Abstract
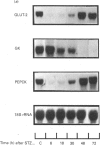
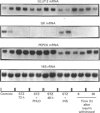
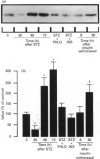
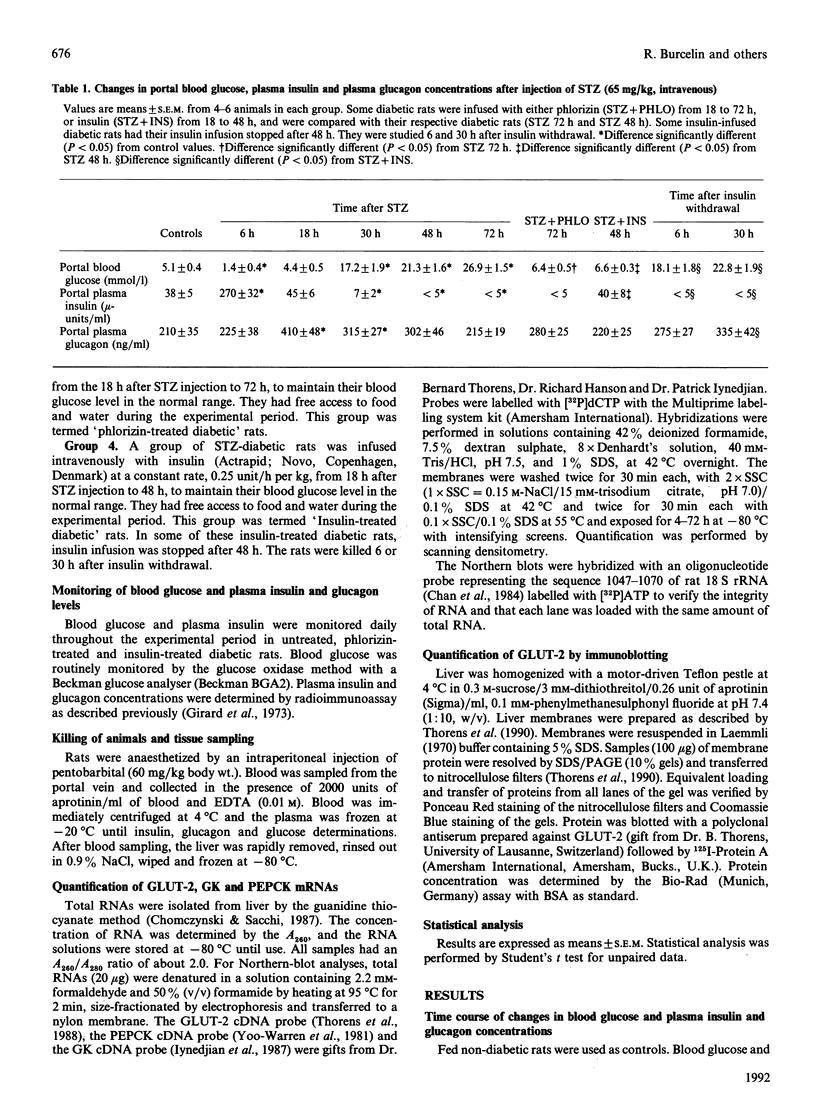
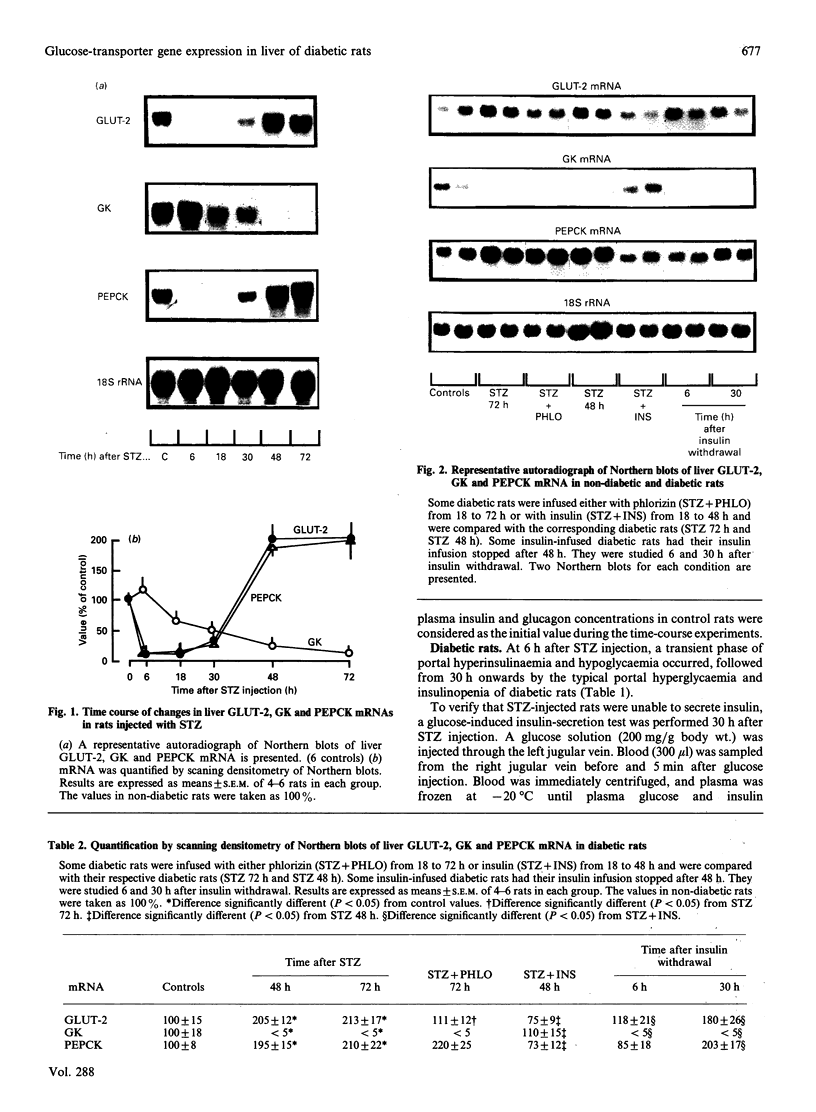
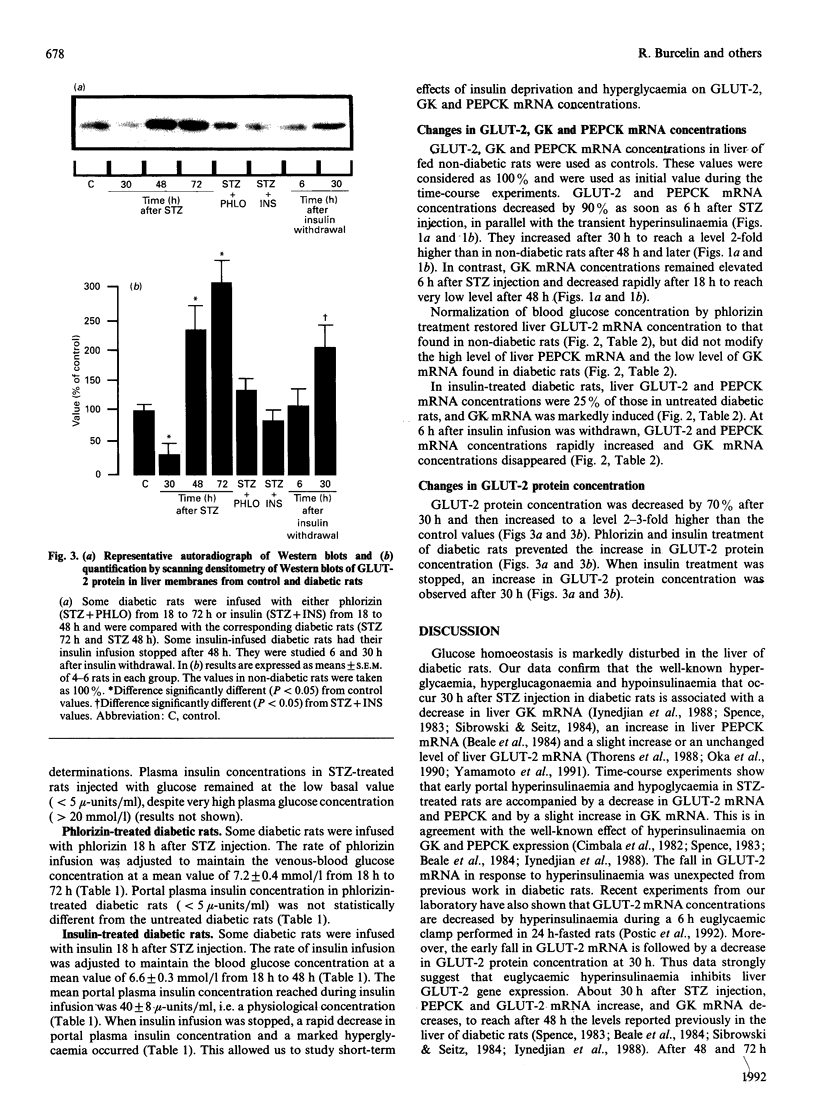
GLUT-2, glucokinase (GK) and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) mRNA expression was studied in the liver of chronically catheterized diabetic rats during the 3 days after an intravenous injection of 65 mg of streptozotocin (STZ)/kg. At 6 h after the STZ injection, portal plasma insulin levels were 270 +/- 32 mu-units/ml and blood glucose was 1.4 +/- 0.4 mmol/l, owing to pancreatic beta-cell destruction. GLUT-2 and PEPCK mRNA concentrations were rapidly and dramatically decreased (> 90%), whereas GK mRNA was increased. After 30 h, plasma insulin concentrations were lower than 5 mu-units/ml and blood glucose was > 20 mmol/l. GLUT-2 and PEPCK mRNA concentrations increased 2-fold and GK mRNA disappeared progressively. In order to assess the relative roles of hyperglycaemia and insulinopenia, blood glucose was clamped at 6.4 +/- 0.5 mmol/l from 18 to 72 h after STZ injection by phlorizin infusion (0.5-2 g/day per kg) or at 6.6 +/- 0.3 mmol/l from 18 to 48 h after STZ injection by insulin infusion (0.25 unit/min per kg). GLUT-2 mRNA concentrations were 50% lower in phlorizin-infused than in untreated diabetic rats. The low levels of GK mRNA and the high levels of PEPCK mRNA were unaffected by normalization of hyperglycaemia in phlorizin-infused diabetic rats. In insulin-infused rats (portal plasma insulin levels of 40 mu-units/ml) GLUT-2 mRNA levels were 25% of those in untreated diabetic rats, and they increased rapidly 6 h after insulin infusion was stopped. Liver GLUT-2 protein concentration showed similar changes in response to STZ injection and to phlorizin or insulin treatment, but after a delay of several hours. From this work we conclude that GLUT-2 gene expression is dramatically and rapidly (< 6 h) decreased by portal hyperinsulinaemia and increased by hyperglycaemia.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asano T., Katagiri H., Tsukuda K., Lin J. L., Ishihara H., Yazaki Y., Oka Y. Upregulation of GLUT2 mRNA by glucose, mannose, and fructose in isolated rat hepatocytes. Diabetes. 1992 Jan;41(1):22–25. