Abstract
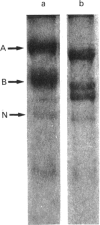
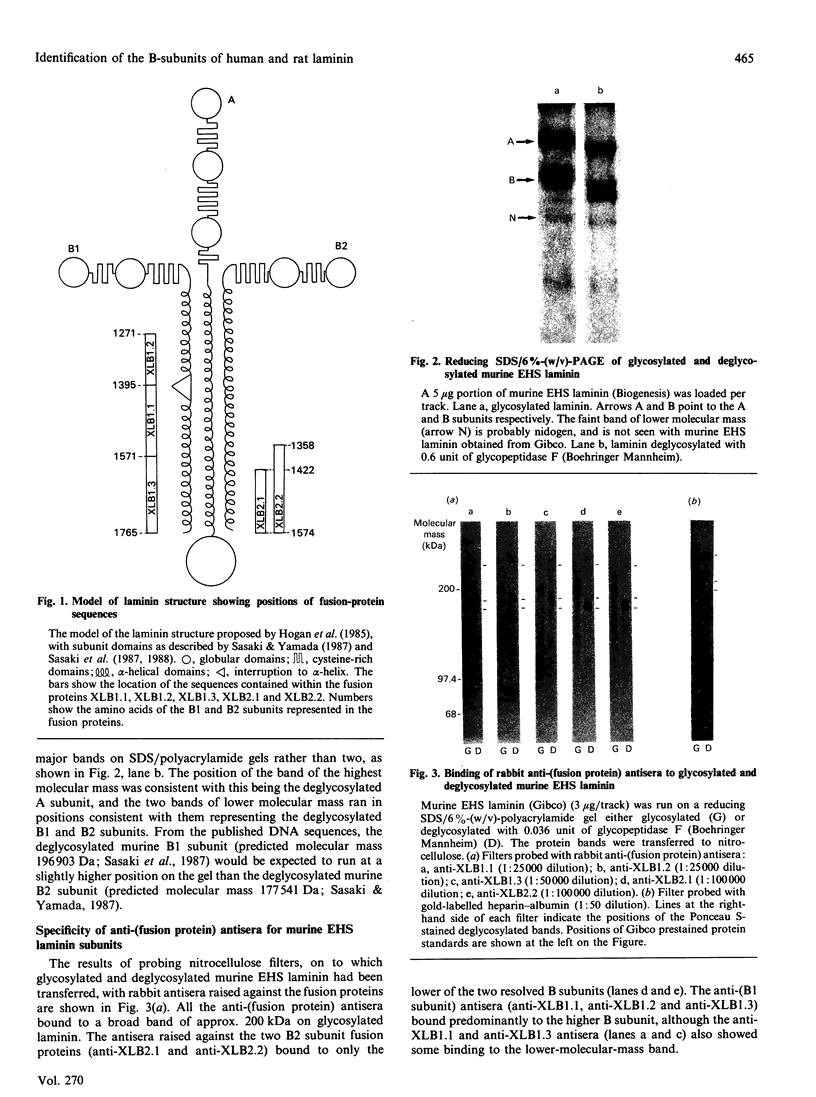
Antisera raised against fusion proteins consisting of murine laminin B1 and B2 subunit sequences fused to the C-terminus of Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase were tested for their subunit specificity on Western blots of deglycosylated murine Engelbreth-Holm-Swarm (EHS) laminin. The antisera raised against B2 subunit sequences (anti-XLB2.1 and anti-XLB2.2) bound only to the EHS laminin B2 subunit. One of the antisera raised against B1 subunit sequences (anti-XLB1.2) was specific for the B1 subunit, whereas two others (anti-XLB1.1 and anti-XLB1.3) cross-reacted with the EHS laminin B2 subunit. Gold-labelled heparin-albumin was shown to bind specifically to the A subunit of deglycosylated EHS laminin on Western blots. These reagents were used to identify the homologous subunits in rat parietal-yolk-sac laminin and human placental laminin. The anti-(fusion protein) antisera identified the B1 and B2 subunits of the rat laminin, and these were similar in size to the murine EHS B subunits. Human placental laminin gave bands of 400, 340, 230, 190 and 180 kDa on reducing SDS/PAGE. The anti-(fusion protein) antisera identified the 230 and 190 kDa bands as the B1 and B2 subunits respectively. Gold-labelled heparin-albumin bound to the 400, 340 and 190 kDa bands of human placental laminin and so did not unambiguously identify a single A subunit. The human placental laminin may contain a mixture of isoforms, with alternative subunits substituting for the A subunit.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aratani Y., Kitagawa Y. Enhanced synthesis and secretion of type IV collagen and entactin during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells and production of unorthodox laminin complex. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16163–16169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arumugham R. G., Trumbore M., Thomas T., Makhlouf S., Tanzer M. L. Separation and characterization of the subunits of the laminin of EHS sarcoma. Connect Tissue Res. 1988;18(2):135–147. doi: 10.3109/03008208809008065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow D. P., Green N. M., Kurkinen M., Hogan B. L. Sequencing of laminin B chain cDNAs reveals C-terminal regions of coiled-coil alpha-helix. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2355–2362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02140.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck K., Hunter I., Engel J. Structure and function of laminin: anatomy of a multidomain glycoprotein. FASEB J. 1990 Feb 1;4(2):148–160. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.2.2404817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charonis A. S., Skubitz A. P., Koliakos G. G., Reger L. A., Dege J., Vogel A. M., Wohlhueter R., Furcht L. T. A novel synthetic peptide from the B1 chain of laminin with heparin-binding and cell adhesion-promoting activities. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1253–1260. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charonis A. S., Tsilibary E. C., Saku T., Furthmayr H. Inhibition of laminin self-assembly and interaction with type IV collagen by antibodies to the terminal domain of the long arm. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1689–1697. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixit S. N. Isolation, purification and characterization of intact and pepsin-derived fragments of laminin from human placenta. Connect Tissue Res. 1985;14(1):31–40. doi: 10.3109/03008208509089841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doorbar J., Campbell D., Grand R. J., Gallimore P. H. Identification of the human papilloma virus-1a E4 gene products. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):355–362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04219.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar D., Timpl R., Thoenen H. Structural requirements for the stimulation of neurite outgrowth by two variants of laminin and their inhibition by antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1299–1306. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblom P. Developmentally regulated conversion of mesenchyme to epithelium. FASEB J. 1989 Aug;3(10):2141–2150. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.10.2666230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J., Odermatt E., Engel A., Madri J. A., Furthmayr H., Rohde H., Timpl R. Shapes, domain organizations and flexibility of laminin and fibronectin, two multifunctional proteins of the extracellular matrix. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Krusius T., Wewer U., Ruoslahti E. Laminin from rat yolk sac tumor: isolation, partial characterization, and comparison with mouse laminin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Apr 15;222(2):649–656. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90562-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. L., Deutzmann R., von der Mark K. Two distinct cell-binding domains in laminin can independently promote nonneuronal cell adhesion and spreading. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):589–598. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf J., Iwamoto Y., Sasaki M., Martin G. R., Kleinman H. K., Robey F. A., Yamada Y. Identification of an amino acid sequence in laminin mediating cell attachment, chemotaxis, and receptor binding. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):989–996. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90707-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant D. S., Tashiro K., Segui-Real B., Yamada Y., Martin G. R., Kleinman H. K. Two different laminin domains mediate the differentiation of human endothelial cells into capillary-like structures in vitro. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):933–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90945-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liesi P., Risteli L. Glial cells of mammalian brain produce a variant form of laminin. Exp Neurol. 1989 Jul;105(1):86–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(89)90175-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manthorpe M., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E., Longo F. M., Davis G. E., Varon S. Laminin promotes neuritic regeneration from cultured peripheral and central neurons. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1882–1890. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. B., Furcht L. T. Laminin and fibronectin promote the haptotactic migration of B16 mouse melanoma cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1474–1480. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ocalan M., Goodman S. L., Kühl U., Hauschka S. D., von der Mark K. Laminin alters cell shape and stimulates motility and proliferation of murine skeletal myoblasts. Dev Biol. 1988 Jan;125(1):158–167. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno M., Martinez-Hernandez A., Ohno N., Kefalides N. A. Isolation of laminin from human placental basement membranes: amnion, chorion and chorionic microvessels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 May 16;112(3):1091–1098. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91730-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno M., Martinez-Hernandez A., Ohno N., Kefalides N. A. Laminin M is found in placental basement membranes, but not in basement membranes of neoplastic origin. Connect Tissue Res. 1986;15(3):199–207. doi: 10.3109/03008208609167143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen D., Nagayoshi T., Fazio M., Peltonen J., Jaakkola S., Sanborn D., Sasaki T., Kuivaniemi H., Chu M. L., Deutzmann R. Human laminin: cloning and sequence analysis of cDNAs encoding A, B1 and B2 chains, and expression of the corresponding genes in human skin and cultured cells. Lab Invest. 1989 Jun;60(6):772–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott U., Odermatt E., Engel J., Furthmayr H., Timpl R. Protease resistance and conformation of laminin. