Abstract

Provided herein are novel imidazopyridine and imidazopyridazine derivatives as DGAT2 inhibitors, pharmaceutical compositions, use of such compounds in treating multiple diseases, and processes for preparing such compounds.
Important Compound Classes

Title
Preparation of Imidazopyridine and Imidazopyridazine Derivatives as Novel Diacylglyceride O-acyltransferase 2 Inhibitors
Patent Publication Number
WO 2024/097573 A1
Publication Date
May 10, 2024
Priority Application
US 63/421,362
Priority Date
November 1, 2022
Inventors
Lim, Y.-H.; Hugelshofer, C. L.; Metwally, E.; Roane, J. P.; Shockley, S. E.
Assignee Company
Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, USA
Disease Area
Hepatic steatosis, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, type-2 diabetes mellitus, obesity, hyperlipidemia, hypercholesterolemia, atherosclerosis, cognitive decline, dementia, chronic kidney diseases and heart failure
Biological Target
Diacylglyceride O-acyltransferase 2
Summary
Triacylglycerols (TGs) serve several functions in living organisms. One such function of TGs is in the storage of energy. TGs also play a role in the synthesis of membrane lipids. TG synthesis in cells may protect them from the potentially toxic effects of excess fatty acid (FA). The glycerol phosphate and the monoacylglycerol pathways are the major pathways for the biosynthesis of TG, However, the last step in the synthesis of TG involves the reaction of a fatty acyl-CoA and diacylglycerol (DAG) to form TG. The reaction is catalyzed by acyl-CoA: diacylglyceride acyltransferase (DGAT) enzymes. These have been identified two DGAT enzymes: DGAT1 and DGAT2. Inactivation of DGAT2 impaired cytosolic lipid droplet growth, whereas inactivation of DGAT1 exerts the opposite effect.
DGAT2 appears to be the dominant DGAT enzyme controlling TG homeostasis in vivo. The metabolic role of DGAT2 has been mostly understood from effort exploiting antisense oligonucleotides (ASO) in rodents. In this setting, DGAT2 knockdown in ob/ob mice with a DGAT2 gene-specific ASO resulted in a dose-dependent decrease in very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) and a reduction in plasma TG, total cholesterol and ApoB. Another study showed that diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance was improved by knocking down DGAT2 in rats.
The present application describes a series of novel imidazopyridine and imidazopyridazine derivatives as DGAT2 inhibitors for the treatment of multiple diseases. Further, the application discloses compounds, their preparation, use, pharmaceutical composition, and treatment.
Definitions
X, Y and Z = N and C(R4);
R1 = 6-membered aryl unsubstituted or substituted with 1, 2, or 3 R5, 6-membered heteroaryl containing 1 or 2 N atoms, -(C1–6)alkyl-aryl, -(C1–6)alkyl-heteroaryl, -(C1–3)haloalkyl, or -(C1–6)alkyl-O-(C1–6)alkyl;
R2 = 4- to 7-membered heterocyclyl containing 1, 2, or 3 heteroatoms selected from N, O and S, phenyl, 5- or 6-membered heteroaryl containing 1, 2, or 3 heteroatoms selected from N, O and S, -(C1–6)alkyl-hetercyclyl, -(C1–6)alkyl-aryl, -(C3–6)cycloalkyl, -(C3–6)cyclic amine, -(C3–6)cycloalkyl-(C1–6)alkyl-SO2-(C1–6)alkyl or 8–10-membered fused bicyclic heterocyclic ring comprising 1 or 2 heteroatoms selected from N, O and S; and
R3 = hydrogen, halogen, hydroxy, (C1–6)alkyl, (C1–6)haloalkyl, (C1–6)alkylhydroxy, (C1–6)alkoxy, C(=O)NH2, C(=O)OH or O-(C1–6)alkyl.
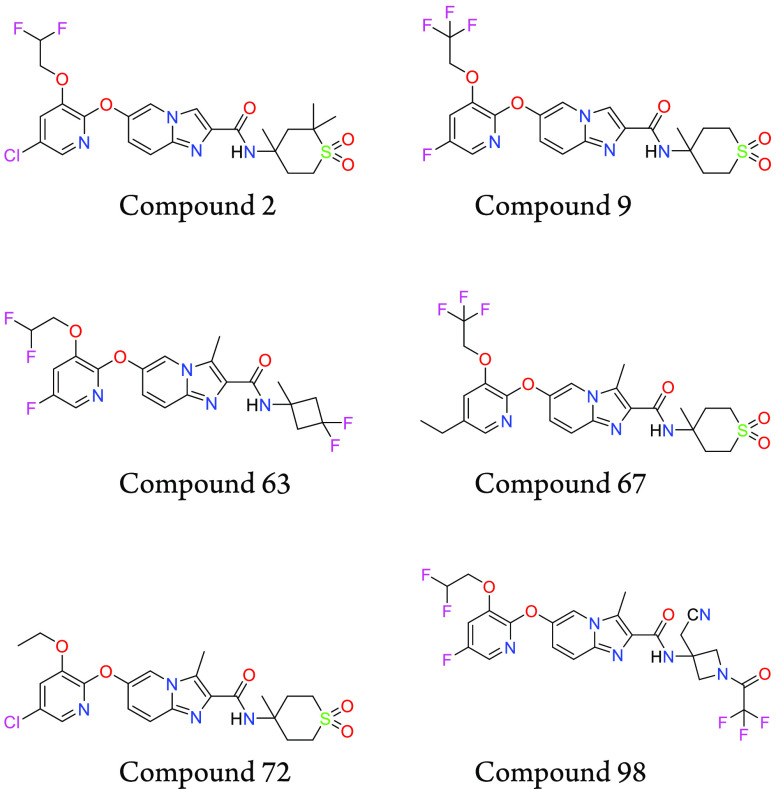
Key Structures
Biological Assay
The DGAT2 enzymatic activity assay was performed. The compounds described in this application were tested for their ability to inhibit DGAT2. The DGAT2 IC50 values (nM) are shown in the following table.
Biological Data
The table below shows representative
compounds that were tested for DGAT2 inhibition and the biological
data obtained from testing representative examples.
Claims
Total claims: 47
Compound claims: 43
Composition claims: 2
Method of treatment claims: 1
Use of compound claims: 1
Recent Review Articles
The author declares no competing financial interest.
References
- Deng B.; Kong W.; Shen X.; Han C.; Zhao Z.; Chen S.; Zhou C.; Bae-Jump V. The role of DGAT1 and DGAT2 in regulating tumor cell growth and their potential clinical implications. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 290. 10.1186/s12967-024-05084-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolk M.; Fedorova M. The lipid droplet lipidome. FEBS Lett. 2024, 598, 1215–1225. 10.1002/1873-3468.14874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amin N. B.; Saxena A. R.; Somayaji V.; Dullea R. Inhibition of Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase 2 Versus Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase 1: Potential Therapeutic Implications of Pharmacology. Clin. Ther. 2023, 45, 55–70. 10.1016/j.clinthera.2022.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabnis R. W. Benzimidazolone Derivatives as DGAT2 Inhibitors for Treating Diseases. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 1004–1005. 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.2c00247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darabi M.; Kontush A. High-density lipoproteins (HDL): Novel function and therapeutic applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2022, 1867, 159058. 10.1016/j.bbalip.2021.159058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]