Abstract
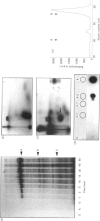
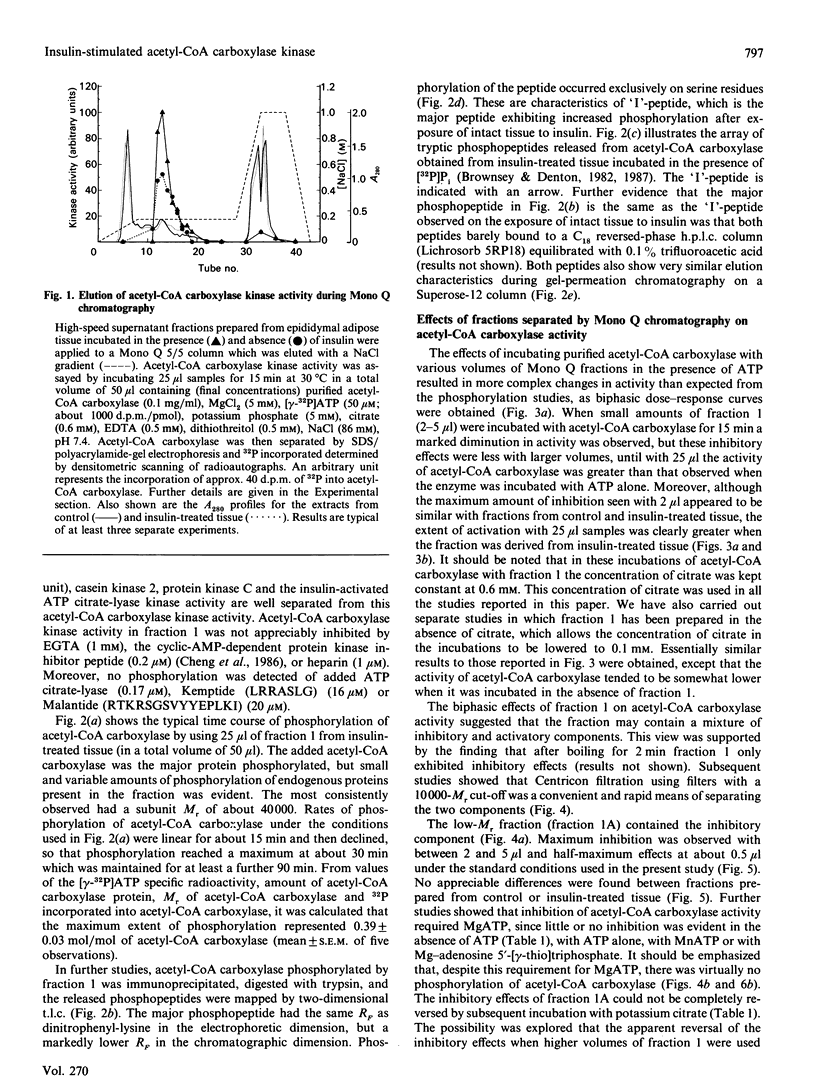
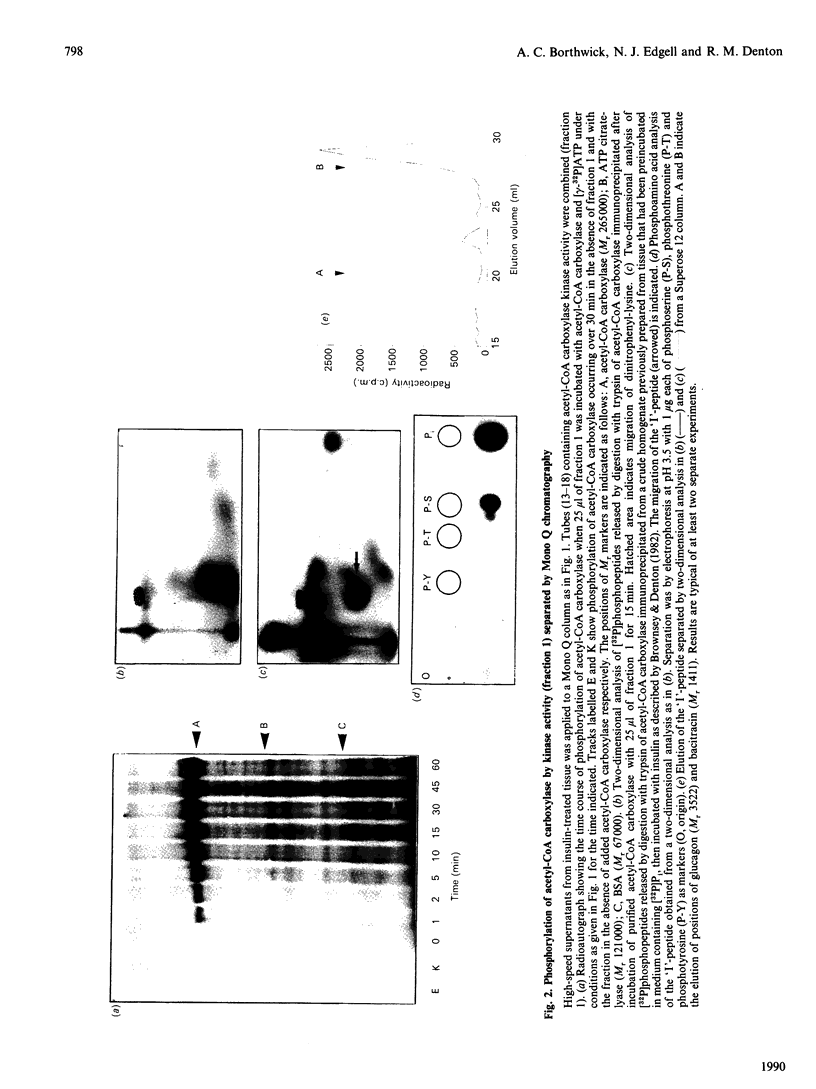
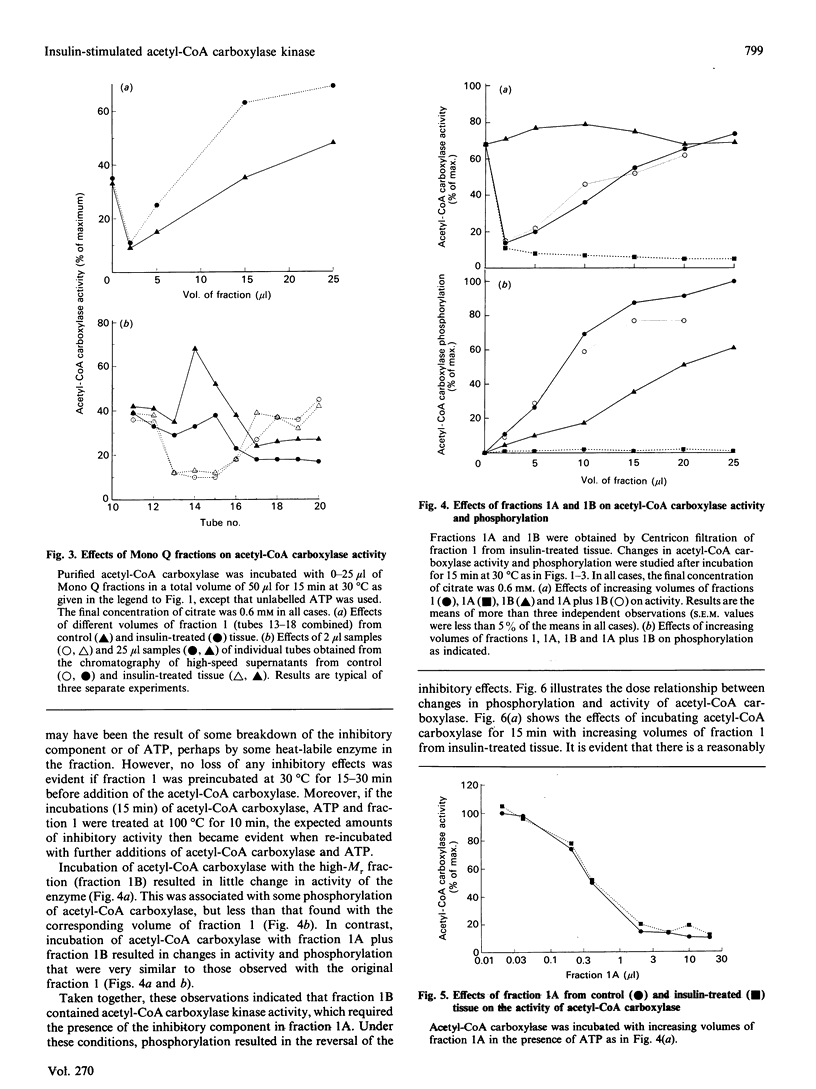
1. Most of the cyclic-nucleotide-independent acetyl-CoA carboxylase kinase activity in an extract of rat epididymal adipose tissue was evaluated from a Mono Q column by 0.175 M-NaCl at pH 7.4. The activity of the kinase in this fraction (fraction 1) was increased after exposure of intact tissue to insulin. 2. Incubation of purified adipose-tissue acetyl-CoA carboxylase with [gamma-32P]ATP and samples of fraction 1 led to the incorporation of up to 0.4 mol of 32P/mol of enzyme subunit. Most of the phosphorylation was on serine residues within a single tryptic peptide. This peptide, on the basis of two-dimensional t.l.c. analysis, h.p.l.c. and Superose 12 chromatography, appeared to be the same as the acetyl-CoA carboxylase peptide ('I'-peptide) which exhibits increased phosphorylation in insulin-treated tissue. 3. Phosphorylation of purified acetyl-CoA carboxylase by the kinase in fraction 1 was found to be associated with a parallel 4-fold increase in activity. However, increases in both phosphorylation and activity were much diminished if fraction 1 was treated by Centricon centrifugation to remove low-Mr components. Among these components was a potent inhibitor of acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity which appeared to be necessary for the kinase in fraction 1 to be fully active. 4. The inhibitor remains to be identified, but inhibition requires MgATP, although the inhibitor itself does not cause any phosphorylation of the carboxylase. No effects of insulin were observed on the activity of the inhibitor. 5. It is concluded that the kinase probably plays an important role in the mechanism whereby insulin brings about the well-established increases in phosphorylation and activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase in adipose tissue.
