Abstract
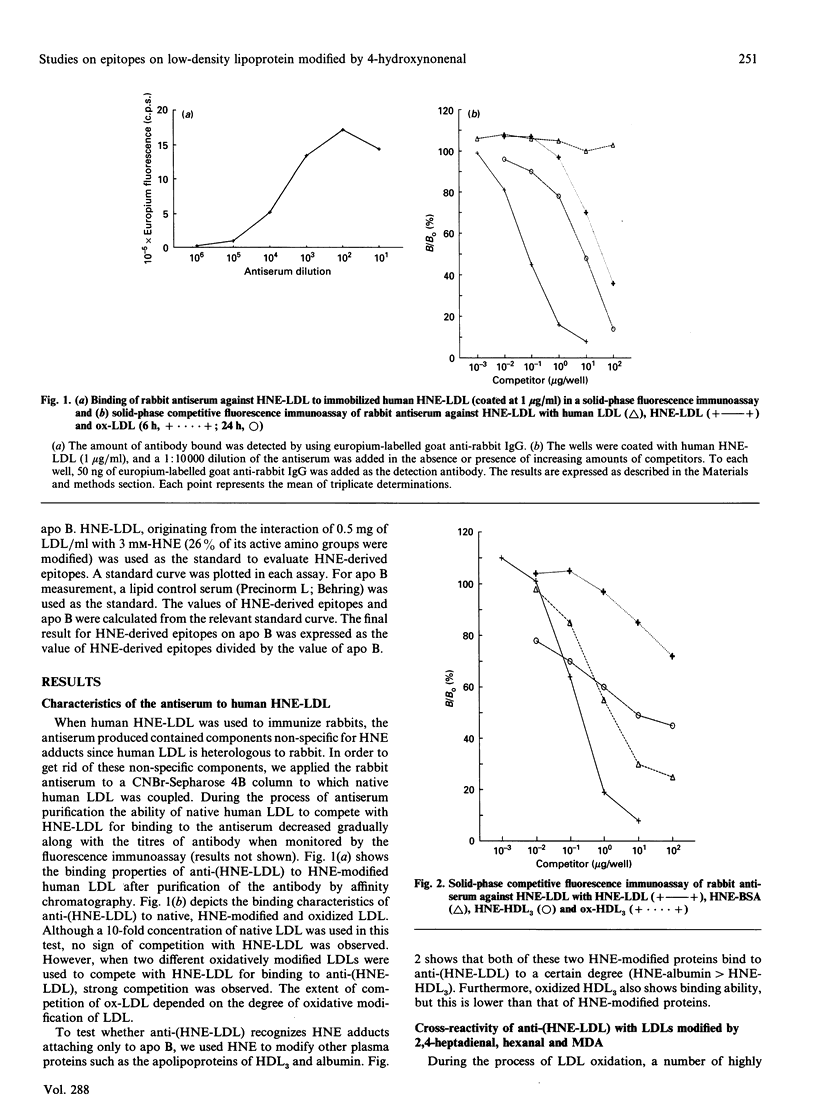
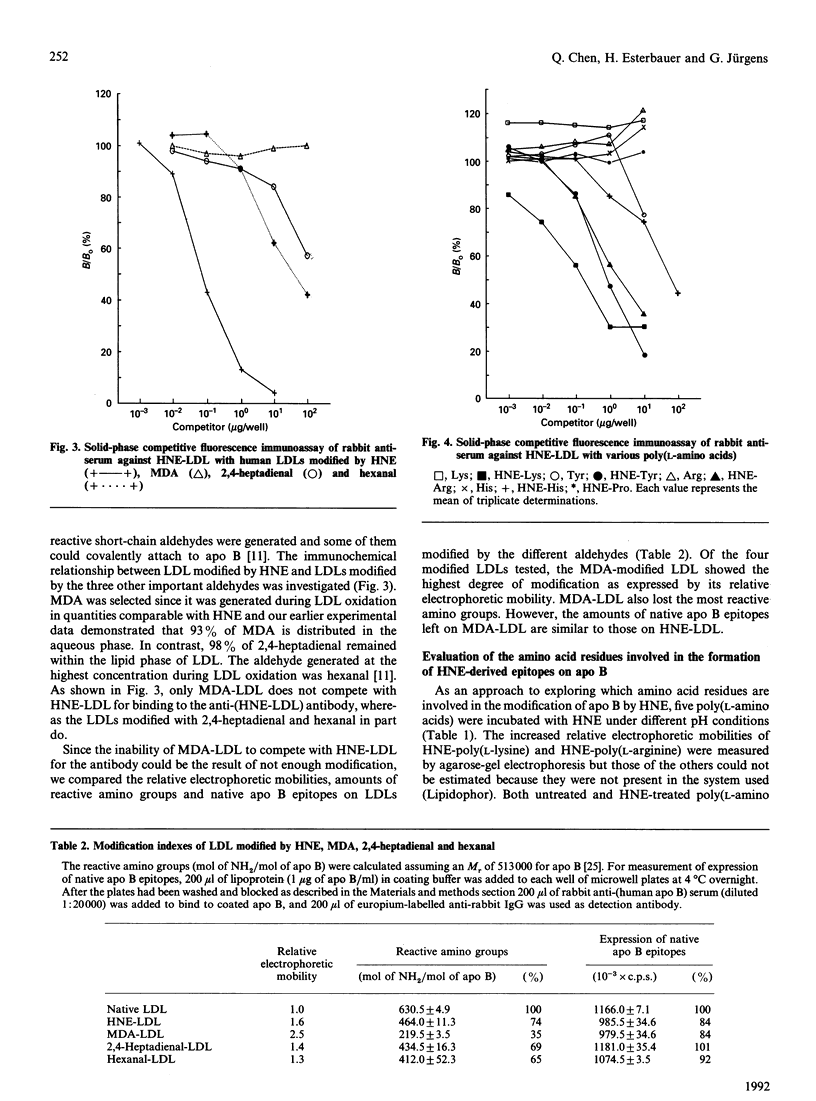
Oxidation of human low-density lipoprotein (LDL) was found to be accompanied by the generation of various reactive aldehydes. One of them, 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE), was shown to modify LDL to a form which represents a good model of oxidized LDL (ox-LDL). In order to investigate the epitopes newly formed on HNE-modified LDL, a polyvalent antiserum to HNE-LDL [anti-(HNE-LDL)] was raised in rabbits and the non-specific components were removed with native LDL coupled to CNBr-Sepharose 4B. Competitive fluorescence immunoassay analysis showed that anti-(HNE-LDL) recognized HNE-LDL, copper-oxidized LDL, HNE-albumin and to a lower extent HNE-modified high-density lipoprotein 3 (HNE-HDL3) and ox-HDL3 but not native LDL. A certain degree of cross-reactivity of the antibody with LDLs modified by either hexanal or 2,4-heptadienal was found. No reaction was obtained with LDL labelled with malondialdehyde. From the abilities of HNE-modified poly(L-amino acids) to compete with HNE-LDL for binding to anti-(HNE-LDL), it is postulated that lysine, tyrosine, arginine and histidine are involved in the formation of HNE-derived epitopes on apolipoprotein B (apo B). Using a double-sandwich fluorescence immunoassay [capture antibody: anti-(apo B); detection antibody: anti-(HNE-LDL)] we found that the HNE-derived epitopes were expressed at a far higher degree in ox-LDL and HNE-LDL than in native LDL.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avogaro P., Bon G. B., Cazzolato G. Presence of a modified low density lipoprotein in humans. Arteriosclerosis. 1988 Jan-Feb;8(1):79–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avogaro P., Cazzolato G., Bittolo-Bon G. Some questions concerning a small, more electronegative LDL circulating in human plasma. Atherosclerosis. 1991 Nov;91(1-2):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(91)90198-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Lipoprotein metabolism in the macrophage: implications for cholesterol deposition in atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:223–261. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carew T. E., Schwenke D. C., Steinberg D. Antiatherogenic effect of probucol unrelated to its hypocholesterolemic effect: evidence that antioxidants in vivo can selectively inhibit low density lipoprotein degradation in macrophage-rich fatty streaks and slow the progression of atherosclerosis in the Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7725–7729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathcart M. K., Morel D. W., Chisolm G. M., 3rd Monocytes and neutrophils oxidize low density lipoprotein making it cytotoxic. J Leukoc Biol. 1985 Aug;38(2):341–350. doi: 10.1002/jlb.38.2.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterbauer H., Dieber-Rotheneder M., Waeg G., Striegl G., Jürgens G. Biochemical, structural, and functional properties of oxidized low-density lipoprotein. Chem Res Toxicol. 1990 Mar-Apr;3(2):77–92. doi: 10.1021/tx00014a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterbauer H., Lang J., Zadravec S., Slater T. F. Detection of malonaldehyde by high-performance liquid chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1984;105:319–328. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)05041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterbauer H., Striegl G., Puhl H., Rotheneder M. Continuous monitoring of in vitro oxidation of human low density lipoprotein. Free Radic Res Commun. 