Abstract
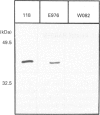
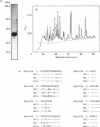
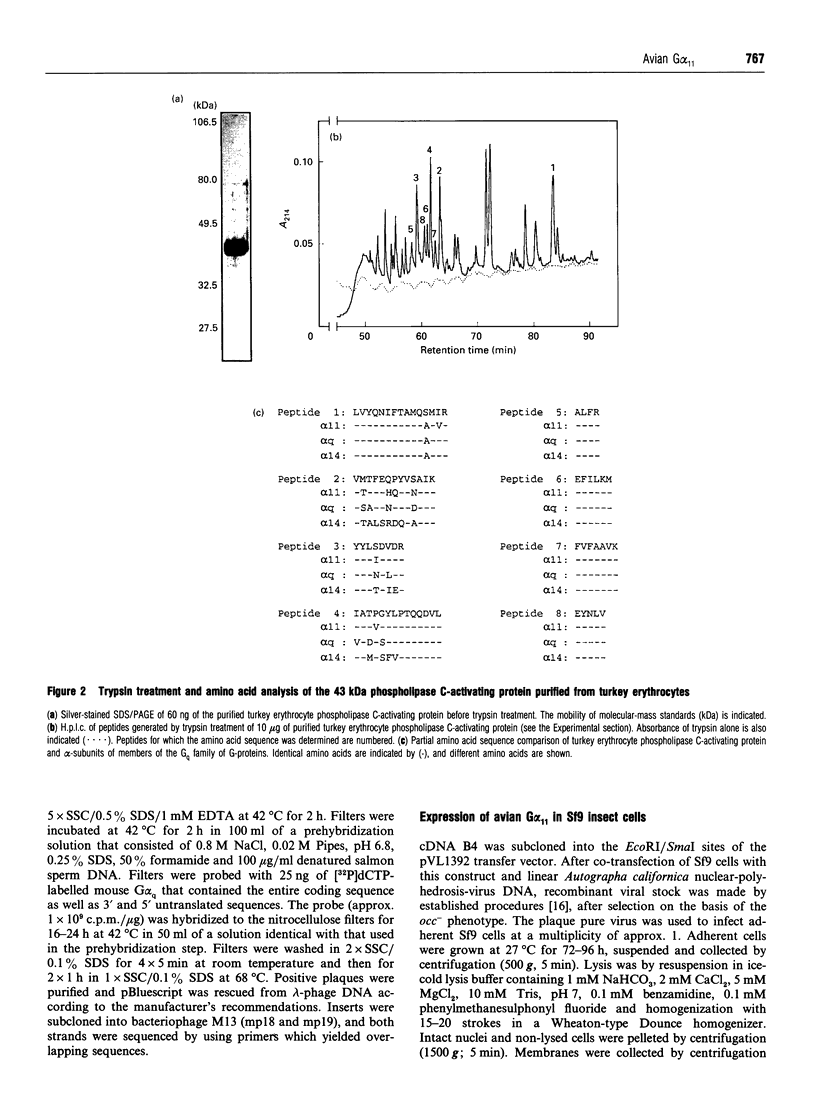
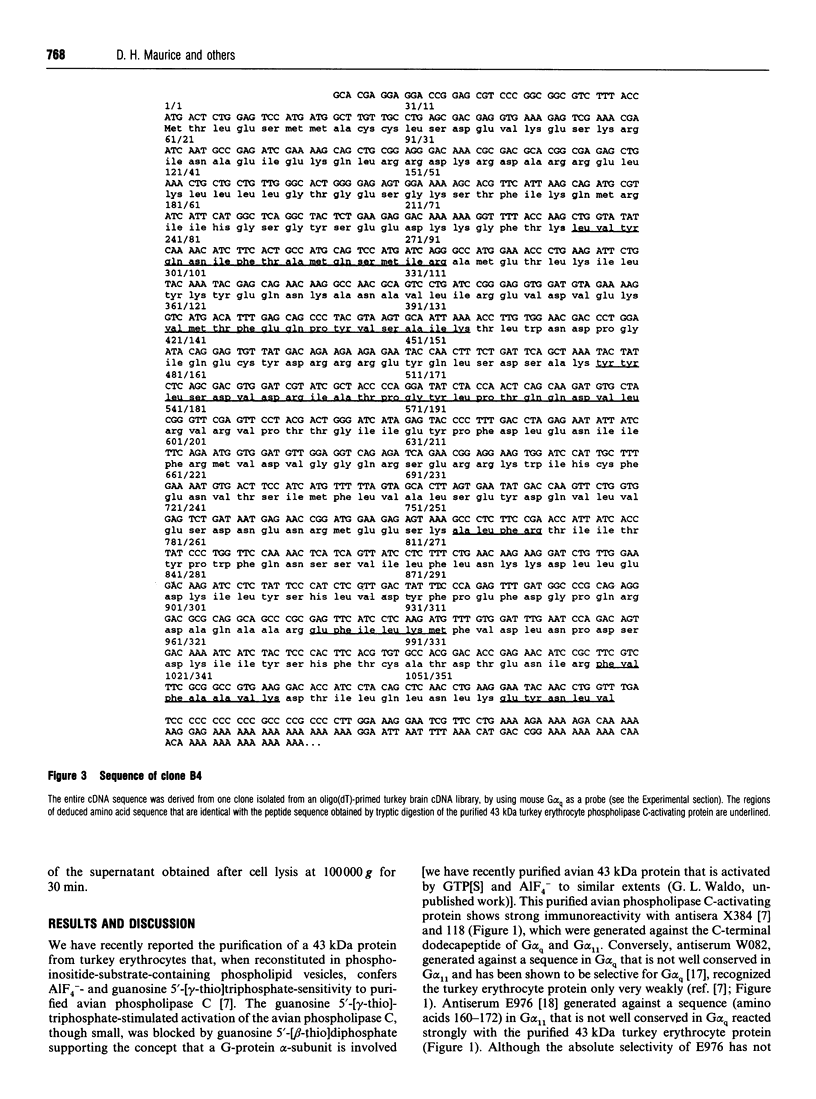
A 43 kDa phospholipase C-activating protein has been purified previously from turkey erythrocytes and shown to express immunological properties expected of that of the Gq family of G-protein alpha-subunits [Waldo, Boyer, Morris and Harden (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266, 14217-14225]. Internal amino acid sequence has now been obtained from this protein which shares 50-100% sequence identity with sequences encoded by mammalian G alpha 11 and G alpha q cDNAs. To identify the purified protein unambiguously, it was necessary to compare its amino acid sequence with the sequence encoded by avian G-protein alpha-subunit cDNA. As such, mouse G alpha q was used as a probe to screen turkey brain and fetal-turkey blood cDNA libraries. A full-length cDNA was identified that encodes avian G alpha 11, on the basis of its 96-98% amino acid identity with mammalian G alpha 11. All eight peptides sequenced from the turkey erythrocyte phospholipase C-activating protein are completely contained within the deduced amino acid sequence of the avian G alpha 11 cDNA. Expression of this cDNA in Sf9 cells by using a baculovirus expression system resulted in the production of a 43 kDa protein that reacts strongly with antisera to the Gq family of G-protein alpha-subunits and activated purified avian phospholipase C in an AlF4(-)-dependent manner. Taken together, these results unambiguously identify the protein purified from turkey erythrocytes, on the basis of its capacity to activate avian phospholipase C, as G alpha 11.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berstein G., Blank J. L., Smrcka A. V., Higashijima T., Sternweis P. C., Exton J. H., Ross E. M. Reconstitution of agonist-stimulated phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis using purified m1 muscarinic receptor, Gq/11, and phospholipase C-beta 1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8081–8088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L. G proteins in signal transduction. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:675–705. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank J. L., Ross A. H., Exton J. H. Purification and characterization of two G-proteins that activate the beta 1 isozyme of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Identification as members of the Gq class. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18206–18216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin B. R., Chabre O., Wong Y. H., Federman A. D., Bourne H. R. Recombinant Gq alpha. Mutational activation and coupling to receptors and phospholipase C. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):31–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutowski S., Smrcka A., Nowak L., Wu D. G., Simon M., Sternweis P. C. Antibodies to the alpha q subfamily of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein alpha subunits attenuate activation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis by hormones. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20519–20524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden T. K. G-protein-regulated phospholipase C. Identification of component proteins. