Abstract
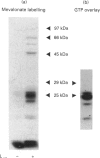
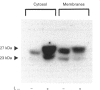
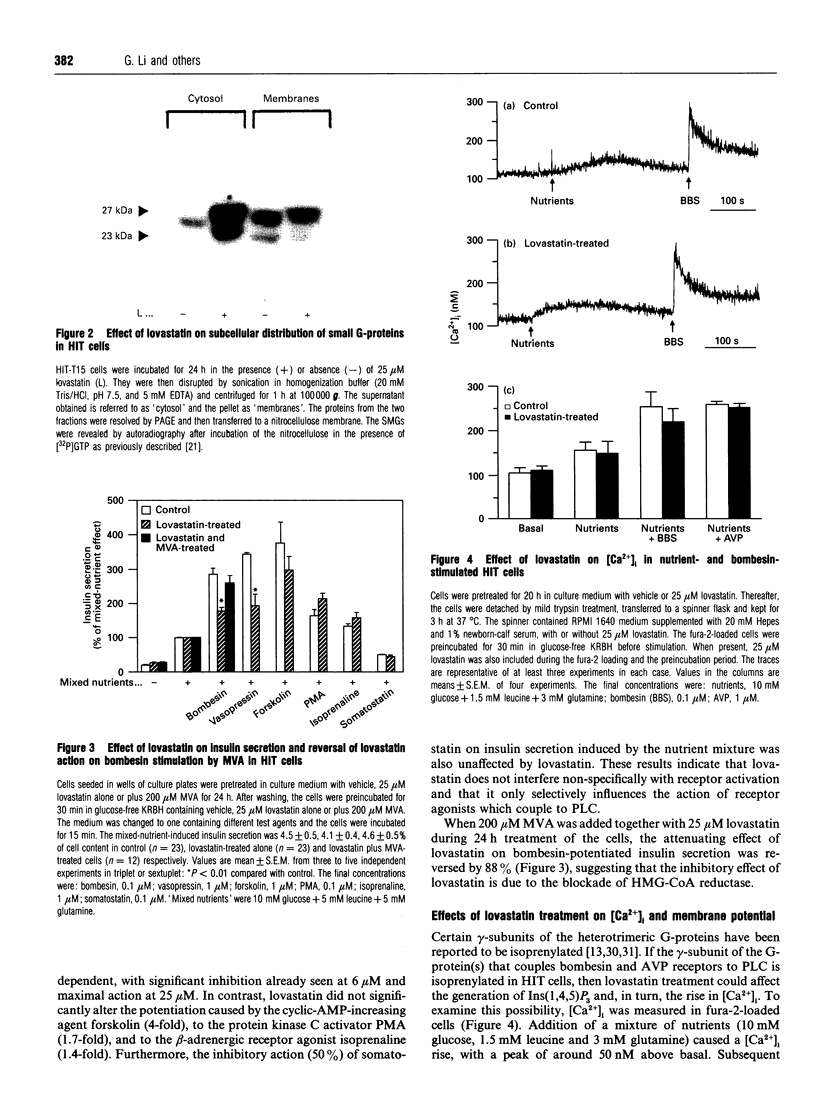
Small G-proteins (SMGs) require isoprenylation for their association with membranes. We have examined protein isoprenylation, subcellular distribution of SMGs, cytosolic Ca2+ changes and insulin secretion in HIT-T15 cells after treatment with lovastatin, which inhibits the production of isoprenoids by blocking mevalonate production by 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase. Numerous proteins in the 20-70 kDa range were found to be isoprenylated. Most of these proteins co-migrated with SMGs (21-27 kDa). Lovastatin treatment (25 microM, 24 h) decreased protein isoprenylation and affected the distribution of several SMGs, causing a large accumulation in the cytosol and a detectable decrease in membranes. Lovastatin selectively attenuated the potentiating action of bombesin and vasopressin, which activate phospholipase C in these cells, on insulin secretion stimulated by nutrients (glucose + leucine + glutamine). This lovastatin effect was overcome by mevalonate. Insulin secretion stimulated by nutrients alone or insulin release in the presence of the potentiating agents forskolin or phorbol myristate acetate remained unaffected. As the modulation of insulin secretion by isoprenaline and somatostatin were not altered by lovastatin, the drug does not non-selectively affect the binding of ligands to their receptors. Lovastatin did not interfere with the activation of phospholipase C by bombesin and vasopressin, since the rise in cytosolic Ca2+ induced by these agents was not changed. Limonene, proposed to block specifically prenyl-protein transferases of SMGs, did not alter protein isoprenylation patterns, but inhibited the stimulated insulin secretion. In conclusion, lovastatin selectively attenuated the potentiation of nutrient-induced insulin secretion by bombesin and vasopressin without affecting their activation of phospholipase C. The concomitant changes in SMG isoprenylation and their subcellular distribution after lovastatin treatment suggest that SMGs could play an important role in the bombesin and vasopressin action on insulin secretion.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts A. W., Chen J., Kuron G., Hunt V., Huff J., Hoffman C., Rothrock J., Lopez M., Joshua H., Harris E. Mevinolin: a highly potent competitive inhibitor of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase and a cholesterol-lowering agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3957–3961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anant J. S., Ong O. C., Xie H. Y., Clarke S., O'Brien P. J., Fung B. K. In vivo differential prenylation of retinal cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase catalytic subunits. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):687–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E. Small GTP-binding proteins in vesicular transport. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Dec;15(12):473–477. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90301-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Prossnitz V. Isoprenoid metabolism is required for stimulation of the respiratory burst oxidase of HL-60 cells. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):402–408. doi: 10.1172/JCI115599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg R. J., Middleton B., Bell G. D., White D. A. Inhibition of hepatic cholesterol synthesis and S-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase by mono and bicyclic monoterpenes administered in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Aug 1;29(15):2125–2127. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowell P. L., Chang R. R., Ren Z. B., Elson C. E., Gould M. N. Selective inhibition of isoprenylation of 21-26-kDa proteins by the anticarcinogen d-limonene and its metabolites. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17679–17685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutts J. L., Scallen T. J., Watson J., Bankhurst A. D. Role of mevalonic acid in the regulation of natural killer cell cytotoxicity. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jun;139(3):550–557. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deanin G. G., Cutts J. L., Pfeiffer J. R., Oliver J. M. Role of isoprenoid metabolism in IgE receptor-mediated signal transduction. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3528–3535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deanin G. G., Pfeiffer J. R., Cutts J. L., Fore M. L., Oliver J. M. Isoprenoid pathway activity is required for IgE receptor-mediated, tyrosine kinase-coupled transmembrane signaling in permeabilized RBL-2H3 rat basophilic leukemia cells. Cell Regul. 1991 Aug;2(8):627–640. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.8.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Der C. J., Cox A. D. Isoprenoid modification and plasma membrane association: critical factors for ras oncogenicity. Cancer Cells. 1991 Sep;3(9):331–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Graves J. D., Warne P. H., Rayter S., Cantrell D. A. Stimulation of p21ras upon T-cell activation. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):719–723. doi: 10.1038/346719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukada Y., Takao T., Ohguro H., Yoshizawa T., Akino T., Shimonishi Y. Farnesylated gamma-subunit of photoreceptor G protein indispensable for GTP-binding. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):658–660. doi: 10.1038/346658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A., Gelb M. H., Farnsworth C. C. Prenyl proteins in eukaryotic cells: a new type of membrane anchor. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Apr;15(4):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90213-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):425–430. doi: 10.1038/343425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomperts B. D. GE: a GTP-binding protein mediating exocytosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:591–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglese J., Glickman J. F., Lorenz W., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Isoprenylation of a protein kinase. Requirement of farnesylation/alpha-carboxyl methylation for full enzymatic activity of rhodopsin kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1422–1425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko I., Hazama-Shimada Y., Endo A. Inhibitory effects on lipid metabolism in cultured cells of ML-236B, a potent inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme-A reductase. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):313–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12380.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita T., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Feedback regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in livers of mice treated with mevinolin, a competitive inhibitor of the reductase. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):1094–1100. doi: 10.1172/JCI109938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. F., Manning D., Reisine T. Identification of the subunits of GTP-binding proteins coupled to somatostatin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):17885–17897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G., Hidaka H., Wollheim C. B. Inhibition of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels and insulin secretion in HIT cells by the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II inhibitor KN-62: comparison with antagonists of calmodulin and L-type Ca2+ channels. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Sep;42(3):489–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G., Pralong W. F., Pittet D., Mayr G. W., Schlegel W., Wollheim C. B. Inositol tetrakisphosphate isomers and elevation of cytosolic Ca2+ in vasopressin-stimulated insulin-secreting RINm5F cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4349–4356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltese W. A. Posttranslational modification of proteins by isoprenoids in mammalian cells. FASEB J. 1990 Dec;4(15):3319–3328. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.15.2123808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Kaibuchi K., Ando S., Musha T., Hiraoka K., Takaishi K., Asada M., Nunoi H., Matsuda I., Takai Y. Regulation of the superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase by a small GTP-binding protein and its stimulatory and inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10215–10218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy C. J., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Aaronson S. A. PDGF induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of GTPase activating protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):711–714. doi: 10.1038/342711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G., Gutowski S., Sternweis P. C. G protein gamma subunits contain a 20-carbon isoprenoid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5873–5877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Matschinsky F. M. Ca2+, cAMP, and phospholipid-derived messengers in coupling mechanisms of insulin secretion. Physiol Rev. 1987 Oct;67(4):1185–1248. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.4.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regazzi R., Li G. D., Deshusses J., Wollheim C. B. Stimulus-response coupling in insulin-secreting HIT cells. Effects of secretagogues on cytosolic Ca2+, diacylglycerol, and protein kinase C activity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15003–15009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regazzi R., Li G., Ullrich S., Jaggi C., Wollheim C. B. Different requirements for protein kinase C activation and Ca2+-independent insulin secretion in response to guanine nucleotides. Endogenously generated diacylglycerol requires elevated Ca2+ for kinase C insertion into membranes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9939–9944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regazzi R., Ullrich S., Kahn R. A., Wollheim C. B. Redistribution of ADP-ribosylation factor during stimulation of permeabilized cells with GTP analogues. Biochem J. 1991 May 1;275(Pt 3):639–644. doi: 10.1042/bj2750639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer W. R., Kim R., Sterne R., Thorner J., Kim S. H., Rine J. Genetic and pharmacological suppression of oncogenic mutations in ras genes of yeast and humans. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):379–385. doi: 10.1126/science.2569235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinensky M., Logel J. Defective macromolecule biosynthesis and cell-cycle progression in a mammalian cell starved for mevalonate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3257–3261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swope S. L., Schonbrunn A. The biphasic stimulation of insulin secretion by bombesin involves both cytosolic free calcium and protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 1;253(1):193–202. doi: 10.1042/bj2530193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Kikuchi A., Kawata M. Small GTP-binding proteins. Int Rev Cytol. 1992;133:187–230. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61861-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich S., Prentki M., Wollheim C. B. Somatostatin inhibition of Ca2(+)-induced insulin secretion in permeabilized HIT-T15 cells. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 15;270(1):273–276. doi: 10.1042/bj2700273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent T. S., Wülfert E., Merler E. Inhibition of growth factor signaling pathways by lovastatin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Nov 14;180(3):1284–1289. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81334-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolda S. L., Glomset J. A. Evidence for modification of lamin B by a product of mevalonic acid. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):5997–6000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamane H. K., Farnsworth C. C., Xie H. Y., Howald W., Fung B. K., Clarke S., Gelb M. H., Glomset J. A. Brain G protein gamma subunits contain an all-trans-geranylgeranylcysteine methyl ester at their carboxyl termini. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5868–5872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]