Abstract
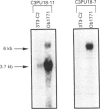
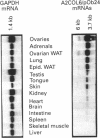
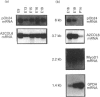
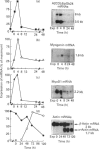
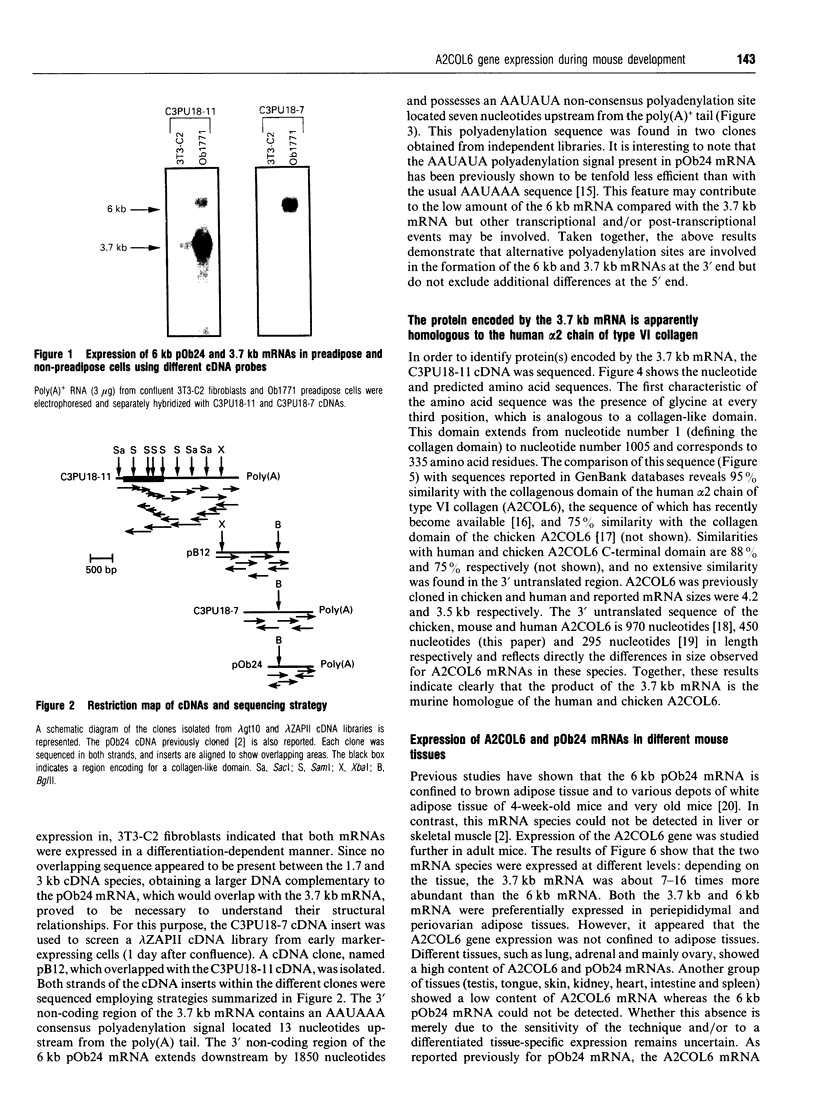
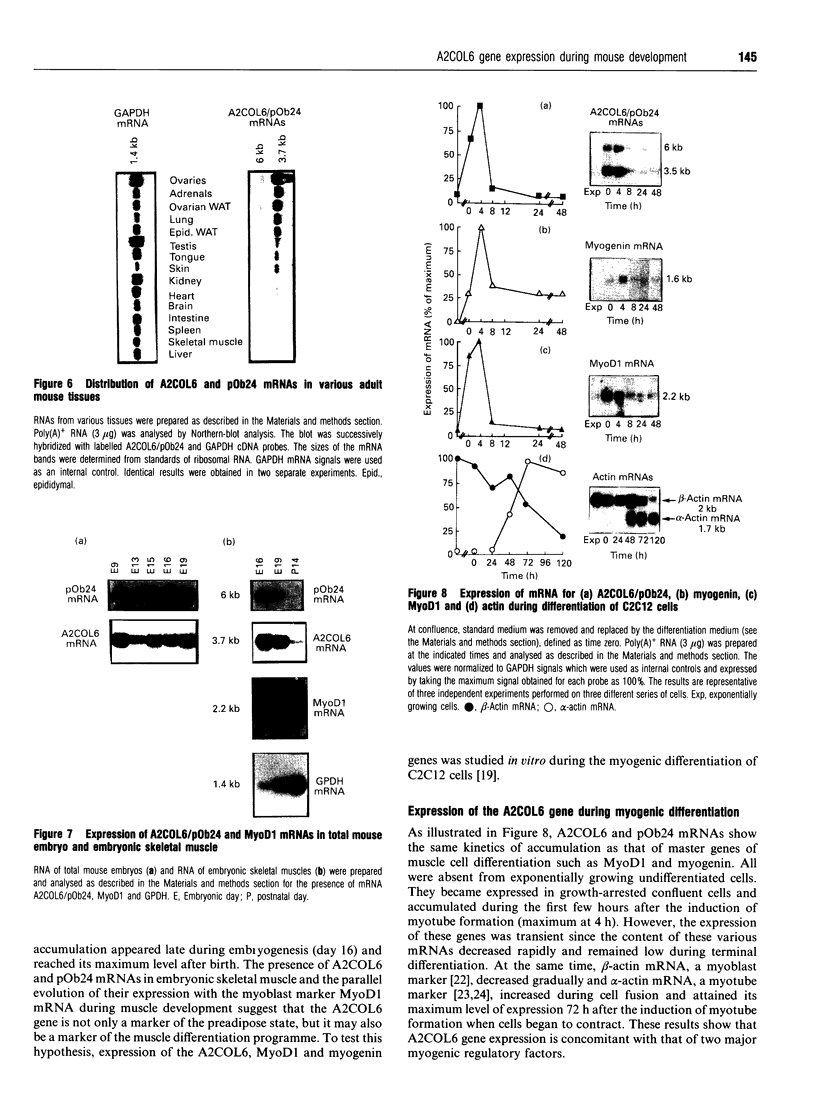
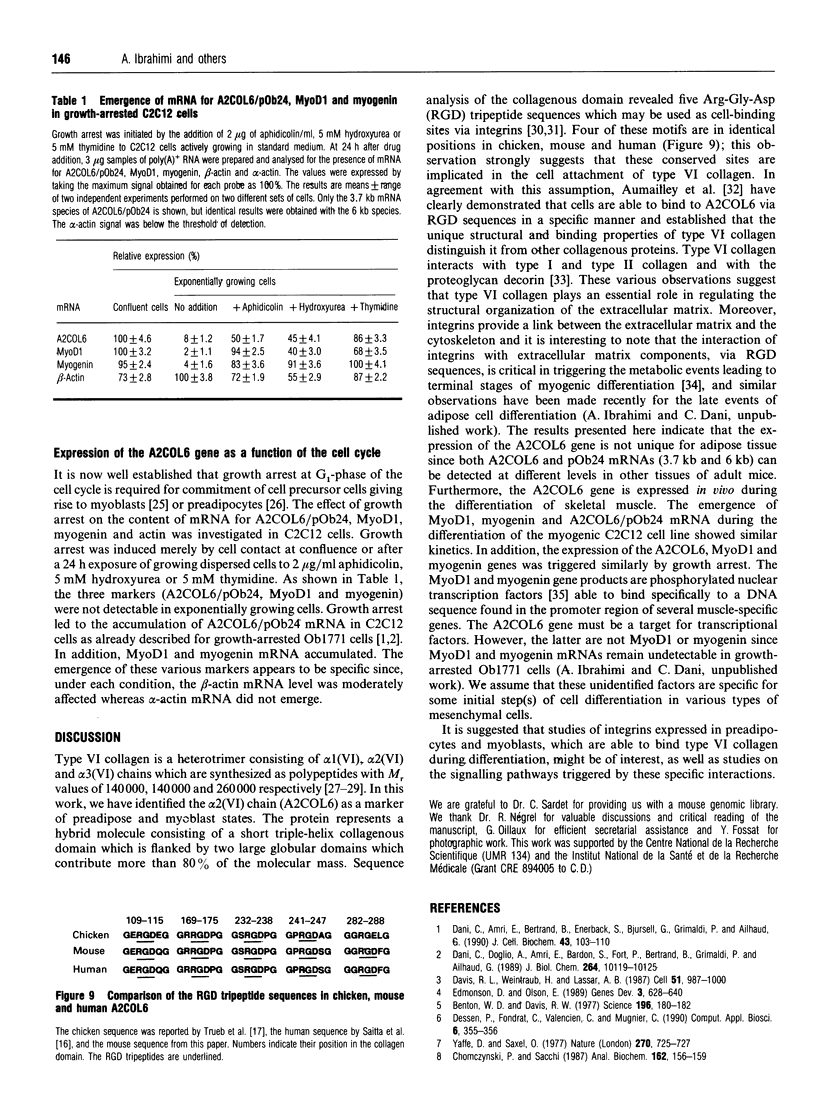
We have previously described the molecular cloning of a cDNA probe which detects a 6 kb mRNA termed pOb24. pOb24 mRNA appeared to be a marker of the preadipose state both in vitro and in vivo. A pOb24 genomic fragment was isolated and used to screen cDNA libraries in order to isolate the full-length pOb24 cDNA and to identify the corresponding protein. The screening yielded a new cDNA clone which detected a 3.7 kb mRNA species in addition to the 6 kb mRNA species. Sequences at the 3' end of the 6 kb and 3.7 kb mRNAs indicate that both mRNAs are generated from the same gene through the use of two different polyadenylation sites. The protein encoded by the 3.7 kb mRNA appeared to be homologous to the human alpha 2 chain of type VI collagen (A2COL6). The expression of the A2COL6 gene was not confined to adipose tissue; mRNA species can be detected in ovaries, adrenal glands and lungs but not in liver and skeletal muscle. The expression appeared specific for initial phase(s) of cell differentiation since it is parallel to that of the MyoD1 gene during muscle embryogenesis in vivo. In the myogenic C2C12 cell line, the A2COL6 gene exhibited the same regulation as MyoD1 and myogenin genes. These results indicate that A2COL6 gene expression is a marker of the preadipose state, but may also be a marker of other differentiation programmes such as that of muscle.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amri E. Z., Dani C., Doglio A., Grimaldi P., Ailhaud G. Coupling of growth arrest and expression of early markers during adipose conversion of preadipocyte cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 13;137(2):903–910. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aumailley M., Mann K., von der Mark H., Timpl R. Cell attachment properties of collagen type VI and Arg-Gly-Asp dependent binding to its alpha 2(VI) and alpha 3(VI) chains. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Apr;181(2):463–474. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidanset D. J., Guidry C., Rosenberg L. C., Choi H. U., Timpl R., Hook M. Binding of the proteoglycan decorin to collagen type VI. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5250–5256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonaldo P., Colombatti A. The carboxyl terminus of the chicken alpha 3 chain of collagen VI is a unique mosaic structure with glycoprotein Ib-like, fibronectin type III, and Kunitz modules. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20235–20239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., Pan T. C., Conway D., Kuo H. J., Glanville R. W., Timpl R., Mann K., Deutzmann R. Sequence analysis of alpha 1(VI) and alpha 2(VI) chains of human type VI collagen reveals internal triplication of globular domains similar to the A domains of von Willebrand factor and two alpha 2(VI) chain variants that differ in the carboxy terminus. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):1939–1946. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03598.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombatti A., Bonaldo P., Ainger K., Bressan G. M., Volpin D. Biosynthesis of chick type VI collagen. I. Intracellular assembly and molecular structure. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14454–14460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Souza S. E., Ginsberg M. H., Plow E. F. Arginyl-glycyl-aspartic acid (RGD): a cell adhesion motif. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jul;16(7):246–250. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90096-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Amri E. Z., Bertrand B., Enerback S., Bjursell G., Grimaldi P., Ailhaud G. Expression and regulation of pOb24 and lipoprotein lipase genes during adipose conversion. J Cell Biochem. 1990 Jun;43(2):103–110. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240430202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Doglio A., Amri E. Z., Bardon S., Fort P., Bertrand B., Grimaldi P., Ailhaud G. Cloning and regulation of a mRNA specifically expressed in the preadipose state. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):10119–10125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessen P., Fondrat C., Valencien C., Mugnier C. BISANCE: a French service for access to biomolecular sequence databases. Comput Appl Biosci. 1990 Oct;6(4):355–356. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/6.4.