Abstract
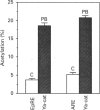
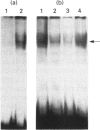
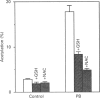
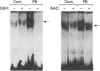
Phenobarbital is an inducer of xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes, such as cytochrome P-450, glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) and NAD(P)H:quinone reductase, as well as being a promoter of hepatocarcinogenesis. The molecular mechanisms regulating these biological activities are, however, unknown. In this paper we show that induction by phenobarbital of GST Ya and quinone reductase gene expression is mediated by regulatory elements, EpRE and ARE respectively, which are composed of two adjacent AP-1-like binding sites. EpRE was recently found to be activated by a Fos/Jun heterodimeric complex (AP-1). Here we show that phenobarbital induces an increase in AP-1 binding activity in nuclear extracts of cultured hepatoma cells. Furthermore, we observe that the induction of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) activity from an EpRE Ya-cat gene construct and of AP-1 binding activity by phenobarbital is inhibited by the thiol compounds N-acetyl-L-cysteine and glutathione. These results suggest that the phenobarbital induction of AP-1 activity, leading to the AP-1-mediated transcriptional activation of the GST Ya and quinone reductase genes, may involve production of reactive oxygen species and an increase in intracellular oxidant levels, which is prevented by thiol compounds. In view of the involvement of AP-1 in the control of cell proliferation and transformation, the induction by phenobarbital of AP-1 binding activity observed here provides a possible molecular mechanism for the tumour-promoting activity of this drug.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abate C., Patel L., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Curran T. Redox regulation of fos and jun DNA-binding activity in vitro. Science. 1990 Sep 7;249(4973):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.2118682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adesnik M., Atchison M. Genes for cytochrome P-450 and their regulation. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;19(3):247–305. doi: 10.3109/10409238609084657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Karin M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 10;1072(2-3):129–157. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aruoma O. I., Halliwell B., Hoey B. M., Butler J. The antioxidant action of N-acetylcysteine: its reaction with hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radical, superoxide, and hypochlorous acid. Free Radic Biol Med. 1989;6(6):593–597. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(89)90066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerutti P. A. Prooxidant states and tumor promotion. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):375–381. doi: 10.1126/science.2981433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel V., Sarid S., Bar-Nun S., Litwack G. Rat ligandin mRNA molecular cloning and sequencing. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Nov;227(1):266–271. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90370-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel V., Sharon R., Bensimon A. Regulatory elements controlling the basal and drug-inducible expression of glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene. DNA. 1989 Jul-Aug;8(6):399–408. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding V. D., Pickett C. B. Transcriptional regulation of rat liver glutathione S-transferase genes by phenobarbital and 3-methylcholanthrene. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Aug 1;240(2):553–559. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90062-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favreau L. V., Pickett C. B. Transcriptional regulation of the rat NAD(P)H:quinone reductase gene. Identification of regulatory elements controlling basal level expression and inducible expression by planar aromatic compounds and phenolic antioxidants. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4556–4561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friling R. S., Bensimon A., Tichauer Y., Daniel V. Xenobiotic-inducible expression of murine glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene is controlled by an electrophile-responsive element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6258–6262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friling R. S., Bergelson S., Daniel V. Two adjacent AP-1-like binding sites form the electrophile-responsive element of the murine glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):668–672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales B. J., Neims A. H. Induction of rat hepatic glutathione S-transferase B by phenobarbital and 3-methylcholanthrene. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Mar 15;26(6):555–556. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell B., Gutteridge J. M. Role of free radicals and catalytic metal ions in human disease: an overview. Methods Enzymol. 1990;186:1–85. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)86093-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M. Signal transduction from cell surface to nucleus in development and disease. FASEB J. 1992 May;6(8):2581–2590. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.8.1317309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okey A. B. Enzyme induction in the cytochrome P-450 system. Pharmacol Ther. 1990;45(2):241–298. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(90)90030-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett C. B., Wells W., Lu A. Y., Hales B. F. Induction of translationally active rat liver glutathione S-transferase B messenger RNA by phenobarbital. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 15;99(3):1002–1010. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91261-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitot H. C., Sirica A. E. The stages of initiation and promotion in hepatocarcinogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 6;605(2):191–215. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(80)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushmore T. H., Pickett C. B. Transcriptional regulation of the rat glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene. Characterization of a xenobiotic-responsive element controlling inducible expression by phenolic antioxidants. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14648–14653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6419–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sies H. Oxidative stress: from basic research to clinical application. Am J Med. 1991 Sep 30;91(3C):31S–38S. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90281-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Azaroff L. Phenobarbital induction of cytochrome P-450 gene expression. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 1;281(Pt 3):577–592. doi: 10.1042/bj2810577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. B., Wang R., Lu A. Y., Pickett C. B. Rat liver DT-diaphorase: regulation of functional mRNA levels by 3-methylcholanthrene, trans-stilbene oxide, and phenobarbital. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Jul;232(1):408–413. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90556-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthoudakis S., Curran T. Identification and characterization of Ref-1, a nuclear protein that facilitates AP-1 DNA-binding activity. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):653–665. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05097.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]