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Mar;123(1):63–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson M., Aumailley M., Deutzmann R., Timpl R., Beck K., Engel J. Laminin-nidogen complex. Extraction with chelating agents and structural characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):11–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson M., Saladin K. Mouse heart laminin. Purification of the native protein and structural comparison with Engelbreth-Holm-Swarm tumor laminin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18726–18732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters B. P., Hartle R. J., Krzesicki R. F., Kroll T. G., Perini F., Balun J. E., Goldstein I. J., Ruddon R. W. The biosynthesis, processing, and secretion of laminin by human choriocarcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14732–14742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikkarainen T., Eddy R., Fukushima Y., Byers M., Shows T., Pihlajaniemi T., Saraste M., Tryggvason K. Human laminin B1 chain. A multidomain protein with gene (LAMB1) locus in the q22 region of chromosome 7. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10454–10462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikkarainen T., Kallunki T., Tryggvason K. Human laminin B2 chain. Comparison of the complete amino acid sequence with the B1 chain reveals variability in sequence homology between different structural domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6751–6758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakashita S., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Basement membrane glycoprotein laminin binds to heparin. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jul 28;116(2):243–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80654-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Kato S., Kohno K., Martin G. R., Yamada Y. Sequence of the cDNA encoding the laminin B1 chain reveals a multidomain protein containing cysteine-rich repeats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):935–939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Kleinman H. K., Huber H., Deutzmann R., Yamada Y. Laminin, a multidomain protein. The A chain has a unique globular domain and homology with the basement membrane proteoglycan and the laminin B chains. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16536–16544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Yamada Y. The laminin B2 chain has a multidomain structure homologous to the B1 chain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17111–17117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skubitz A. P., McCarthy J. B., Charonis A. S., Furcht L. T. Localization of three distinct heparin-binding domains of laminin by monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4861–4868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Luzio J. P. Construction of a new family of high efficiency bacterial expression vectors: identification of cDNA clones coding for human liver proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1429–1434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Gómez C. M., Plummer T. H., Jr Deglycosylation of asparagine-linked glycans by peptide:N-glycosidase F. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 13;24(17):4665–4671. doi: 10.1021/bi00338a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Rohde H., Robey P. G., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., Martin G. R. Laminin--a glycoprotein from basement membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9933–9937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wewer U., Albrechtsen R., Manthorpe M., Varon S., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Human laminin isolated in a nearly intact, biologically active form from placenta by limited proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12654–12660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Friedman R., Chung A. E. Analysis of the assembly of laminin and the laminin-entactin complex with laminin chain specific monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8780–8787. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]