Abstract
The primary phase of ADP-induced aggregation of human platelets does not involve appreciable formation of thromboxane A2 or release of granule contents; lack of formation of inositol trisphosphate has also been noted. Because these responses of platelets to ADP differ so markedly from their responses to other aggregating agents, the roles in ADP-induced aggregation of diacylglycerol, protein kinase C, increases in cytosolic [Ca2+], phosphorylation of pleckstrin (47 kDa) and phosphatases 1 and 2a were investigated. Washed human platelets, prelabelled with [14C]5-hydroxytryptamine and suspended in Tyrode solution (2 mM Ca2+, 1 mM Mg2+), were used for comparisons between the aggregation induced by 2-4 microM ADP, in the presence of fibrinogen, and that induced by 0.05 units/ml thrombin. The diacylglycerol kinase inhibitor 6-(2-[(4-fluorophenyl)phenyl-methylene]-1-piperidinylethyl)-7-meth yl-5H-thiazolo[3,2-a]-pyrimidin-5-one (R59022; 25 microM) had no, or only a slight, enhancing effect on ADP-induced aggregation, but potentiated thrombin-induced responses to a much greater extent. 1,2-Dihexanoyl-sn-glycerol or 1-oleoyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol (25 microM) added with or 30-90 s before ADP greatly potentiated aggregation without formation of thromboxane; staurosporine, an inhibitor of protein kinase C, reduced this potentiation. Staurosporine (25 nM) did not inhibit ADP-induced aggregation, although it strongly inhibited thrombin-induced aggregation and release of [14C]5-hydroxytryptamine. All these observations indicate little or no dependence of primary ADP-induced aggregation on the formation of diacylglycerol or on the activation of protein kinase C. At 2-4 microM, ADP did not significantly increase the phosphorylation of pleckstrin (studied with platelets prelabelled with [32P]orthophosphate), but 1,2-dihexanoyl-sn-glycerol- induced phosphorylation of pleckstrin was increased by ADP. Surprisingly, the diacylglycerols strongly inhibited the ADP-induced rise in cytosolic [Ca2+] concurrently with potentiation of ADP-induced aggregation; thus the extent of primary aggregation is independent of the level to which cytosolic [Ca2+] rises. Incubation of platelets with 1,2-dihexanoyl-sn-glycerol or 1-oleoyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol for several minutes reversed their potentiating effects on aggregation, and inhibition was observed. Incubation of platelets with okadaic acid, an inhibitor of phosphatases 1 and 2a, inhibited ADP- and thrombin-induced aggregation; although the reason for this effect is unknown, it is unlikely to involve inhibition of phospholipase C, since formation of diacylglycerol appears to have little involvement in the primary phase of ADP-induced aggregation.