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. A gene with homology to the myc similarity region of MyoD1 is expressed during myogenesis and is sufficient to activate the muscle differentiation program. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):628–640. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. A gene with homology to the myc similarity region of MyoD1 is expressed during myogenesis and is sufficient to activate the muscle differentiation program. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):628–640. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings K. E., Emerson C. P., Jr cDNA clone analysis of six co-regulated mRNAs encoding skeletal muscle contractile proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1553–1557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E. VLA proteins in the integrin family: structures, functions, and their role on leukocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:365–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessle H., Engvall E. Type VI collagen. Studies on its localization, structure, and biosynthetic form with monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3955–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller E., Winterhalter K. H., Trueb B. The globular domains of type VI collagen are related to the collagen-binding domains of cartilage matrix protein and von Willebrand factor. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1073–1077. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03475.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak L. P., Birkenmeier E. H. Mouse sn-glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: molecular cloning and genetic mapping of a cDNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3020–3024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menko A. S., Boettiger D. Occupation of the extracellular matrix receptor, integrin, is a control point for myogenic differentiation. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):51–57. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadal-Ginard B. Commitment, fusion and biochemical differentiation of a myogenic cell line in the absence of DNA synthesis. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):855–864. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90270-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitta B., Wang Y. M., Renkart L., Zhang R. Z., Pan T. C., Timpl R., Chu M. L. The exon organization of the triple-helical coding regions of the human alpha 1(VI) and alpha 2(VI) collagen genes is highly similar. Genomics. 