Abstract
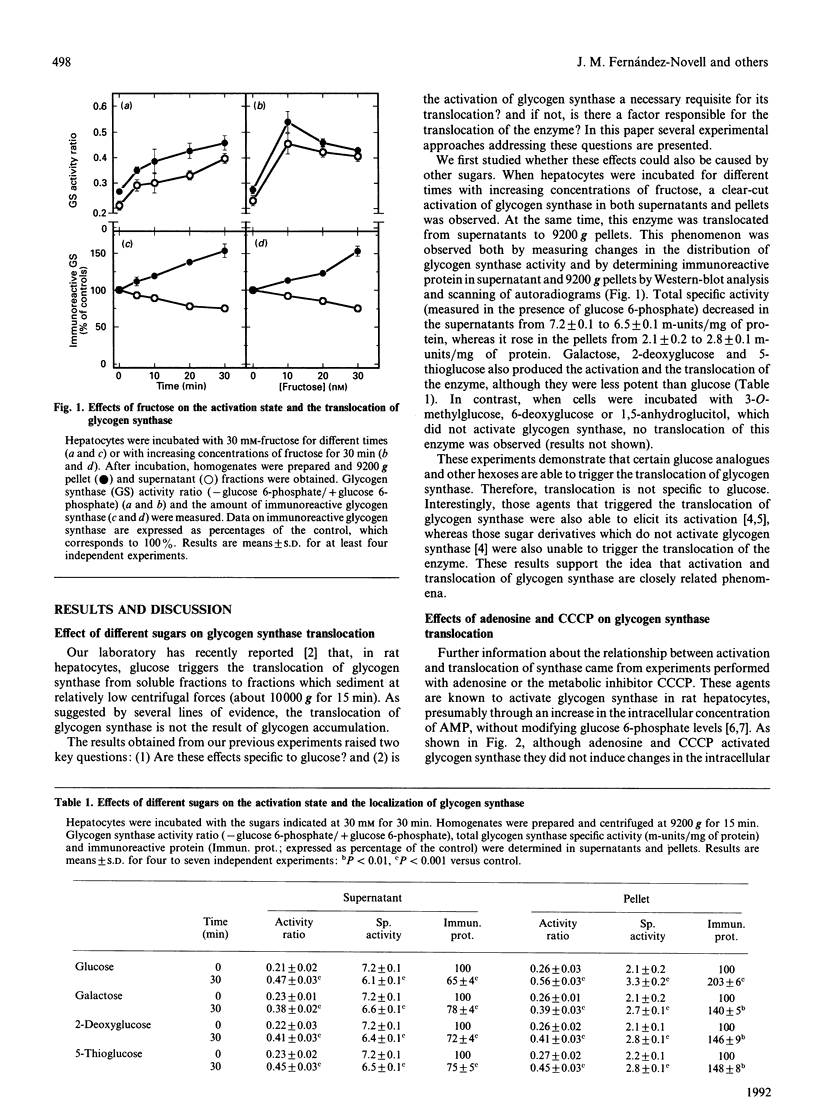
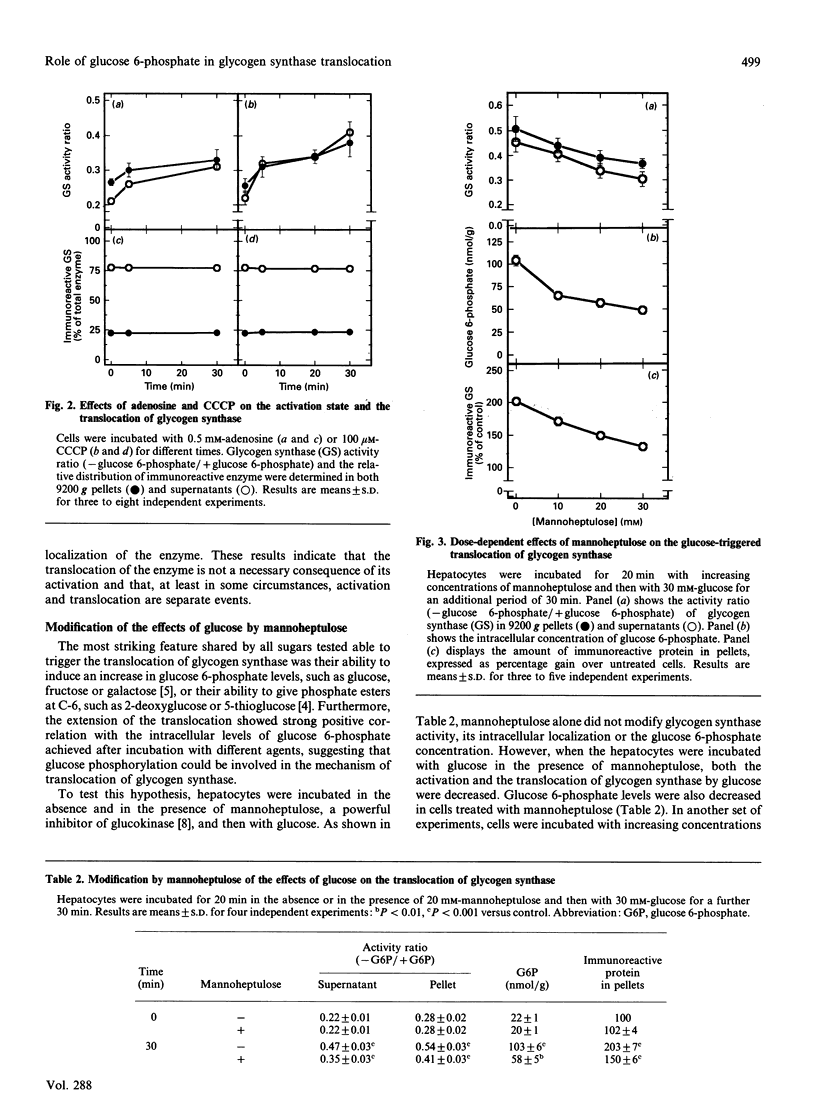
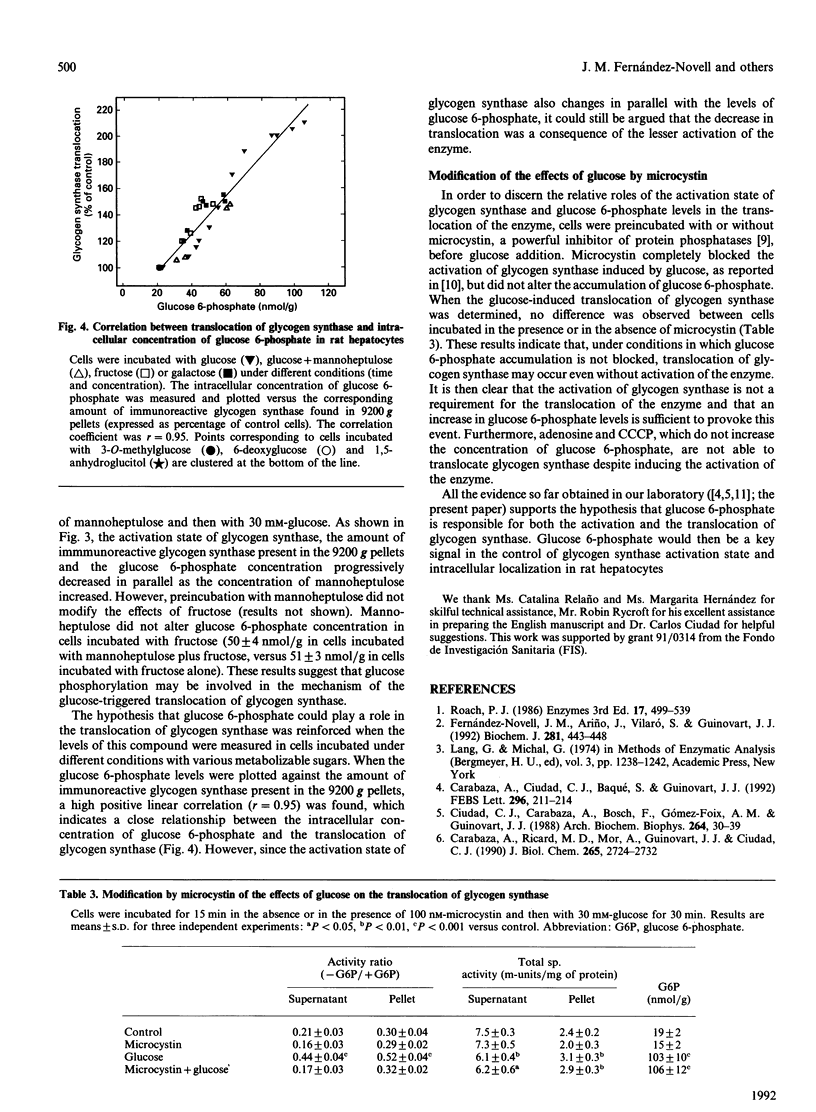
Incubation of rat hepatocytes with glucose induces the translocation of glycogen synthase from soluble fractions to fractions which sediment at 10,000 g. Incubation of the cells with fructose, galactose, 2-deoxyglucose or 5-thioglucose, which activate glycogen synthase, also resulted in the translocation of the enzyme, whereas 3-O-methylglucose, 6-deoxyglucose and 1,5-anhydroglucitol, which do not cause the activation of the enzyme, were ineffective. Adenosine and carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone, although activating glycogen synthase, did not induce its translocation. Mannoheptulose, which inhibits glucose phosphorylation, impaired the translocation of glycogen synthase induced by glucose. Furthermore, the extent of the translocation of the enzyme triggered by glucose and other sugars showed a high positive correlation with the intracellular concentration of glucose 6-phosphate. Microcystin, which blocks the activation of glycogen synthase by glucose, but not the accumulation of glucose 6-phosphate, did not affect the translocation of the enzyme. These results indicate that glucose 6-phosphate plays a role in the translocation of glycogen synthase in rat hepatocytes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carabaza