Full text
PDF


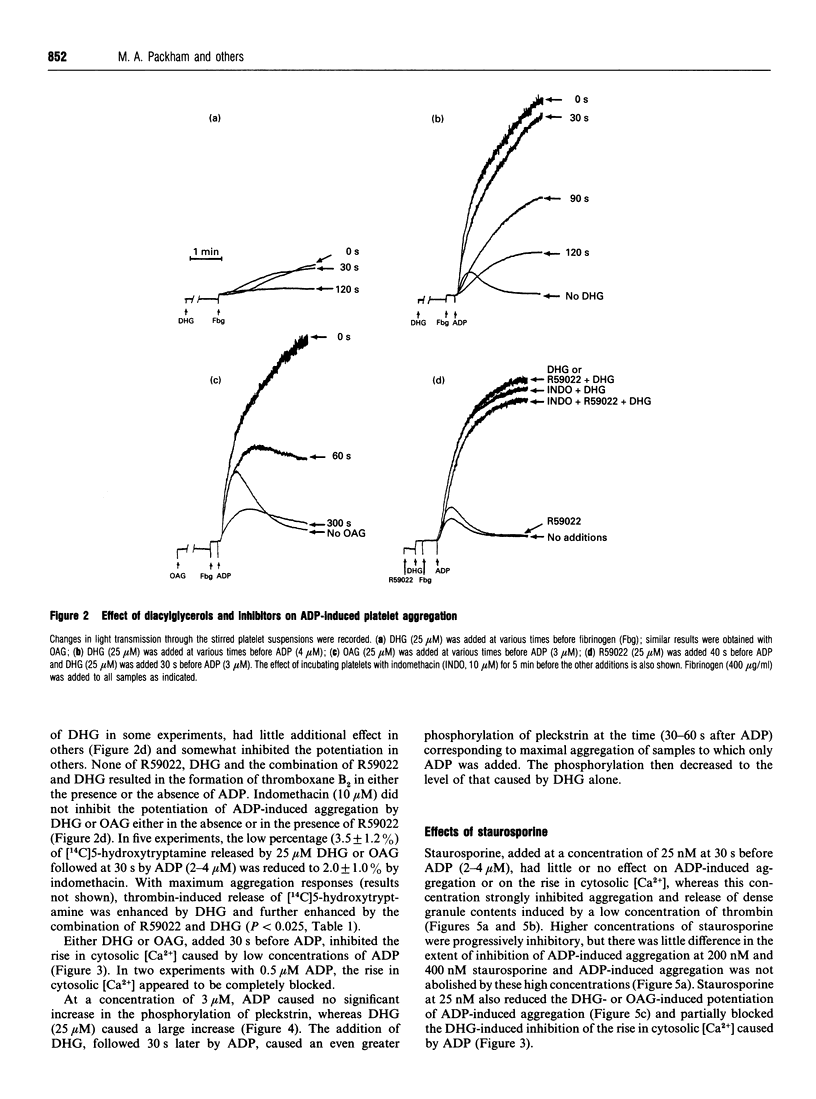
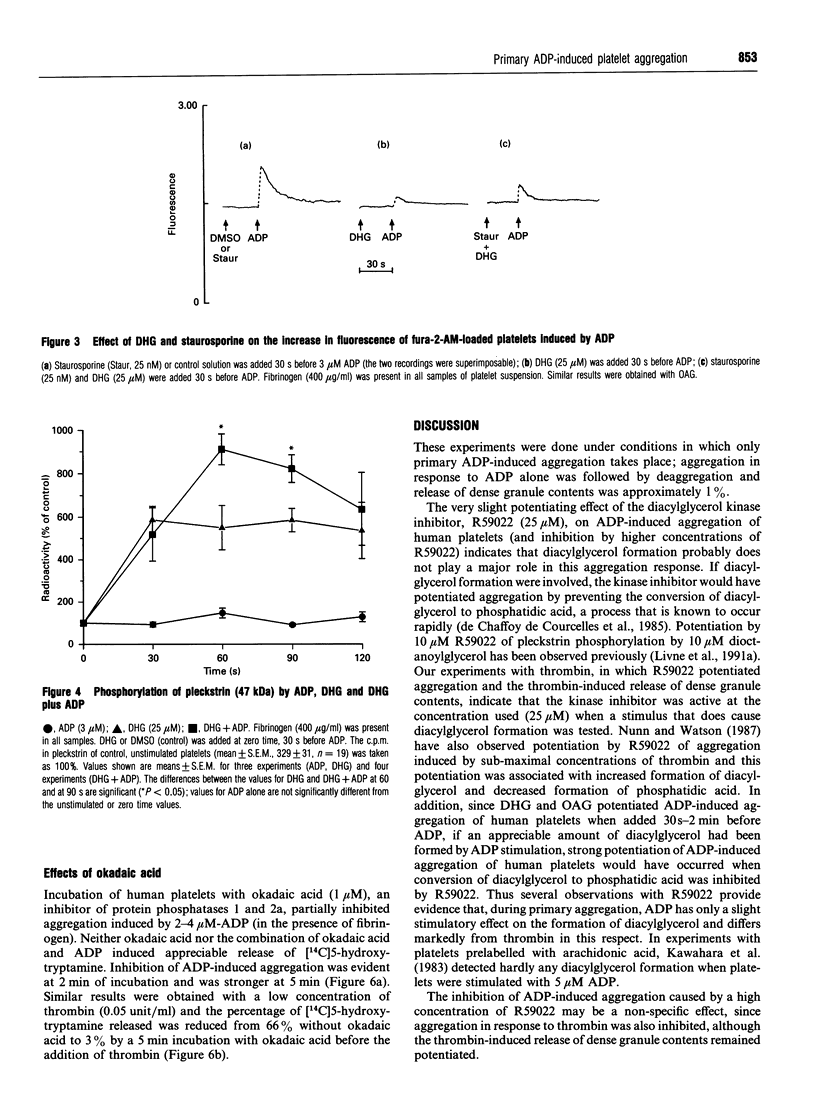
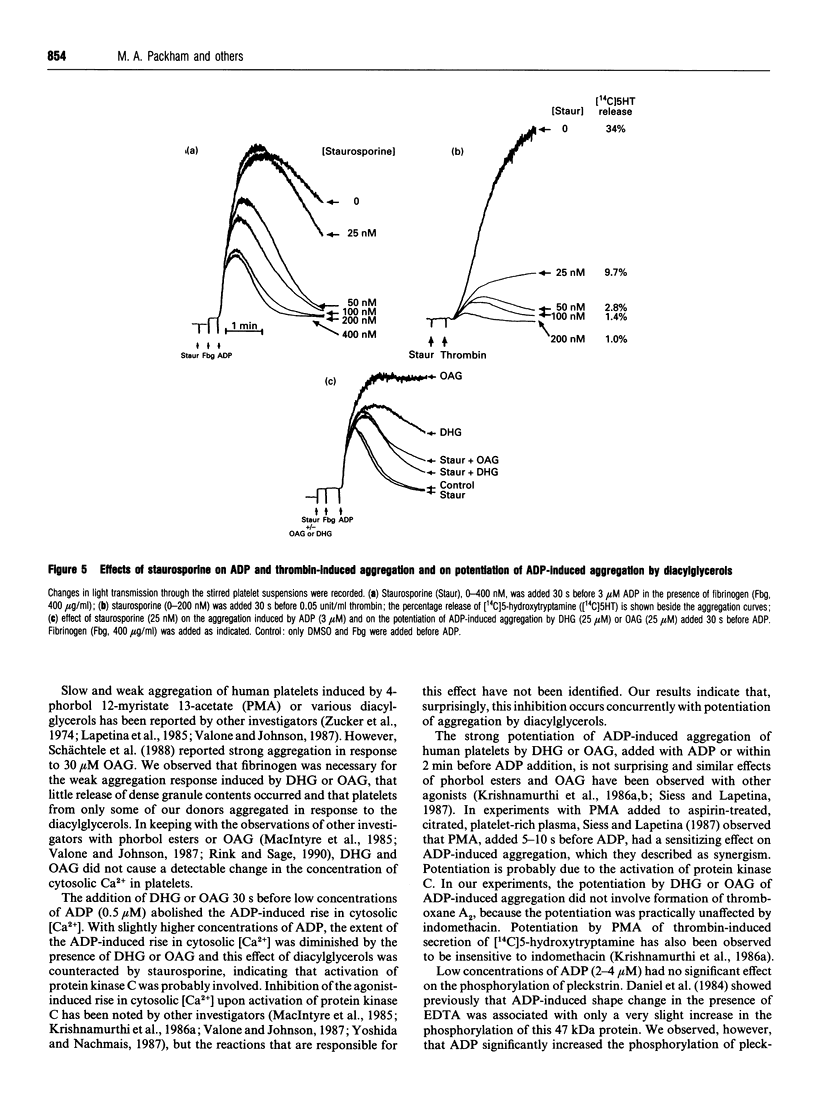
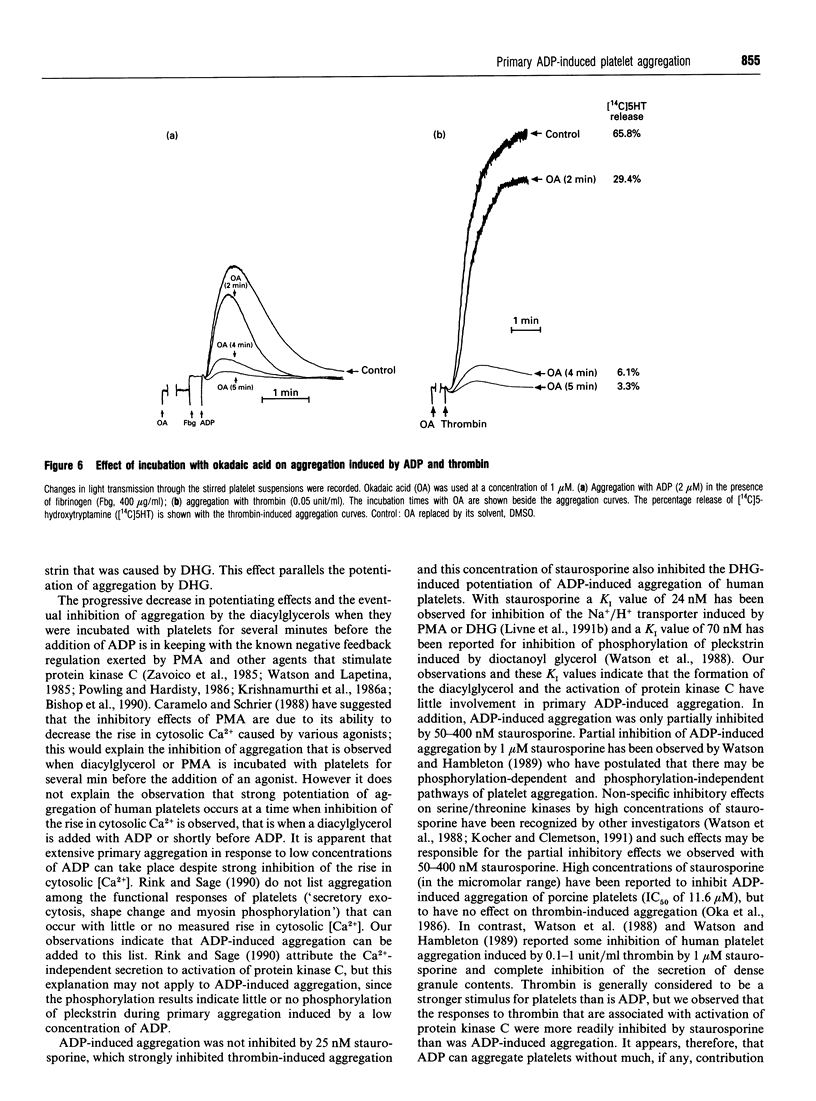

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop W. R., August J., Petrin J. M., Pai J. K. Regulation of sn-1,2-diacylglycerol second-messenger formation in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. Potentiation by protein kinase C inhibitors. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):465–473. doi: 10.1042/bj2690465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caramelo C., Schrier R. W. Platelet activation by phorbol esters. Thromb Res. 1988 Jun 1;50(5):747–748. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90334-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel J. L., Dangelmaier C. A., Selak M., Smith J. B. ADP stimulates IP3 formation in human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 6;206(2):299–303. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81000-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel J. L., Molish I. R., Rigmaiden M., Stewart G. Evidence for a role of myosin phosphorylation in the initiation of the platelet shape change response. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9826–9831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher G. J., Bakshian S., Baldassare J. J. Activation of human platelets by ADP causes a rapid rise in cytosolic free calcium without hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jun 28;129(3):958–964. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91984-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gachet C., Cazenave J. P. ADP induced blood platelet activation: a review. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1991;33(5):347–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J., Packham M. A., Cazenave J. P., Reimers H. J., Mustard J. F. Effects on platelet function of removal of platelet sialic acid by neuraminidase. Lab Invest. 1975 Apr;32(4):476–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Lynham J. A. Relationship between phosphorylation of blood platelet proteins and secretion of platelet granule constituents. I. Effects of different aggregating agents. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 25;77(2):714–722. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haystead T. A., Sim A. T., Carling D., Honnor R. C., Tsukitani Y., Cohen P., Hardie D. G. Effects of the tumour promoter okadaic acid on intracellular protein phosphorylation and metabolism. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):78–81. doi: 10.1038/337078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajikawa N., Kikkawa U., Itoh K., Nishizuka Y. Membrane-permeable diacylglycerol, its application to platelet secretion, and regulation of platelet protein kinase C. Methods Enzymol. 1989;169:430–442. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)69079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara Y., Yamanishi J., Tsunemitsu M., Fukuzaki H. Protein phosphorylation and diglyceride production during serotonin release induced by epinephrine plus ADP in human platelets. Thromb Res. 1983 Jun 1;30(5):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90182-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocher M., Clemetson K. J. Staurosporine both activates and inhibits serine/threonine kinases in human platelets. Biochem J. 1991 Apr 15;275(Pt 2):301–306. doi: 10.1042/bj2750301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthi S., Joseph S. K., Kakkar V. V. Lack of inhibition of thrombin-induced rise in intracellular Ca2+ levels and 5-hydroxytryptamine secretion by 1-oleoyl-2-acetylglycerol in human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1986 Feb 17;196(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80281-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthi S., Joseph S., Kakkar V. V. Synergistic potentiation of 5-hydroxytryptamine secretion by platelet agonists and phorbol myristate acetate despite inhibition of agonist-induced arachidonate/thromboxane and beta-thromboglobulin release and Ca2+ mobilization by phorbol myristate acetate. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 15;238(1):193–199. doi: 10.1042/bj2380193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll M. H., Schafer A. I. Biochemical mechanisms of platelet activation. Blood. 1989 Sep;74(4):1181–1195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Reep B., Ganong B. R., Bell R. M. Exogenous sn-1,2-diacylglycerols containing saturated fatty acids function as bioregulators of protein kinase C in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1358–1361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerea K. M. Thrombin-induced effects are selectively inhibited following treatment of intact human platelets with okadaic acid. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 16;30(28):6819–6824. doi: 10.1021/bi00242a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livne A. A., Aharonovitz O., Fridman H., Tsukitani Y., Markus S. Modulation of Na+/H+ exchange and intracellular pH by protein kinase C and protein phosphatase in blood platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Sep 30;1068(2):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90205-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livne A. A., Sardet C., Pouyssegur J. The Na+/H+ exchanger is phosphorylated in human platelets in response to activating agents. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jun 24;284(2):219–222. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80689-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. M., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Thrombin-induced protein phosphorylation in human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):924–936. doi: 10.1172/JCI108172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLNAR J., LORAND L. Studies on apyrases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 May;93:353–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90278-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre D. E., McNicol A., Drummond A. H. Tumour-promoting phorbol esters inhibit agonist-induced phosphatidate formation and Ca2+ flux in human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 28;180(2):160–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata K., Sakon M., Kambayashi J., Yukawa M., Ariyoshi H., Shiba E., Kawasaki T., Kang J., Mori T. The effects of okadaic acid and calyculin A on thrombin induced platelet reaction. Biochem Int. 1992 Feb;26(2):327–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn D. L., Watson S. P. A diacylglycerol kinase inhibitor, R59022, potentiates secretion by and aggregation of thrombin-stimulated human platelets. Biochem J. 1987 May 1;243(3):809–813. doi: 10.1042/bj2430809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packham M. A., Bryant N. L., Guccione M. A., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Mustard J. F. Effect of the concentration of Ca2+ in the suspending medium on the responses of human and rabbit platelets to aggregating agents. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Nov 24;62(3):968–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packham M. A., Rand M. L., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L. Similarities and differences between rabbit and human platelet characteristics and functions. Comp Biochem Physiol Comp Physiol. 1992 Sep;103(1):35–54. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(92)90239-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock W. K., Rink T. J., Irvine R. F. Liberation of [3H]arachidonic acid and changes in cytosolic free calcium in fura-2-loaded human platelets stimulated by ionomycin and collagen. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):869–877. doi: 10.1042/bj2350869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powling M. J., Hardisty R. M. Differential effects of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate on platelet responses to various agonists in the presence and absence of extracellular Ca2+. Thromb Res. 1986 Oct 15;44(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(86)90134-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Sage S. O. Calcium signaling in human platelets. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:431–449. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.002243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schächtele C., Seifert R., Osswald H. Stimulus-dependent inhibition of platelet aggregation by the protein kinase C inhibitors polymyxin B, H-7 and staurosporine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 29;151(1):542–547. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90628-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Lapetina E. G. Phorbol esters sensitize platelets to activation by physiological agonists. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1373–1381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W. Molecular mechanisms of platelet activation. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jan;69(1):58–178. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweatt J. D., Blair I. A., Cragoe E. J., Limbird L. E. Inhibitors of Na+/H+ exchange block epinephrine- and ADP-induced stimulation of human platelet phospholipase C by blockade of arachidonic acid release at a prior step. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8660–8666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyers M., Haslam R. J., Rachubinski R. A., Harley C. B. Molecular analysis of pleckstrin: the major protein kinase C substrate of platelets. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Jun;40(2):133–145. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240400202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valone F. H., Johnson B. Modulation of platelet-activating-factor-induced calcium influx and intracellular calcium release in platelets by phorbol esters. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 1;247(3):669–674. doi: 10.1042/bj2470669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickers J. D., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Packham M. A., Mustard J. F. Inositol phospholipid metabolism in human platelets stimulated by ADP. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Oct 24;193(2):521–528. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19367.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. R., Watson S. P. Okadaic acid inhibits activation of phospholipase C in human platelets by mimicking the actions of protein kinases A and C. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;105(3):627–631. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09030.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Hambleton S. Phosphorylation-dependent and -independent pathways of platelet aggregation. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 1;258(2):479–485. doi: 10.1042/bj2580479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Lapetina E. G. 1,2-Diacylglycerol and phorbol ester inhibit agonist-induced formation of inositol phosphates in human platelets: possible implications for negative feedback regulation of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2623–2626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., McNally J., Shipman L. J., Godfrey P. P. The action of the protein kinase C inhibitor, staurosporine, on human platelets. Evidence against a regulatory role for protein kinase C in the formation of inositol trisphosphate by thrombin. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 15;249(2):345–350. doi: 10.1042/bj2490345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Nachmias V. T. Phorbol ester stimulates calcium sequestration in saponized human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16048–16054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavoico G. B., Halenda S. P., Sha'afi R. I., Feinstein M. B. Phorbol myristate acetate inhibits thrombin-stimulated Ca2+ mobilization and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis in human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3859–3862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Troll W., Belman S. The tumor-promoter phorbol ester (12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate), a potent aggregating agent for blood platelets. J Cell Biol. 1974 Feb;60(2):325–336. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Chaffoy de Courcelles D. C., Roevens P., Van Belle H. R 59 022, a diacylglycerol kinase inhibitor. Its effect on diacylglycerol and thrombin-induced C kinase activation in the intact platelet. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15762–15770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