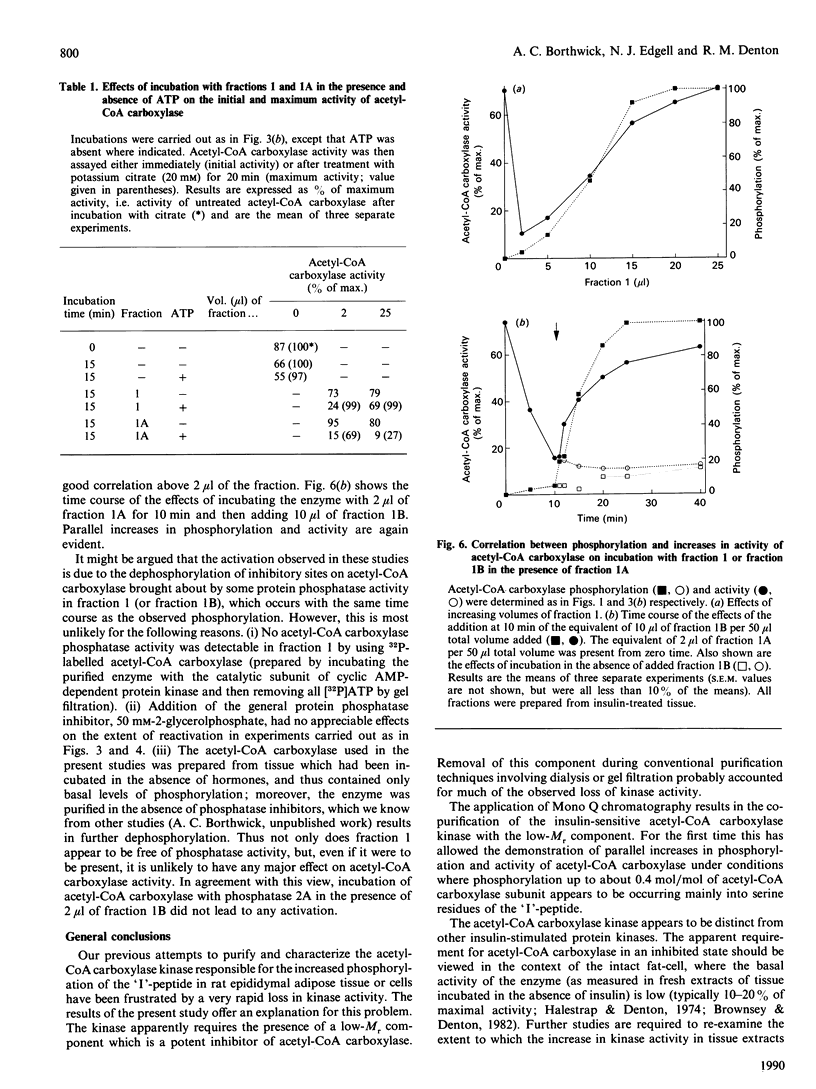
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borthwick A. C., Edgell N. J., Denton R. M. Mechanisms involved in the short-term regulation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase by insulin. Biochem Soc Trans. 1986 Jun;14(3):563–565. doi: 10.1042/bst0140563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borthwick A. C., Edgell N. J., Denton R. M. Use of rapid gel-permeation chromatography to explore the inter-relationships between polymerization, phosphorylation and activity of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Effects of insulin and phosphorylation by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 1;241(3):773–782. doi: 10.1042/bj2410773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownsey R. W., Belsham G. J., Denton R. M. Evidence for phosphorylation and activation of acetyl CoA carboxylase by a membrane-associated cyclic AMP-independent protein kinase. Relationship to the activation of acetyl CoA carboxylase by insulin. FEBS Lett. 1981 Feb 23;124(2):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80123-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownsey R. W., Denton R. M. Evidence that insulin activates fat-cell acetyl-CoA carboxylase by increased phosphorylation at a specific site. Biochem J. 1982 Jan 15;202(1):77–86. doi: 10.1042/bj2020077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownsey R. W., Dong G. W., Lam V., McGreer W. Studies on protein phosphorylation using subcellular fractions from insulin-treated white adipose tissue of rats. Biochem Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;66(4):296–308. doi: 10.1139/o88-039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownsey R. W., Edgell N. J., Hopkirk T. J., Denton R. M. Studies on insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase, ATP citrate lyase and other proteins in rat epididymal adipose tissue. Evidence for activation of a cyclic AMP-independent protein kinase. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 15;218(3):733–743. doi: 10.1042/bj2180733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownsey R. W., Hughes W. A., Denton R. M. Adrenaline and the regulation of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase in rat epididymal adipose tissue. Inactivation of the enzyme is associated with phosphorylation and can be reversed on dephosphorylation. Biochem J. 1979 Oct 15;184(1):23–32. doi: 10.1042/bj1840023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownsey R. W., Hughes W. A., Denton R. M. Demonstration of the phosphorylation of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase within intact rat epididymal fat-cells. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 15;168(3):441–445. doi: 10.1042/bj1680441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buechler K. F., Beynen A. C., Geelen M. J. Studies on the assay, activity and sedimentation behaviour of acetyl-CoA carboxylase from isolated hepatocytes incubated with insulin or glucagon. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 1;221(3):869–874. doi: 10.1042/bj2210869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H. C., Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B., Smith A. J., Misconi L., Van Patten S. M., Walsh D. A. A potent synthetic peptide inhibitor of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):989–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Brownsey R. W., Belsham G. J. A partial view of the mechanism of insulin action. Diabetologia. 