1991 Sep;11(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90111-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. J., Rothblum K. N. Gene switching in myogenesis: differential expression of the chicken actin multigene family. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4122–4129. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shani M., Nudel U., Zevin-Sonkin D., Zakut R., Givol D., Katcoff D., Carmon Y., Reiter J., Frischauf A. M., Yaffe D. Skeletal muscle actin mRNA. Characterization of the 3' untranslated region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 11;9(3):579–589. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.3.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shani M., Zevin-Sonkin D., Saxel O., Carmon Y., Katcoff D., Nudel U., Yaffe D. The correlation between the synthesis of skeletal muscle actin, myosin heavy chain, and myosin light chain and the accumulation of corresponding mRNA sequences during myogenesis. Dev Biol. 1981 Sep;86(2):483–492. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90206-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets M. D., Ogg S. C., Wickens M. P. Point mutations in AAUAAA and the poly (A) addition site: effects on the accuracy and efficiency of cleavage and polyadenylation in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5799–5805. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Thayer M. J., Cheng P. F., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. MyoD1: a nuclear phosphoprotein requiring a Myc homology region to convert fibroblasts to myoblasts. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):405–411. doi: 10.1126/science.3175662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trüeb B., Schaeren-Wiemers N., Schreier T., Winterhalter K. H. Molecular cloning of chicken type VI collagen. Primary structure of the subunit alpha 2(VI)-pepsin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):136–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D., Saxel O. Serial passaging and differentiation of myogenic cells isolated from dystrophic mouse muscle. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):725–727. doi: 10.1038/270725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]