Abstract
A cDNA clone, DTJP03, encoding an orphan receptor, was isolated from a canine thyroid library, and found to exhibit 68.6% amino-acid identity with the recently described human C5a receptor. This relatively low similarity first suggested that DTJP03 encoded either a C5a receptor subtype, or the presumably related C3a receptor. Binding studies performed on membranes from COS-7 cells expressing the recombinant receptor demonstrated that DTJP03 encoded a high-affinity C5a receptor, with a Kd of 1.2 nM. C3a was unable to compete for C5a binding. Intracellular free calcium concentrations were measured by Quin-2 fluorescence assays in Chinese hamster ovary cells stably transfected with the canine C5a receptor. C5a addition elicited an increase in the intracellular calcium concentration. Extracellular EGTA partially prevented this response, suggesting that activation of the C5a receptor promotes both the release of calcium from intracellular stores, and the influx of extracellular calcium. Genes encoding C5a-receptor subtypes were subsequently searched for by PCR in genomic DNA from human, canine, rat and bovine sources. The result was the amplification of a single gene fragment from each species, with about 70% identity between any two of them. The canine C5a receptor has therefore to be considered as orthologous to the human C5a receptor described previously. The low similarity between C5a receptors from different mammalian species is quite unusual for a G-protein-coupled receptor.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bause E. Structural requirements of N-glycosylation of proteins. Studies with proline peptides as conformational probes. Biochem J. 1983 Feb 1;209(2):331–336. doi: 10.1042/bj2090331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., DeBlasi A., Stone W. C., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: primary structure delineates a multigene family. Science. 1989 Oct 13;246(4927):235–240. doi: 10.1126/science.2552582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I. Domains of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors that confer specificity of G protein coupling. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Feb;13(2):48–50. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90021-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulay F., Tardif M., Brouchon L., Vignais P. Synthesis and use of a novel N-formyl peptide derivative to isolate a human N-formyl peptide receptor cDNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 May 16;168(3):1103–1109. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91143-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenoweth D. E., Goodman M. G., Weigle W. O. Demonstration of a specific receptor for human C5a anaphylatoxin on murine macrophages. J Exp Med. 1982 Jul 1;156(1):68–78. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman H. G., Thorner J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Model systems for the study of seven-transmembrane-segment receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:653–688. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doré M., Slauson D. O., Suyemoto M. M., Neilsen N. R. Calcium mobilization in C5a-stimulated adult and newborn bovine neutrophils. Inflammation. 1990 Feb;14(1):71–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00914031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Wong W. W. Complement ligand-receptor interactions that mediate biological responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:243–271. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feramisco J. R., Glass D. B., Krebs E. G. Optimal spatial requirements for the location of basic residues in peptide substrates for the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4240–4245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez H. N., Hugli T. E. Primary structural analysis of the polypeptide portion of human C5a anaphylatoxin. Polypeptide sequence determination and assignment of the oligosaccharide attachment site in C5a. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6955–6964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank M. M., Fries L. F. The role of complement in inflammation and phagocytosis. Immunol Today. 1991 Sep;12(9):322–326. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90009-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard N. P., Gerard C. The chemotactic receptor for human C5a anaphylatoxin. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):614–617. doi: 10.1038/349614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. B., el-Maghrabi M. R., Pilkis S. J. Synthetic peptides corresponding to the site phosphorylated in 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase as substrates of cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2987–2993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