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baur H., Heldt H. W. Transport of hexoses across the liver-cell membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Apr 1;74(2):397–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale E., Andreone T., Koch S., Granner M., Granner D. Insulin and glucagon regulate cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) mRNA in rat liver. Diabetes. 1984 Apr;33(4):328–332. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.4.328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Biswas C., Vicario P. P., Strout H. V., Saperstein R., Pilch P. F. Decreased expression of the insulin-responsive glucose transporter in diabetes and fasting. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):70–72. doi: 10.1038/340070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourey R. E., Koranyi L., James D. E., Mueckler M., Permutt M. A. Effects of altered glucose homeostasis on glucose transporter expression in skeletal muscle of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):542–547. doi: 10.1172/JCI114742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burant C. F., Sivitz W. I., Fukumoto H., Kayano T., Nagamatsu S., Seino S., Pessin J. E., Bell G. I. Mammalian glucose transporters: structure and molecular regulation. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1991;47:349–388. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571147-0.50015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L., Gutell R., Noller H. F., Wool I. G. The nucleotide sequence of a rat 18 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene and a proposal for the secondary structure of 18 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):224–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimbala M. A., Lamers W. H., Nelson K., Monahan J. E., Yoo-Warren H., Hanson R. W. Rapid changes in the concentration of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase mRNA in rat liver and kidney. Effects of insulin and cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7629–7636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey W. T., Huecksteadt T. P., Birnbaum M. J. Pretranslational suppression of an insulin-responsive glucose transporter in rats with diabetes mellitus. