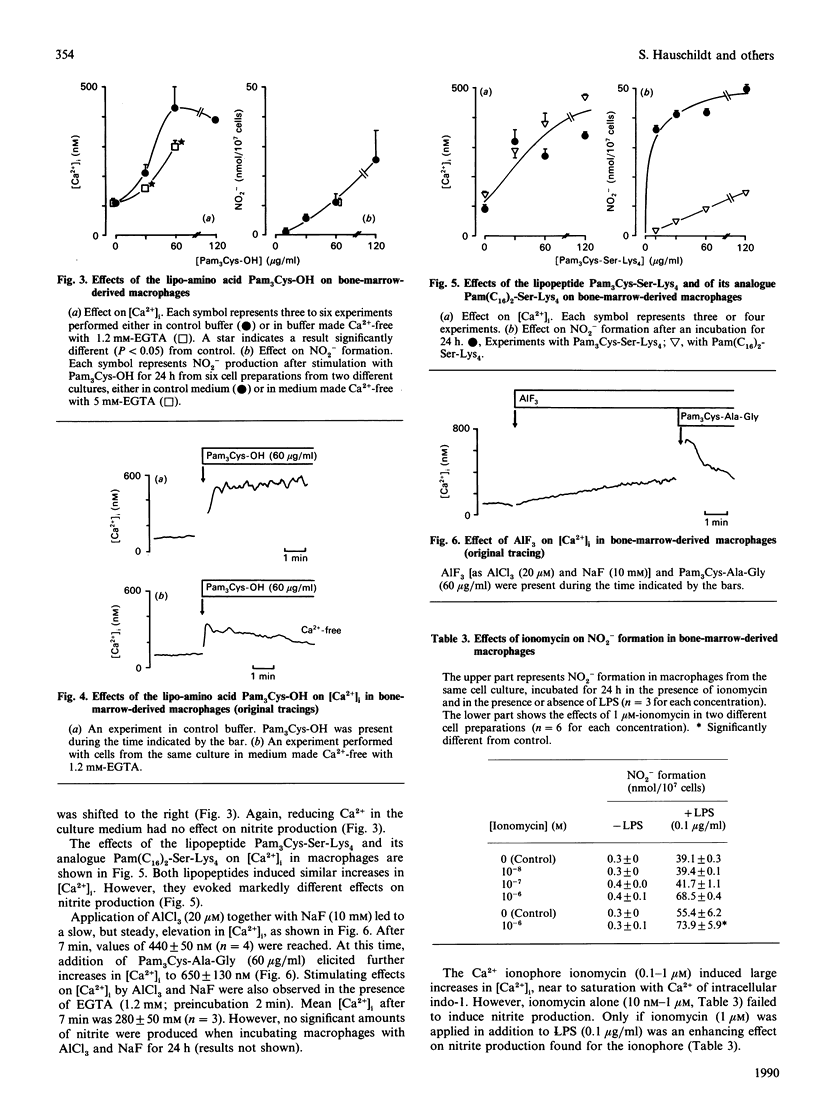
The aim of the present study was to analyse whether an increase in the intracellular free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) plays a role as a signal mediating synthesis of nitric oxide (NO) in bone-marrow-derived macrophages, either by stimulating induction of NO synthase or by regulating the activity of the enzyme. Therefore we compared the effects of various synthetic analogues of bacterial lipopeptide and of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on NO production (assessed as nitrite formation during an incubation for 24 h) and on [Ca2+]i [measured with the fluorescent probe indo-1 (1-[2-amino-5-(6-carboxyindol-2-yl)phenoxy]-2- 2-(2'-amino-5'-methylphenoxy)ethane-NNN'N'-tetra-acetic acid)]. Strongly dissociating effects were evoked on nitrite formation and on [Ca2+]i by the stimuli. LPS was preferentially effective on nitrite formation, whereas the Ca2+ ionophore ionomycin and AlF3 induced increases only in [Ca2+]i. The lipopeptides N-palmitoyl-(S)-[2,3-bis(palmitoyloxy)-(2RS)- propyl]-(R)-cysteinylalanylglycine, N-palmitoyl-(S)-[2,3-bis(palmitoyloxy)- (2RS)-propyl]-(R)-cysteinylseryl-lysyl-lysyl-lysine and (S)-(1,2- dicarboxyhexadecyl)ethyl-N-palmitoylcysteinylseryl-lysyl-lys yl-lysine stimulated both parameters, but the maximal effects on nitrite formation and the shape of the dose-response curves did not parallel the effects on [Ca2+]i. Reduction of extracellular Ca2+ with EGTA significantly inhibited increases in [Ca2+]i, but did not change nitrite formation. Furthermore, NO synthesis in the cytosolic fraction of stimulated macrophages was not affected by Ca2+ over the concentration range 10 nM-2 microM. We conclude that increases in [Ca2+]i are not required for NO production in bone-marrow-derived macrophages. Thus the cellular regulation of NO production strikingly differs from that in the vascular endothelium, brain and adrenal gland.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Isolation of nitric oxide synthetase, a calmodulin-requiring enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):682–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhme E., Schmidt H. H. Nitric oxide and cytosolic guanylate cyclase: components of an intercellular signalling system. Z Kardiol. 1989;78 (Suppl 6):75–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colden-Stanfield M., Schilling W. P., Ritchie A. K., Eskin S. G., Navarro L. T., Kunze D. L. Bradykinin-induced increases in cytosolic calcium and ionic currents in cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Circ Res. 1987 Nov;61(5):632–640. doi: 10.1161/01.res.61.5.632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J., Charles S. L., Chess-Williams R. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor release on activation of NMDA receptors suggests role as intercellular messenger in the brain. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):385–388. doi: 10.1038/336385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. C., Wagner D. A., Glogowski J., Skipper P. L., Wishnok J. S., Tannenbaum S. R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1982 Oct;126(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschildt S., Bassenge E., Bessler W., Busse R., Mülsch A. L-arginine-dependent nitric oxide formation and nitrite release in bone marrow-derived macrophages stimulated with bacterial lipopeptide and lipopolysaccharide. Immunology. 1990 Jul;70(3):332–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschildt S., Hirt W., Bessler W. Modulation of protein kinase C activity by NaF in bone marrow derived macrophages. FEBS Lett. 1988 Mar 28;230(1-2):121–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80654-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschildt S., Hoffmann P., Beuscher H. U., Dufhues G., Heinrich P., Wiesmüller K. H., Jung G., Bessler W. G. Activation of bone marrow-derived mouse macrophages by bacterial lipopeptide: cytokine production, phagocytosis and Ia expression. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jan;20(1):63–68. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschildt S., Wolf B., Lückhoff A., Bessler W. G. Determination of second messengers and protein kinase C in bone marrow derived macrophages stimulated with a bacterial lipopeptide. Mol Immunol. 1990 Jun;27(6):473–479. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90065-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Vavrin Z. Macrophage cytotoxicity: role for L-arginine deiminase and imino nitrogen oxidation to nitrite. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):473–476. doi: 10.1126/science.2432665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann P., Wiesmüller K. H., Metzger J., Jung G., Bessler W. G. Induction of tumor cytotoxicity in murine bone marrow-derived macrophages by two synthetic lipopeptide analogues. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1989 Jun;370(6):575–582. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1989.370.1.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Palacios M., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Formation of nitric oxide from L-arginine in the central nervous system: a transduction mechanism for stimulation of the soluble guanylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5159–5162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lückhoff A., Busse R. Increased free calcium in endothelial cells under stimulation with adenine nucleotides. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Mar;126(3):414–420. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041260312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lückhoff A., Pohl U., Mülsch A., Busse R. Differential role of extra- and intracellular calcium in the release of EDRF and prostacyclin from cultured endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;95(1):189–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb16564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A. Nitric oxide: biosynthesis and biological significance. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Dec;14(12):488–492. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A., Yoon P. S., Iyengar R., Leaf C. D., Wishnok J. S. Macrophage oxidation of L-arginine to nitrite and nitrate: nitric oxide is an intermediate. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8706–8711. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Biosynthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine. A pathway for the regulation of cell function and communication. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 1;38(11):1709–1715. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90403-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mülsch A., Bassenge E., Busse R. Nitric oxide synthesis in endothelial cytosol: evidence for a calcium-dependent and a calcium-independent mechanism. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;340(6 Pt 2):767–770. doi: 10.1007/BF00169688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios M., Knowles R. G., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Nitric oxide from L-arginine stimulates the soluble guanylate cyclase in adrenal glands. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 15;165(2):802–809. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80037-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R., Matthews G., Neher E. Regulation of calcium influx by second messengers in rat mast cells. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):499–504. doi: 10.1038/334499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitermann A., Metzger J., Wiesmüller K. H., Jung G., Bessler W. G. Lipopeptide derivatives of bacterial lipoprotein constitute potent immune adjuvants combined with or covalently coupled to antigen or hapten. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1989 Apr;370(4):343–352. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1989.370.1.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Nathan C. F. Nitric oxide. A macrophage product responsible for cytostasis and respiratory inhibition in tumor target cells. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1543–1555. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhoutte P. M. Vascular physiology: the end of the quest? Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):459–460. doi: 10.1038/327459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesmüller K. H., Bessler W., Jung G. Synthesis of the mitogenic S-[2,3-bis(palmitoyloxy)propyl]-N-palmitoylpentapeptide from Escherichia coli lipoprotein. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1983 May;364(5):593–606. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1983.364.1.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