A., Ciudad C. J., Baqué S., Guinovart J. J. Glucose has to be phosphorylated to activate glycogen synthase, but not to inactivate glycogen phosphorylase in hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jan 20;296(2):211–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80381-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carabaza A., Guinovart J. J., Ciudad C. J. Activation of hepatocyte glycogen synthase by metabolic inhibitors. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Nov 1;250(2):469–475. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90751-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carabaza A., Ricart M. D., Mor A., Guinovart J. J., Ciudad C. J. Role of AMP on the activation of glycogen synthase and phosphorylase by adenosine, fructose, and glutamine in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2724–2732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciudad C. J., Carabaza A., Bosch F., Gòmez I Foix A. M., Guinovart J. J. Glycogen synthase activation by sugars in isolated hepatocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jul;264(1):30–39. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90566-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciudad C. J., Carabaza A., Guinovart J. J. Glucose 6-phosphate plays a central role in the activation of glycogen synthase by glucose in hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 30;141(3):1195–1200. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80171-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coore H. G., Randle P. J. Inhibition of glucose phosphorylation by mannoheptulose. Biochem J. 1964 Apr;91(1):56–59. doi: 10.1042/bj0910056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Novell J. M., Ariño J., Vilaró S., Guinovart J. J. Glucose induces the translocation and the aggregation of glycogen synthase in rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 15;281(Pt 2):443–448. doi: 10.1042/bj2810443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavoie L., Bollen M., Stalmans W., van de Werve G. Increased synthase phosphatase activity is responsible for the super-activation of glycogen synthase in hepatocytes from fasted obese Zucker rats. Endocrinology. 1991 Nov;129(5):2674–2678. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-5-2674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKintosh C., Beattie K. A., Klumpp S., Cohen P., Codd G. A. Cyanobacterial microcystin-LR is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A from both mammals and higher plants. FEBS Lett. 1990 May 21;264(2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80245-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