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):60–63. doi: 10.1126/science.2662408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard J. R., Cuendet G. S., Marliss E. B., Kervran A., Rieutort M., Assan R. Fuels, hormones, and liver metabolism at term and during the early postnatal period in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3190–3200. doi: 10.1172/JCI107519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iynedjian P. B., Gjinovci A., Renold A. E. Stimulation by insulin of glucokinase gene transcription in liver of diabetic rats. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):740–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iynedjian P. B., Jotterand D., Nouspikel T., Asfari M., Pilot P. R. Transcriptional induction of glucokinase gene by insulin in cultured liver cells and its repression by the glucagon-cAMP system. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21824–21829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iynedjian P. B., Ucla C., Mach B. Molecular cloning of glucokinase cDNA. Developmental and dietary regulation of glucokinase mRNA in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6032–6038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Charron M. J., Lodish H. F., Cushman S. W., Flier J. S. Differential regulation of two glucose transporters in adipose cells from diabetic and insulin-treated diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):404–411. doi: 10.1172/JCI114180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer S., Höppner W., Seitz H. J. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional effects of glucose on liver phosphoenolpyruvate-carboxykinase gene expression. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 18;202(3):985–991. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16460.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narkewicz M. R., Iynedjian P. B., Ferre P., Girard J. Insulin and tri-iodothyronine induce glucokinase mRNA in primary cultures of neonatal rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1990 Nov 1;271(3):585–589. doi: 10.1042/bj2710585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka Y., Asano T., Shibasaki Y., Lin J. L., Tsukuda K., Akanuma Y., Takaku F. Increased liver glucose-transporter protein and mRNA in streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1990 Apr;39(4):441–446. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.4.