Abstract
We have expressed a bovine synthetic acyl-CoA-binding protein (ACBP) gene in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) under the control of the GAL1 promoter. The heterologously expressed bovine ACBP constituted up to 6.4% of total cellular protein and the processing was identical with that of native bovine ACBP, i.e. the initiating methionine was removed and the following serine residue was N-acetylated. The expression of this protein did not affect the growth rate of the cells. Determination of the yeast acyl-CoA pool size showed a close positive correlation between the ACBP content of the cells and the size of the acyl-CoA pool. Thus ACBP can act as an intracellular acyl-CoA pool former. Possible physiological functions of ACBP in cells are discussed.
Full text
PDF
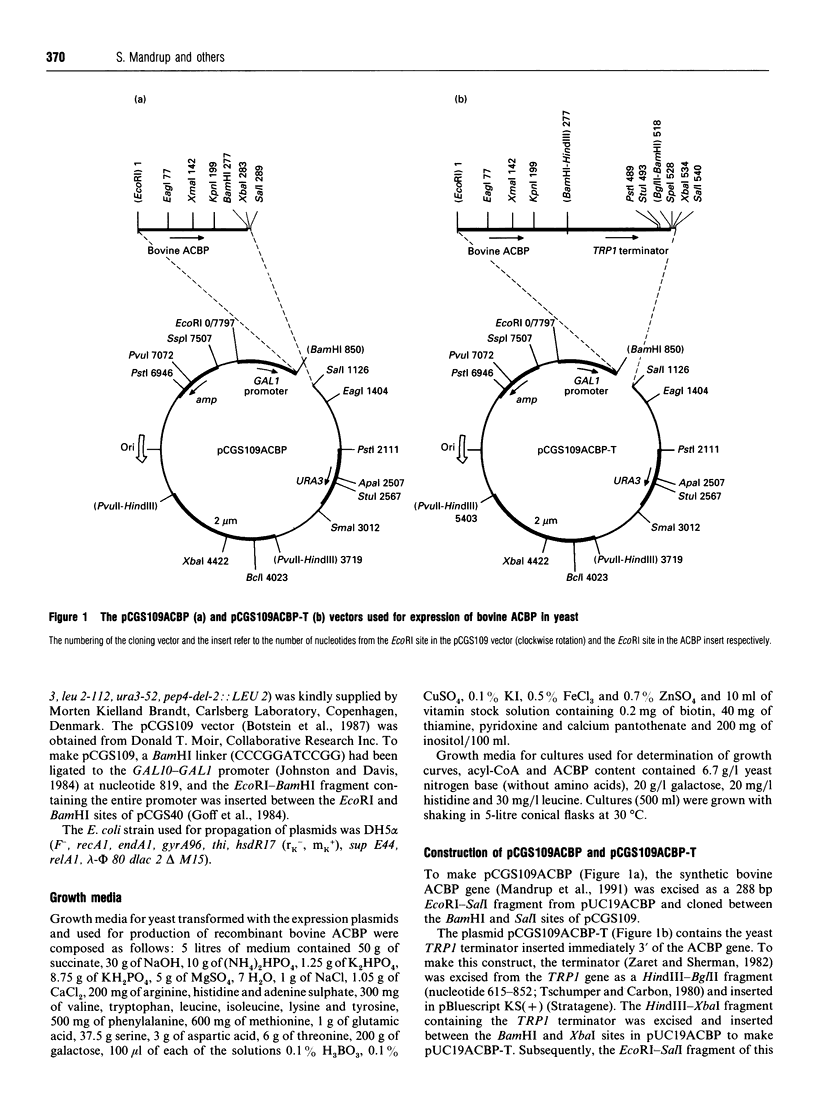

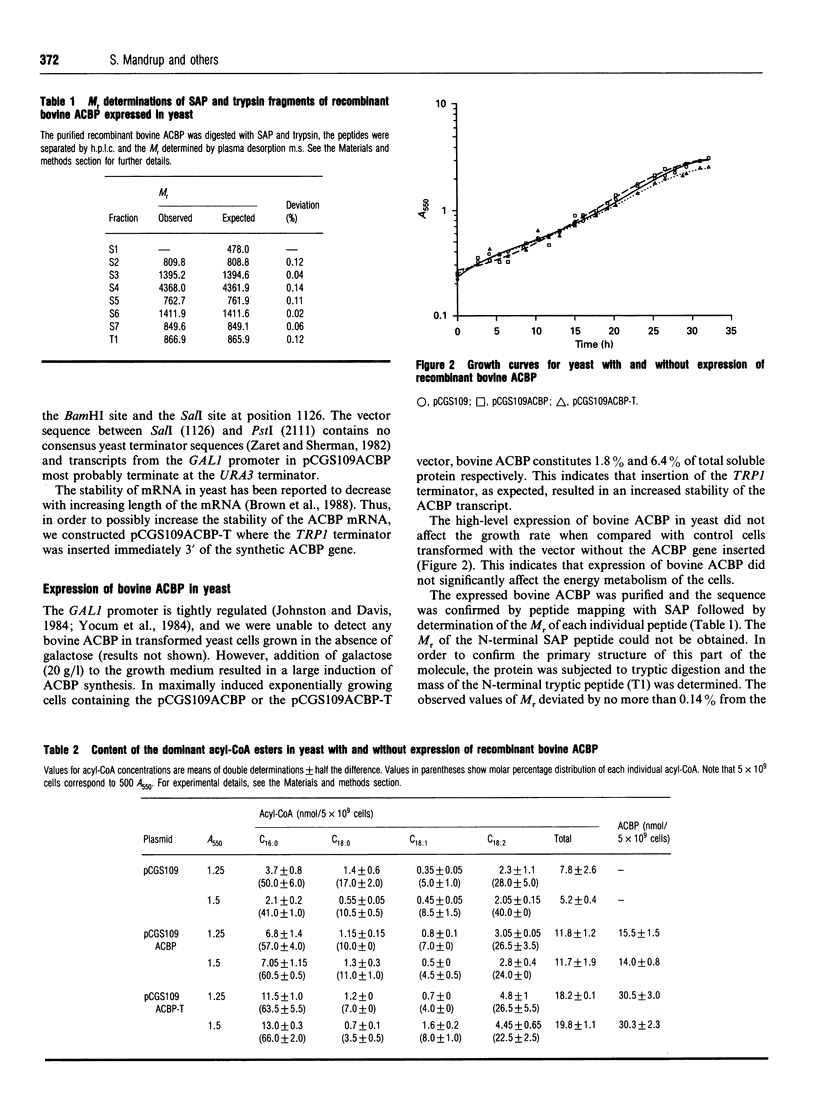


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alho H., Harjuntausta T., Schultz R., Pelto-Huikko M., Bovolin P. Immunohistochemistry of diazepam binding inhibitor (DBI) in the central nervous system and peripheral organs: its possible role as an endogenous regulator of different types of benzodiazepine receptors. Neuropharmacology. 1991 Dec;30(12B):1381–1386. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(11)80005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berge R. K., Farstad M. Purification and characterization of long-chain acyl-CoA hydrolase from rat liver mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1979 May 15;96(2):393–401. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13051.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berge R. K., Flatmark T., Osmundsen H. Enhancement of long-chain acyl-CoA hydrolase activity in peroxisomes and mitochondria of rat liver by peroxisomal proliferators. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 15;141(3):637–644. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berge R. K. Purification and characterization of a long-chain acyl-CoA hydrolase from rat liver microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 30;574(2):321–333. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besman M. J., Yanagibashi K., Lee T. D., Kawamura M., Hall P. F., Shively J. E. Identification of des-(Gly-Ile)-endozepine as an effector of corticotropin-dependent adrenal steroidogenesis: stimulation of cholesterol delivery is mediated by the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4897–4901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bovolin P., Schlichting J., Miyata M., Ferrarese C., Guidotti A., Alho H. Distribution and characterization of diazepam binding inhibitor (DBI) in peripheral tissues of rat. Regul Pept. 1990 Jul 30;29(2-3):267–281. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(90)90089-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. J., Purvis I. J., Santiago T. C., Bettany A. J., Loughlin L., Moore J. Messenger RNA degradation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):151–160. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90137-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. S., Hall P. F., Shoyab M., Papadopoulos V. Endozepine/diazepam binding inhibitor in adrenocortical and Leydig cell lines: absence of hormonal regulation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1992 Jan;83(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(92)90189-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa E., Corda M. G., Guidotti A. On a brain polypeptide functioning as a putative effector for the recognition sites of benzodiazepine and beta-carboline derivatives. Neuropharmacology. 1983 Dec;22(12B):1481–1492. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(83)90116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa E., Guidotti A. Diazepam binding inhibitor (DBI): a peptide with multiple biological actions. Life Sci. 1991;49(5):325–344. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90440-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff C. G., Moir D. T., Kohno T., Gravius T. C., Smith R. A., Yamasaki E., Taunton-Rigby A. Expression of calf prochymosin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1984 Jan;27(1):35–46. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90236-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Glaister D., Seeburg P. H., Guidotti A., Costa E. Cloning and expression of cDNA for human diazepam binding inhibitor, a natural ligand of an allosteric regulatory site of the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7547–7551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti A., Forchetti C. M., Corda M. G., Konkel D., Bennett C. D., Costa E. Isolation, characterization, and purification to homogeneity of an endogenous polypeptide with agonistic action on benzodiazepine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3531–3535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hach M., Pedersen S. N., Börchers T., Højrup P., Knudsen J. Determination by photoaffinity labelling of the hydrophobic part of the binding site for acyl-CoA esters on acyl-CoA-binding protein from bovine liver. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 1;271(1):231–236. doi: 10.1042/bj2710231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen H. O., Andreasen P. H., Mandrup S., Kristiansen K., Knudsen J. Induction of acyl-CoA-binding protein and its mRNA in 3T3-L1 cells by insulin during preadipocyte-to-adipocyte differentiation. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 15;277(Pt 2):341–344. doi: 10.1042/bj2770341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Davis R. W. Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1440–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen J., Højrup P., Hansen H. O., Hansen H. F., Roepstorff P. Acyl-CoA-binding protein in the rat. Purification, binding characteristics, tissue concentrations and amino acid sequence. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):513–519. doi: 10.1042/bj2620513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen J., Nielsen M. Diazepam-binding inhibitor: a neuropeptide and/or an acyl-CoA ester binding protein? Biochem J. 1990 Feb 1;265(3):927–929. doi: 10.1042/bj2650927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lust G., Lynen F. The inhibition of the fatty acid synthetase multienzyme complex of yeast by long-chain acyl coenzyme A compounds. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Dec;7(1):68–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb19575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrup S., Højrup P., Kristiansen K., Knudsen J. Gene synthesis, expression in Escherichia coli, purification and characterization of the recombinant bovine acyl-CoA-binding protein. Biochem J. 1991 Jun 15;276(Pt 3):817–823. doi: 10.1042/bj2760817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massotti M., Slobodyansky E., Konkel D., Costa E., Guidotti A. Regulation of diazepam binding inhibitor in rat adrenal gland by adrenocorticotropin. Endocrinology. 1991 Aug;129(2):591–596. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-2-591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen J., Højrup P., Nielsen P. F., Roepstorff P., Knudsen J. Amino acid sequence of acyl-CoA-binding protein from cow liver. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):857–861. doi: 10.1042/bj2450857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocchetti I., Einstein R., Brosius J. Putative diazepam binding inhibitor peptide: cDNA clones from rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7221–7225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen I. B., Schulenberg H., Hansen H. O., Spener F., Knudsen J. A novel acyl-CoA-binding protein from bovine liver. Effect on fatty acid synthesis. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):189–192. doi: 10.1042/bj2410189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel F., Lauquin G., Lunardi J., Duszynski J., Vignais P. V. An appraisal of the functional significance of the inhibitory effect of long chain acyl-CoAs on mitochondrial transports. FEBS Lett. 1974 Feb 15;39(2):133–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikawa J., Tanabe T., Ogiwara H., Shiba T., Numa S. Inhibitory effects of long-chain acyl coenzyme A analogues on rat liver acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 15;102(2):223–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. F., Wenger J. I., Neely J. R. Regulation of long chain fatty acid activation in heart muscle. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):73–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos V., Berkovich A., Krueger K. E., Costa E., Guidotti A. Diazepam binding inhibitor and its processing products stimulate mitochondrial steroid biosynthesis via an interaction with mitochondrial benzodiazepine receptors. Endocrinology. 1991 Sep;129(3):1481–1488. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-3-1481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfanner N., Glick B. S., Arden S. R., Rothman J. E. Fatty acylation promotes fusion of transport vesicles with Golgi cisternae. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):955–961. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfanner N., Orci L., Glick B. S., Amherdt M., Arden S. R., Malhotra V., Rothman J. E. Fatty acyl-coenzyme A is required for budding of transport vesicles from Golgi cisternae. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90872-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen J. T., Börchers T., Knudsen J. Comparison of the binding affinities of acyl-CoA-binding protein and fatty-acid-binding protein for long-chain acyl-CoA esters. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 1;265(3):849–855. doi: 10.1042/bj2650849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal J., Knudsen J. A fast and versatile method for extraction and quantitation of long-chain acyl-CoA esters from tissue: content of individual long-chain acyl-CoA esters in various tissues from fed rat. Anal Biochem. 1992 Nov 15;207(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90500-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacterle G. R., Pollack R. L. A simplified method for the quantitative assay of small amounts of protein in biologic material. Anal Biochem. 1973 Feb;51(2):654–655. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoyab M., Gentry L. E., Marquardt H., Todaro G. J. Isolation and characterization of a putative endogenous benzodiazepineoid (endozepine) from bovine and human brain. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):11968–11973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzue G., Marcel Y. L. Kinetic studies on the chain length specificity of long chain acyl coenzyme A synthetase from rat liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6781–6783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong Y., Toranzo D., Pelletier G. Localization of diazepam-binding inhibitor (DBI) mRNA in the rat brain by high resolution in situ hybridization. Neuropeptides. 1991 Sep;20(1):33–40. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(91)90037-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschumper G., Carbon J. Sequence of a yeast DNA fragment containing a chromosomal replicator and the TRP1 gene. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagibashi K., Ohno Y., Kawamura M., Hall P. F. The regulation of intracellular transport of cholesterol in bovine adrenal cells: purification of a novel protein. Endocrinology. 1988 Oct;123(4):2075–2082. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-4-2075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocum R. R., Hanley S., West R., Jr, Ptashne M. Use of lacZ fusions to delimit regulatory elements of the inducible divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1985–1998. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


