Abstract
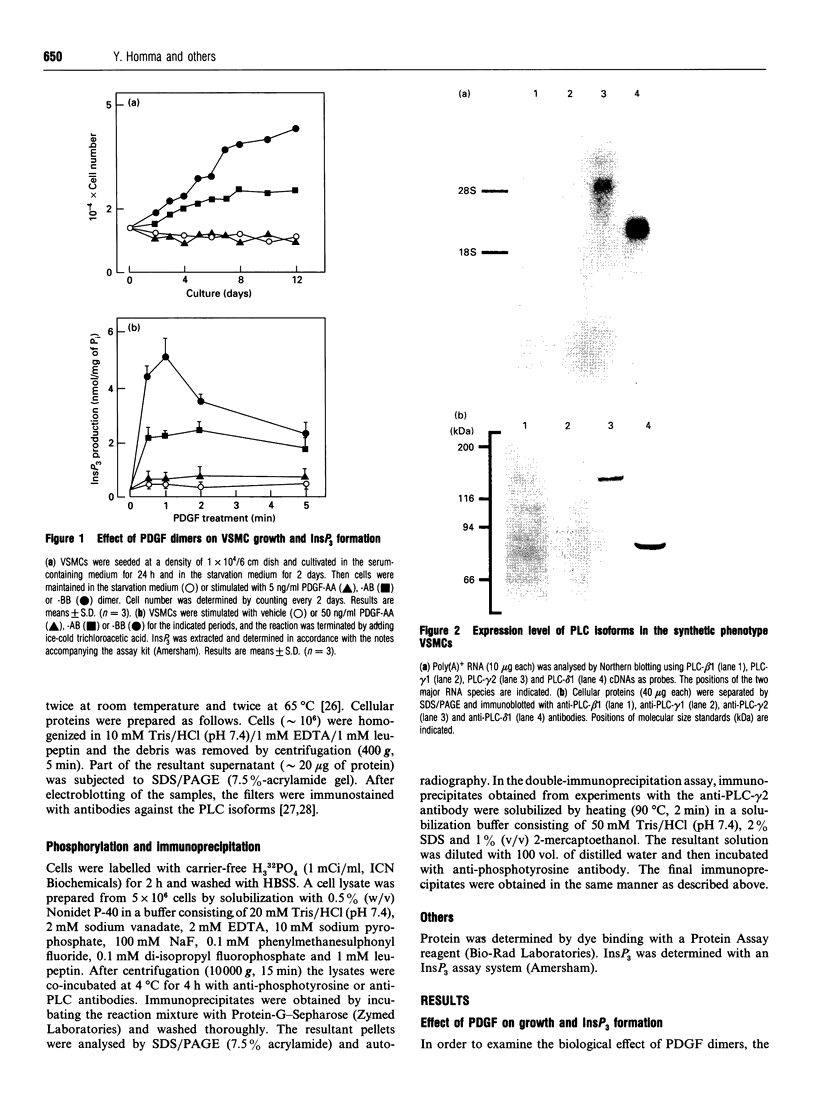
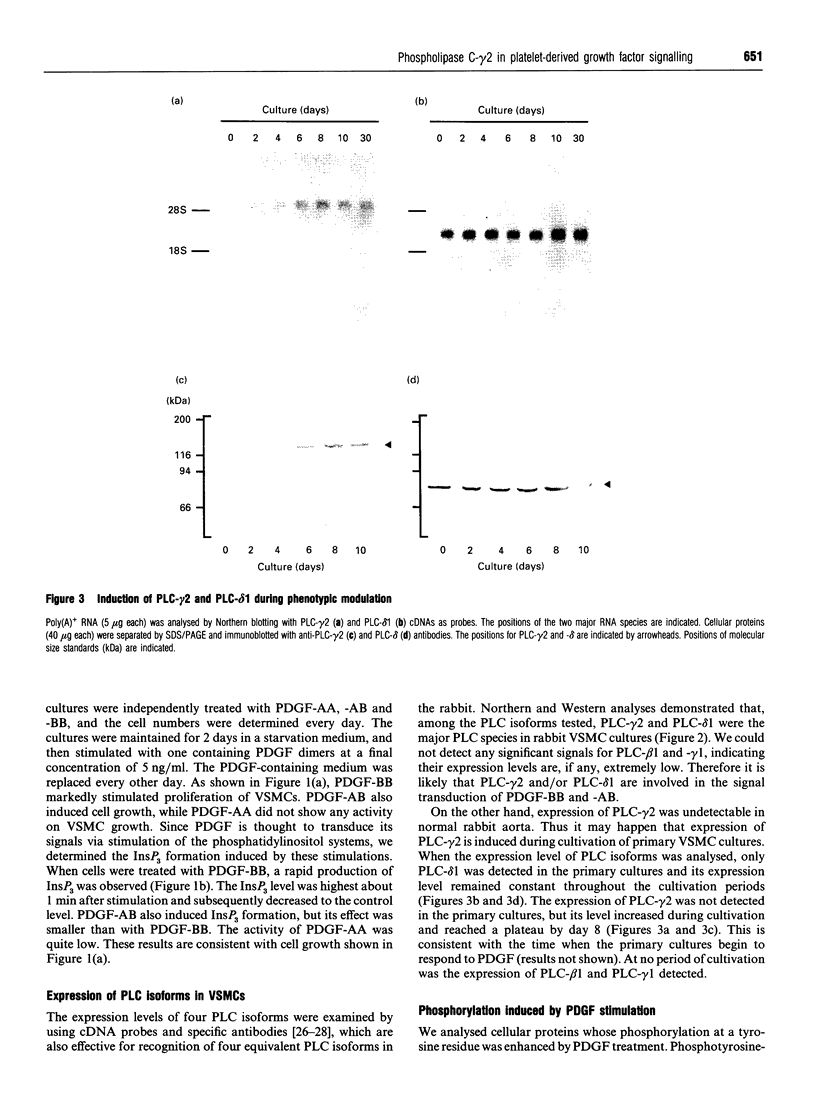
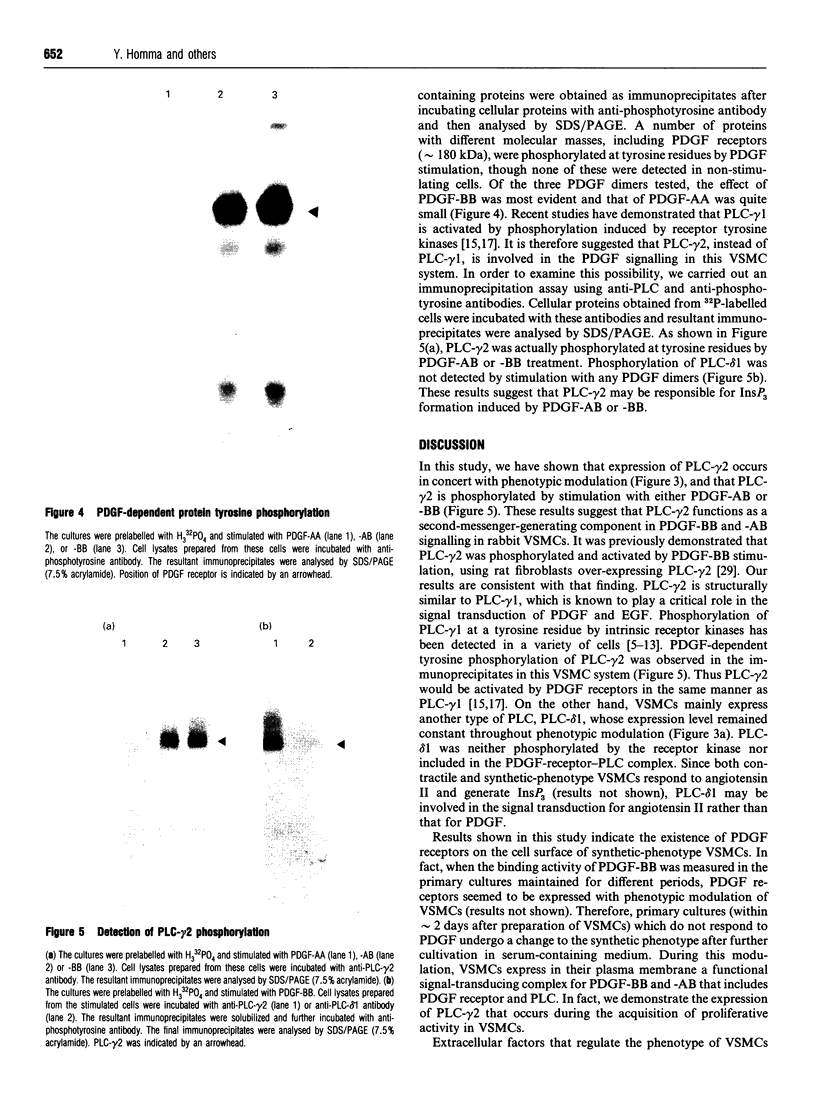
In order to examine the mechanisms underlying smooth-muscle cell proliferation, we investigated effect of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) dimers on proliferation of rabbit vascular smooth-muscle cells (VSMCs) and also involvement of phospholipase C (PLC) isoforms in the signal transduction. PDGF-BB and -AB, but not -AA, stimulated cell proliferation and intracellular production of inositol trisphosphate. Northern and Western analyses demonstrated that VSMCs mainly expressed PLC-gamma 2 and PLC-delta 1 among four PLC isoforms tested. A number of cellular proteins, including PLC-gamma 2, but not PLC-delta 1, were phosphorylated on a tyrosine residue by the stimulation of either PDGF-BB or -AB. These results suggest a functional association of PDGF receptor and PLC-gamma 2 that might be responsible for PDGF-dependent VSMC growth. In addition, the expression of PLC-gamma 2 was extremely low in the primary VSMC cultures and was induced during further cultivation of the primary cultures, indicating that an acquisition of PDGF-signal-transducing components, including PLC-gamma 2, may be an important step for proliferation of smooth-muscle cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R. Platelet-derived growth factor. II. Specific binding to cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5161–5171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell G. R., Chamley-Campbell J. H. Invited review: the cellular pathobiology of atherosclerosis. Pathology. 1981 Jul;13(3):423–440. doi: 10.3109/00313028109059061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamley-Campbell J., Campbell G. R., Ross R. The smooth muscle cell in culture. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jan;59(1):1–61. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori Y., Homma Y., Sorimachi H., Kawasaki H., Nakanishi O., Suzuki K., Takenawa T. A second type of rat phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C containing a src-related sequence not essential for phosphoinositide-hydrolyzing activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21885–21890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Kim J. W., Machesky L. M., Rhee S. G., Pollard T. D. Regulation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by profilin and tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1231–1233. doi: 10.1126/science.1848725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Machesky L. M., Baldassare J. J., Pollard T. D. The actin-binding protein profilin binds to PIP2 and inhibits its hydrolysis by phospholipase C. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1575–1578. doi: 10.1126/science.2157283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunther S., Alexander R. W., Atkinson W. J., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Functional angiotensin II receptors in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):289–298. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Wasteson A. Specific receptors for platelet-derived growth factor on cells derived from connective tissue and glia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3664–3668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma Y., Emori Y., Shibasaki F., Suzuki K., Takenawa T. Isolation and characterization of a gamma-type phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C (PLC-gamma 2). Biochem J. 1990 Jul 1;269(1):13–18. doi: 10.1042/bj2690013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma Y., Emori Y., Takenawa T. Purification of recombinant SH2/SH3 proteins of phospholipase C-gamma 1 and -gamma 2 and their inhibitory effect on PIP2-hydrolysis induced by both types of phospholipase C-gamma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 14;182(3):1402–1407. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91889-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma Y., Takenawa T., Emori Y., Sorimachi H., Suzuki K. Tissue- and cell type-specific expression of mRNAs for four types of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 16;164(1):406–412. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91734-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim U. H., Fink D., Jr, Kim H. S., Park D. J., Contreras M. L., Guroff G., Rhee S. G. Nerve growth factor stimulates phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1359–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Bellot F., Honegger A. M., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Zilberstein A. Tyrosine kinase activity is essential for the association of phospholipase C-gamma with the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):435–441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum E., Parker P. J., Carozzi A. The PtdIns-PLC superfamily and signal transduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 19;1092(1):49–71. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90177-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Koch C. A., Anderson D., Ellis C., England L., Martin G. S., Pawson T. Src homology region 2 domains direct protein-protein interactions in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8622–8626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Rhee S. G., Williams L. T. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-dependent association of phospholipase C-gamma with the PDGF receptor signaling complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2359–2366. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro J. M., Cotran R. S. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: atherogenesis and inflammation. Lab Invest. 1988 Mar;58(3):249–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Hernández-Sotomayor S. M., Tonks N. K., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Increase of the catalytic activity of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1253–1256. doi: 10.1126/science.1700866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Lee S. Y. Studies of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):546–550. doi: 10.1126/science.2541501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J., Kariya B., Harker L. A platelet-dependent serum factor that stimulates the proliferation of arterial smooth muscle cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1207–1210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Masuda J., Raines E. W., Gown A. M., Katsuda S., Sasahara M., Malden L. T., Masuko H., Sato H. Localization of PDGF-B protein in macrophages in all phases of atherogenesis. Science. 1990 May 25;248(4958):1009–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.2343305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Nist C., Kariya B., Rivest M. J., Raines E., Callis J. Physiological quiescence in plasma-derived serum: influence of platelet-derived growth factor on cell growth in culture. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Dec;97(3 Pt 2 Suppl 1):497–508. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040970325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis--an update. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 20;314(8):488–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602203140806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford R. B., Ross R. Platelet factors stimulate fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells quiescent in plasma serum to proliferate. J Cell Biol. 1976 Apr;69(1):196–203. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.1.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. M., Campbell G. R., Campbell J. H. Replication of smooth muscle cells in vascular disease. Circ Res. 1986 Apr;58(4):427–444. doi: 10.1161/01.res.58.4.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolich J. J., Walker A. M., Campbell G. R., Adamson T. M. Left and right ventricular myocardial morphometry in fetal, neonatal, and adult sheep. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jul;257(1 Pt 2):H1–H9. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.257.1.H1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzman L., Ellis C., Lin L. L., Pawson T., Knopf J. Platelet-derived growth factor increases the in vivo activity of phospholipase C-gamma 1 and phospholipase C-gamma 2. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2018–2025. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thyberg J., Hedin U., Sjölund M., Palmberg L., Bottger B. A. Regulation of differentiated properties and proliferation of arterial smooth muscle cells. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Nov-Dec;10(6):966–990. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.6.966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetter M. L., Martin-Zanca D., Parada L. F., Bishop J. M., Kaplan D. R. Nerve growth factor rapidly stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by a kinase activity associated with the product of the trk protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5650–5654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Daniel T. O., Carpenter G. Antiphosphotyrosine recovery of phospholipase C activity after EGF treatment of A-431 cells. Science. 1988 Aug 19;241(4868):968–970. doi: 10.1126/science.2457254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Tremble P., Antoniades H. N. Platelet-derived growth factor binds specifically to receptors on vascular smooth muscle cells and the binding becomes nondissociable. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5867–5870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonezawa N., Homma Y., Yahara I., Sakai H., Nishida E. A short sequence responsible for both phosphoinositide binding and actin binding activities of cofilin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17218–17221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]