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1992;26:11–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. J., Waldo G. L., Downes C. P., Harden T. K. A receptor and G-protein-regulated polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C from turkey erythrocytes. I. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13501–13507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. J., Waldo G. L., Downes C. P., Harden T. K. A receptor and G-protein-regulated polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C from turkey erythrocytes. II. P2Y-purinergic receptor and G-protein-mediated regulation of the purified enzyme reconstituted with turkey erythrocyte ghosts. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13508–13514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura F., Ogata K., Shiozaki K., Kameyama K., Ohara K., Haga T., Nukada T. Identification of two novel GTP-binding protein alpha-subunits that lack apparent ADP-ribosylation sites for pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12676–12681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang I. H., Sternweis P. C. Purification of unique alpha subunits of GTP-binding regulatory proteins (G proteins) by affinity chromatography with immobilized beta gamma subunits. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18707–18712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. I., Strathmann M. P., Gautam N. Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):802–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1902986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smrcka A. V., Hepler J. R., Brown K. O., Sternweis P. C. Regulation of polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C activity by purified Gq. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):804–807. doi: 10.1126/science.1846707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann M., Simon M. I. G protein diversity: a distinct class of alpha subunits is present in vertebrates and invertebrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9113–9117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann M., Wilkie T. M., Simon M. I. Diversity of the G-protein family: sequences from five additional alpha subunits in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7407–7409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. J., Exton J. H. Two alpha subunits of the Gq class of G proteins stimulate phosphoinositide phospholipase C-beta 1 activity. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 29;286(1-2):214–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80976-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. J., Smith J. A., Exton J. H. Purification from bovine liver membranes of a guanine nucleotide-dependent activator of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Immunologic identification as a novel G-protein alpha subunit. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17150–17156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldo G. L., Boyer J. L., Morris A. J., Harden T. K. Purification of an AlF4- and G-protein beta gamma-subunit-regulated phospholipase C-activating protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14217–14225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D. Q., Lee C. H., Rhee S. G., Simon M. I. Activation of phospholipase C by the alpha subunits of the Gq and G11 proteins in transfected Cos-7 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1811–1817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]