1981 Oct;21(4):347–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00252681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halestrap A. P., Denton R. M. Insulin and the regulation of adipose tissue acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;132(3):509–517. doi: 10.1042/bj1320509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halestrap A. P., Denton R. M. Specific inhibition of pyruvate transport in rat liver mitochondria and human erythrocytes by alpha-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamate. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;138(2):313–316. doi: 10.1042/bj1380313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haystead T. A., Campbell D. G., Hardie D. G. Analysis of sites phosphorylated on acetyl-CoA carboxylase in response to insulin in isolated adipocytes. Comparison with sites phosphorylated by casein kinase-2 and the calmodulin-dependent multiprotein kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 1;175(2):347–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haystead T. A., Hardie D. G. Both insulin and epidermal growth factor stimulate lipogenesis and acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity in isolated adipocytes. Importance of homogenization procedure in avoiding artefacts in acetyl-CoA carboxylase assay. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 1;234(2):279–284. doi: 10.1042/bj2340279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haystead T. A., Hardie D. G. Insulin and phorbol ester stimulate phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase at similar sites in isolated adipocytes. Lack of correspondence with sites phosphorylated on the purified enzyme by protein kinase C. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 1;175(2):339–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. G., Denton R. M. Evidence that fatty acid synthesis in the interscapular brown adipose tissue of cold-adapted rats is increased in vivo by insulin by mechanisms involving parallel activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase and acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 15;166(3):627–630. doi: 10.1042/bj1660627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munday M. R., Hardie D. G. Isolation of three cyclic-AMP-independent acetyl-CoA carboxylase kinases from lactating rat mammary gland and characterization of their effects on enzyme activity. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 15;141(3):617–627. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munday M. R., Williamson D. H. Effects of starvation, insulin or prolactin deficiency on the activity of acetyl-CoA carboxylase in mammary gland and liver of lactating rats. FEBS Lett. 1982 Feb 22;138(2):285–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80462-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper J. P., Bacon G. W., Witters L. A. Phosphorylation of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase by casein kinase I and casein kinase II. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Dec;227(2):386–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90468-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A. Insulin stimulates the phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 29;100(2):872–878. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80254-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A., Moriarity D., Martin D. B. Regulation of hepatic acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase by insulin and glucagon. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6644–6649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A., Watts T. D., Daniels D. L., Evans J. L. Insulin stimulates the dephosphorylation and activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5473–5477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]