1989;6(1):67–75. doi: 10.3109/10715768909073429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong L. G., Parthasarathy S., Witztum J. L., Steinberg D. Nonenzymatic oxidative cleavage of peptide bonds in apoprotein B-100. J Lipid Res. 1987 Dec;28(12):1466–1477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberland M. E., Fong D., Cheng L. Malondialdehyde-altered protein occurs in atheroma of Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbits. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):215–218. doi: 10.1126/science.2455346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinecke J. W., Rosen H., Chait A. Iron and copper promote modification of low density lipoprotein by human arterial smooth muscle cells in culture. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1890–1894. doi: 10.1172/JCI111609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen T., Mahoney E. M., Steinberg D. Enhanced macrophage degradation of biologically modified low density lipoprotein. Arteriosclerosis. 1983 Mar-Apr;3(2):149–159. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.3.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen T., Mahoney E. M., Steinberg D. Enhanced macrophage degradation of low density lipoprotein previously incubated with cultured endothelial cells: recognition by receptors for acetylated low density lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6499–6503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff H. F., O'Neil J., Chisolm G. M., 3rd, Cole T. B., Quehenberger O., Esterbauer H., Jürgens G. Modification of low density lipoprotein with 4-hydroxynonenal induces uptake by macrophages. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Jul-Aug;9(4):538–549. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.4.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janero D. R. Malondialdehyde and thiobarbituric acid-reactivity as diagnostic indices of lipid peroxidation and peroxidative tissue injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 1990;9(6):515–540. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(90)90131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessup W., Jurgens G., Lang J., Esterbauer H., Dean R. T. Interaction of 4-hydroxynonenal-modified low-density lipoproteins with the fibroblast apolipoprotein B/E receptor. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 15;234(1):245–248. doi: 10.1042/bj2340245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jürgens G., Ashy A., Esterbauer H. Detection of new epitopes formed upon oxidation of low-density lipoprotein, lipoprotein (a) and very-low-density lipoprotein. Use of an antiserum against 4-hydroxynonenal-modified low-density lipoprotein. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):605–608. doi: 10.1042/bj2650605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jürgens G., Hoff H. F., Chisolm G. M., 3rd, Esterbauer H. Modification of human serum low density lipoprotein by oxidation--characterization and pathophysiological implications. Chem Phys Lipids. 1987 Nov-Dec;45(2-4):315–336. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(87)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jürgens G., Lang J., Esterbauer H. Modification of human low-density lipoprotein by the lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 3;875(1):103–114. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean L. R., Hagaman K. A. Effect of probucol on the physical properties of low-density lipoproteins oxidized by copper. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):321–327. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palinski W., Rosenfeld M. E., Ylä-Herttuala S., Gurtner G. C., Socher S. S., Butler S. W., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Steinberg D., Witztum J. L. Low density lipoprotein undergoes oxidative modification in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1372–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palinski W., Ylä-Herttuala S., Rosenfeld M. E., Butler S. W., Socher S. A., Parthasarathy S., Curtiss L. K., Witztum J. L. Antisera and monoclonal antibodies specific for epitopes generated during oxidative modification of low density lipoprotein. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 May-Jun;10(3):325–335. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parums D. V., Brown D. L., Mitchinson M. J. Serum antibodies to oxidized low-density lipoprotein and ceroid in chronic periaortitis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1990 Apr;114(4):383–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. E., Khoo J. C., Miller E., Parthasarathy S., Palinski W., Witztum J. L. Macrophage-derived foam cells freshly isolated from rabbit atherosclerotic lesions degrade modified lipoproteins, promote oxidation of low-density lipoproteins, and contain oxidation-specific lipid-protein adducts. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):90–99. doi: 10.1172/JCI115006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. E., Palinski W., Ylä-Herttuala S., Butler S., Witztum J. L. Distribution of oxidation specific lipid-protein adducts and apolipoprotein B in atherosclerotic lesions of varying severity from WHHL rabbits. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 May-Jun;10(3):336–349. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.3.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon S., Maziere C., Theron L., Beucler I., Ayrault-Jarrier M., Goldstein S., Polonovski J. Immunological detection of low-density lipoproteins modified by malondialdehyde in vitro or in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Aug 15;920(3):215–220. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90097-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen J. T., Ylä-Herttuala S., Yamamoto R., Butler S., Korpela H., Salonen R., Nyyssönen K., Palinski W., Witztum J. L. Autoantibody against oxidised LDL and progression of carotid atherosclerosis. Lancet. 1992 Apr 11;339(8798):883–887. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90926-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimano H., Yamada N., Ishibashi S., Mokuno H., Mori N., Gotoda T., Harada K., Akanuma Y., Murase T., Yazaki Y. Oxidation-labile subfraction of human plasma low density lipoprotein isolated by ion-exchange chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1991 May;32(5):763–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater T. F., Sawyer B. C. The stimulatory effects of carbon tetrachloride and other halogenoalkanes on peroxidative reactions in rat liver fractions in vitro. General features of the systems used. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;123(5):805–814. doi: 10.1042/bj1230805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg D., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Khoo J. C., Witztum J. L. Beyond cholesterol. Modifications of low-density lipoprotein that increase its atherogenicity. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 6;320(14):915–924. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904063201407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbrecher U. P. Oxidation of human low density lipoprotein results in derivatization of lysine residues of apolipoprotein B by lipid peroxide decomposition products. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3603–3608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylä-Herttuala S., Palinski W., Rosenfeld M. E., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Butler S., Witztum J. L., Steinberg D. Evidence for the presence of oxidatively modified low density lipoprotein in atherosclerotic lesions of rabbit and man. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1086–1095. doi: 10.1172/JCI114271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