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibrowski W., Seitz H. J. Rapid action of insulin and cyclic AMP in the regulation of functional messenger RNA coding for glucokinase in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):343–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Hormonal regulation of mammalian glucose transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1059–1089. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivitz W. I., DeSautel S. L., Kayano T., Bell G. I., Pessin J. E. Regulation of glucose transporter messenger RNA in insulin-deficient states. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):72–74. doi: 10.1038/340072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spence J. T. Levels of translatable mRNA coding for rat liver glucokinase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9143–9146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Flier J. S., Lodish H. F., Kahn B. B. Differential regulation of two glucose transporters in rat liver by fasting and refeeding and by diabetes and insulin treatment. Diabetes. 1990 Jun;39(6):712–719. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.6.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Sarkar H. K., Kaback H. R., Lodish H. F. Cloning and functional expression in bacteria of a novel glucose transporter present in liver, intestine, kidney, and beta-pancreatic islet cells. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. F., Exton J. H., Park C. R., Regen D. M. Stereospecific transport of glucose in the perfused rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1968 Nov;215(5):1200–1209. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.5.1200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Fukumoto H., Koh G., Yano H., Yasuda K., Masuda K., Ikeda H., Imura H., Seino Y. Liver and muscle-fat type glucose transporter gene expression in obese and diabetic rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 29;175(3):995–1002. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91663-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo-Warren H., Cimbala M. A., Felz K., Monahan J. E., Leis J. P., Hanson R. W. Identification of a DNA clone to phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) from rat cytosol. Alterations in phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase RNA levels detectable by hybridization. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10224–10227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]