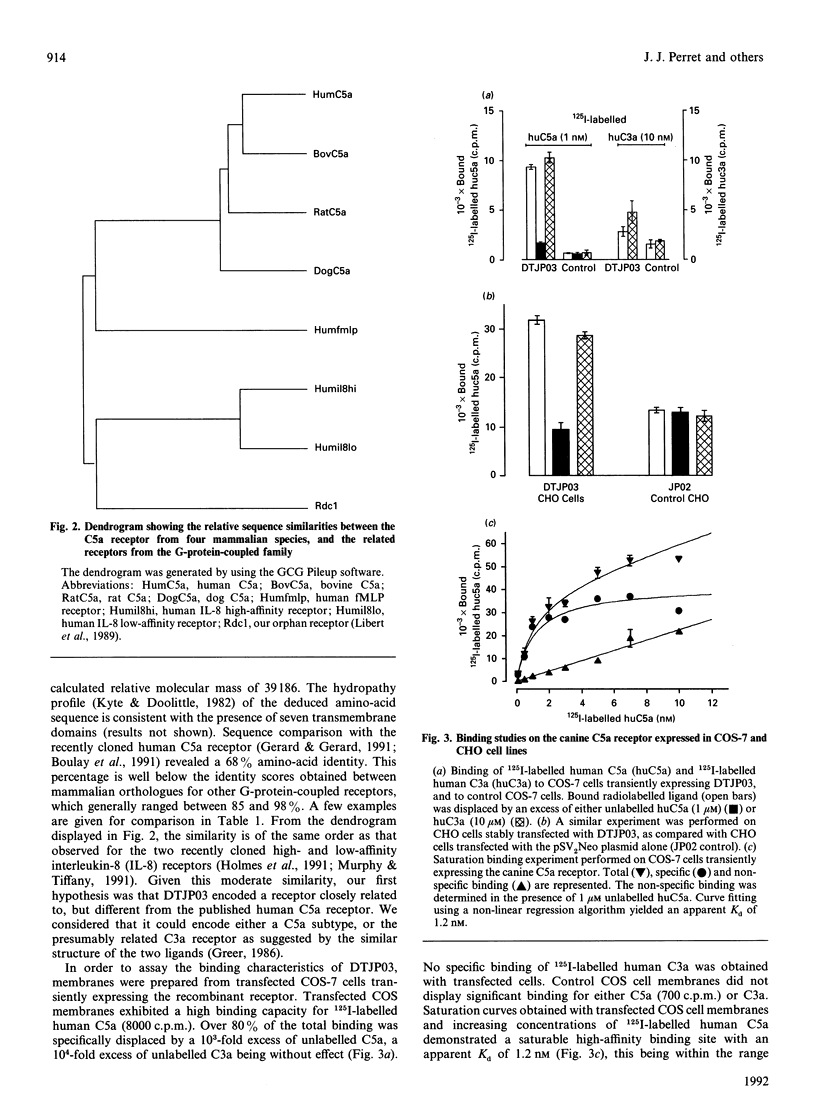
- Greer J. Comparative structural anatomy of the complement anaphylatoxin proteins C3a, C4a and C5a. Enzyme. 1986;36(1-2):150–163. doi: 10.1159/000469285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gérard C. M., Mollereau C., Vassart G., Parmentier M. Molecular cloning of a human cannabinoid receptor which is also expressed in testis. Biochem J. 1991 Oct 1;279(Pt 1):129–134. doi: 10.1042/bj2790129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes W. E., Lee J., Kuang W. J., Rice G. C., Wood W. I. Structure and functional expression of a human interleukin-8 receptor. Science. 1991 Sep 13;253(5025):1278–1280. doi: 10.1126/science.1840701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huey R., Hugli T. E. Characterization of a C5a receptor on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN). J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2063–2068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugli T. E. The structural basis for anaphylatoxin and chemotactic functions of C3a, C4a, and C5a. Crit Rev Immunol. 1981 Feb;1(4):321–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
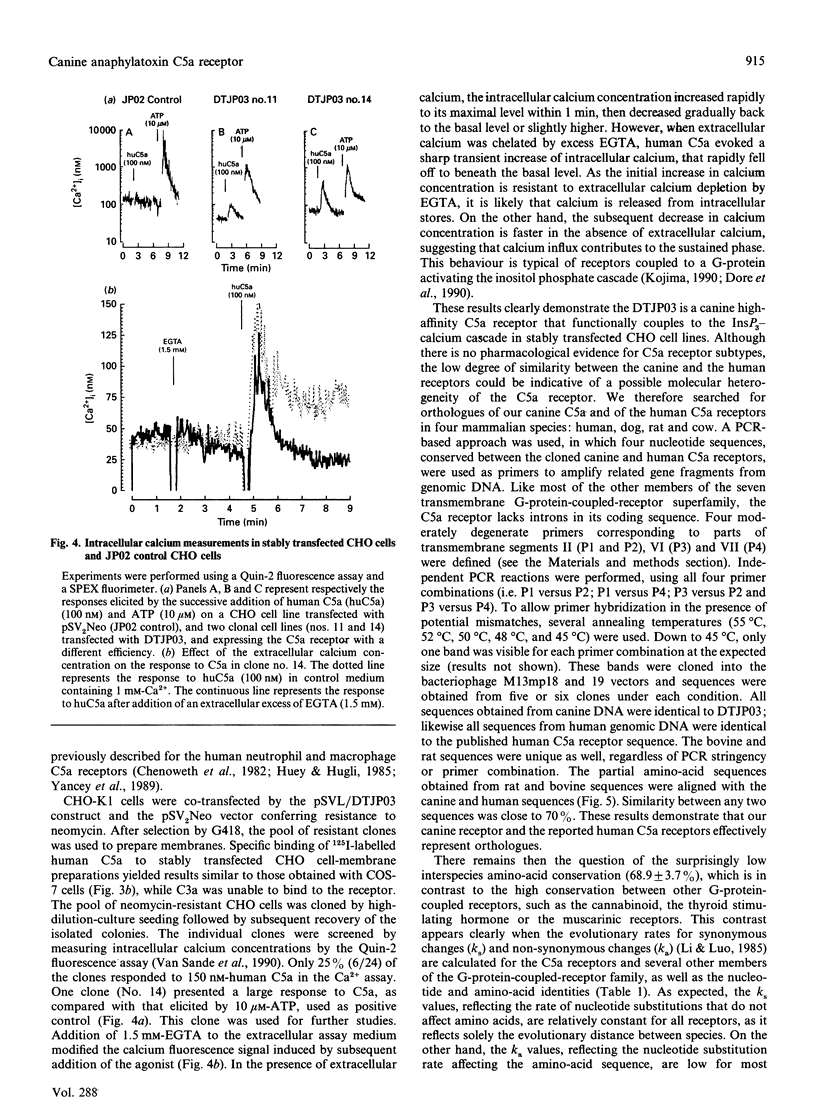
- Kernen P., Wymann M. P., von Tscharner V., Deranleau D. A., Tai P. C., Spry C. J., Dahinden C. A., Baggiolini M. Shape changes, exocytosis, and cytosolic free calcium changes in stimulated human eosinophils. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):2012–2017. doi: 10.1172/JCI115230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefort A., Lecocq R., Libert F., Lamy F., Swillens S., Vassart G., Dumont J. E. Cloning and sequencing of a calcium-binding protein regulated by cyclic AMP in the thyroid. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):111–116. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03354.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. H., Wu C. I., Luo C. C. A new method for estimating synonymous and nonsynonymous rates of nucleotide substitution considering the relative likelihood of nucleotide and codon changes. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Mar;2(2):150–174. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libert F., Parmentier M., Lefort A., Dinsart C., Van Sande J., Maenhaut C., Simons M. J., Dumont J. E., Vassart G. Selective amplification and cloning of four new members of the G protein-coupled receptor family. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):569–572. doi: 10.1126/science.2541503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libert F., Schiffmann S. N., Lefort A., Parmentier M., Gérard C., Dumont J. E., Vanderhaeghen J. J., Vassart G. The orphan receptor cDNA RDC7 encodes an A1 adenosine receptor. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1677–1682. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07691.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maenhaut C., Van Sande J., Libert F., Abramowicz M., Parmentier M., Vanderhaegen J. J., Dumont J. E., Vassart G., Schiffmann S. RDC8 codes for an adenosine A2 receptor with physiological constitutive activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 31;173(3):1169–1178. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80909-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollison K. W., Mandecki W., Zuiderweg E. R., Fayer L., Fey T. A., Krause R. A., Conway R. G., Miller L., Edalji R. P., Shallcross M. A. Identification of receptor-binding residues in the inflammatory complement protein C5a by site-directed mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):292–296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk P. N., Banks P. Evidence for the involvement of multiple signalling pathways in C5a-induced actin polymerization and nucleation in human monocyte-like cells. J Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jun;6(3):241–247. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0060241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk P. N., Banks P. The role of protein kinase C activation and inositol phosphate production in the regulation of cell-surface expression of Mac-1 by complement fragment C5a. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 17;1092(2):251–255. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90164-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P. M., Tiffany H. L. Cloning of complementary DNA encoding a functional human interleukin-8 receptor. Science. 1991 Sep 13;253(5025):1280–1283. doi: 10.1126/science.1891716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nourshargh S., Williams T. J. Evidence that a receptor-operated event on the neutrophil mediates neutrophil accumulation in vivo. Pretreatment of 111In-neutrophils with pertussis toxin in vitro inhibits their accumulation in vivo. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;145(8):2633–2638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmentier M., Libert F., Maenhaut C., Lefort A., Gérard C., Perret J., Van Sande J., Dumont J. E., Vassart G. Molecular cloning of the thyrotropin receptor. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1620–1622. doi: 10.1126/science.2556796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmentier M., Libert F., Schurmans S., Schiffmann S., Lefort A., Eggerickx D., Ledent C., Mollereau C., Gérard C., Perret J. Expression of members of the putative olfactory receptor gene family in mammalian germ cells. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):453–455. doi: 10.1038/355453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perret J., Ludgate M., Libert F., Gerard C., Dumont J. E., Vassart G., Parmentier M. Stable expression of the human TSH receptor in CHO cells and characterization of differentially expressing clones. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 28;171(3):1044–1050. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90789-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pless D. D., Lennarz W. J. Enzymatic conversion of proteins to glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):134–138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimland J., Xin W., Sweetnam P., Saijoh K., Nestler E. J., Duman R. S. Sequence and expression of a neuropeptide Y receptor cDNA. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;40(6):869–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins T. E., Siciliano S., Kobayashi S., Cianciarulo D. N., Bonilla-Argudo V., Collier K., Springer M. S. Purification of the active C5a receptor from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes as a receptor-Gi complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):971–975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. A., Yancey K. B., MacGlashan D. W., Jr The effect of pertussis toxin on mediator release from human basophils. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):161–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson M. P., Madison V. S. Three-dimensional structure of porcine C5adesArg from 1H nuclear magnetic resonance data. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 27;29(12):2895–2905. doi: 10.1021/bi00464a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgett J. R., Gould K. L., Hunter T. Substrate specificity of protein kinase C. Use of synthetic peptides corresponding to physiological sites as probes for substrate recognition requirements. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):177–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey K. B., Lawley T. J., Dersookian M., Harvath L. Analysis of the interaction of human C5a and C5a des Arg with human monocytes and neutrophils: flow cytometric and chemotaxis studies. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Feb;92(2):184–189. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12276710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerli W., Reber A. M., Dahinden C. A. The role of formylpeptide receptors, C5a receptors, and cytosolic-free calcium in neutrophil priming. J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):242–249. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuiderweg E. R., Nettesheim D. G., Mollison K. W., Carter G. W. Tertiary structure of human complement component C5a in solution from nuclear magnetic resonance data. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):172–185. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



