Abstract
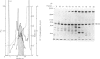
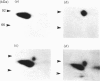
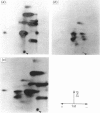
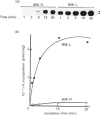
A Mr-80,000 acidic phosphoprotein ('80K protein') is a specific substrate for protein kinase C. We attempted to purify the 80K protein from a human squamous-cell carcinoma cell line, Ca9-22, by the sequential use of heat treatment, (NH4)2SO4 precipitation, Mono Q column chromatography, proRPC column chromatography and gel filtration. The 80K protein was assayed by phosphorylation in vitro by using partially purified human type III protein kinase C, and was fractionated into two distinct molecular species with slightly different Mr values, designated 80K-L and 80K-H proteins. Phosphorylation occurred mainly at serine residues of these proteins. Two-dimensional phosphopeptide maps after trypsin digestion and kinetic profiles of phosphorylation were different from each other. Ca2(+)- and phospholipid-dependency of the phosphorylation in vitro confirmed that both 80K-L and 80K-H proteins are true substrates for three subtypes of protein kinase C. The 80K-L protein was a preferential substrate for type III protein kinase C, and the 80K-H protein was phosphorylated more effectively by type I and type II protein kinase C. The possible roles of these two distinct 80K proteins in signal transduction are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Ghany M., el-Gendy K., Zhang S., Raden D., Racker E. Brain protein kinase C phosphorylating poly(arginine,serine) or lamin B is stimulated by anions and by an activator purified from bovine serum albumin preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1761–1765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert K. A., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. The 87-kDa protein, a major specific substrate for protein kinase C: purification from bovine brain and characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7046–7050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert K. A., Walaas S. I., Wang J. K., Greengard P. Widespread occurrence of "87 kDa," a major specific substrate for protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2822–2826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J., Stumpo D. J., Huang J. K., Nemenoff R. A., Spach D. H. Protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways of proto-oncogene induction in human astrocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7774–7781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J., Wen L., Glynn B. P., Witters L. A. Protein kinase C-stimulated phosphorylation in vitro of a Mr 80,000 protein phosphorylated in response to phorbol esters and growth factors in intact fibroblasts. Distinction from protein kinase C and prominence in brain. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1459–1469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J., Witters L. A., Girard P. R., Kuo J. F., Quamo S. N. Growth factor-stimulated protein phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 cells. Evidence for protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13304–13315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamou S., Hirai M., Rikimaru K., Enomoto S., Shimizu N. Biosynthesis of the epidermal growth factor receptor in human squamous cell carcinoma lines: secretion of the truncated receptor is not common to epidermal growth factor receptor-hyperproducing cells. Cell Struct Funct. 1988 Feb;13(1):25–38. doi: 10.1247/csf.13.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Tanaka T., Onoda K., Hagiwara M., Watanabe M., Ohta H., Ito Y., Tsurudome M., Yoshida T. Cell type-specific expression of protein kinase C isozymes in the rabbit cerebellum. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4523–4526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai M., Gamou S., Kobayashi M., Shimizu N. Lung cancer cells often express high levels of protein kinase C activity. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1989 Mar;80(3):204–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1989.tb02292.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai M., Gamou S., Minoshima S., Shimizu N. Two independent mechanisms for escaping epidermal growth factor-mediated growth inhibition in epidermal growth factor receptor-hyperproducing human tumor cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):791–799. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai M., Shimizu N. Stimulation of a MR 80,000 protein phosphorylation by EGF in EGF receptor-hyperproducing human tumor cells. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Apr;139(1):9–17. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isacke C. M., Meisenhelder J., Brown K. D., Gould K. L., Gould S. J., Hunter T. Early phosphorylation events following the treatment of Swiss 3T3 cells with bombesin and the mammalian bombesin-related peptide, gastrin-releasing peptide. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2889–2898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04584.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwashita S., Fox C. F. Epidermal growth factor and potent phorbol tumor promoters induce epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylation in a similar but distinctively different manner in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2559–2567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata T., Sullivan N. F., Wooten M. W. Reduced protein kinase C activity in a ras-resistant cell line derived from Ki-MSV transformed cells. Oncogene. 1987 Mar;1(1):37–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karns L. R., Ng S. C., Freeman J. A., Fishman M. C. Cloning of complementary DNA for GAP-43, a neuronal growth-related protein. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):597–600. doi: 10.1126/science.2437653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto S., Hidaka H. 1-(5-Isoquinolinesulfonyl)-2-methylpiperazine (H-7) is a selective inhibitor of protein kinase C in rabbit platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 30;125(1):258–264. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80362-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kligman D., Patel J. A protein modulator stimulates C kinase-dependent phosphorylation of a 90K substrate in synaptic membranes. J Neurochem. 1986 Jul;47(1):298–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb02862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laumas S., Abdel-Ghany M., Leister K., Resnick R., Kandrach A., Racker E. Decreased susceptibility of a 70-kDa protein to cathepsin L after phosphorylation by protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3021–3025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris C., Rozengurt E. Purification of a phosphoprotein from rat brain closely related to the 80 kDa substrate of protein kinase C identified in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 25;231(2):311–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80840-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Kikkawa U., Ogita K., Fujii T., Kurokawa T., Asaoka Y., Sekiguchi K., Ase K., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. Expression and properties of two types of protein kinase C: alternative splicing from a single gene. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1116–1120. doi: 10.1126/science.3576226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel J., Kligman D. Purification and characterization of an Mr 87,000 protein kinase C substrate from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16686–16691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E. Early signals in the mitogenic response. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):161–166. doi: 10.1126/science.3018928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Rodriguez-Pena M., Smith K. A. Phorbol esters, phospholipase C, and growth factors rapidly stimulate the phosphorylation of a Mr 80,000 protein in intact quiescent 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7244–7248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahai A., Feuerstein N., Cooper H. L., Salomon D. S. Effect of epidermal growth factor and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate on the phosphorylation of soluble acidic proteins in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1986 Aug;46(8):4143–4150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai K., Hirai M., Minoshima S., Kudoh J., Fukuyama R., Shimizu N. Isolation of cDNAs encoding a substrate for protein kinase C: nucleotide sequence and chromosomal mapping of the gene for a human 80K protein. Genomics. 1989 Aug;5(2):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90063-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpo D. J., Graff J. M., Albert K. A., Greengard P., Blackshear P. J. Molecular cloning, characterization, and expression of a cDNA encoding the "80- to 87-kDa" myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate: a major cellular substrate for protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4012–4016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyers M., Rachubinski R. A., Stewart M. I., Varrichio A. M., Shorr R. G., Haslam R. J., Harley C. B. Molecular cloning and expression of the major protein kinase C substrate of platelets. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):470–473. doi: 10.1038/333470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsumi J., Iizuka M., Kobayashi S. Interferon production with multitray culture system on a large scale. J Interferon Res. 1984;4(1):9–16. doi: 10.1089/jir.1984.4.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W. C., Walaas S. I., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Calcium/phospholipid regulates phosphorylation of a Mr "87k" substrate protein in brain synaptosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5249–5253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]