Abstract
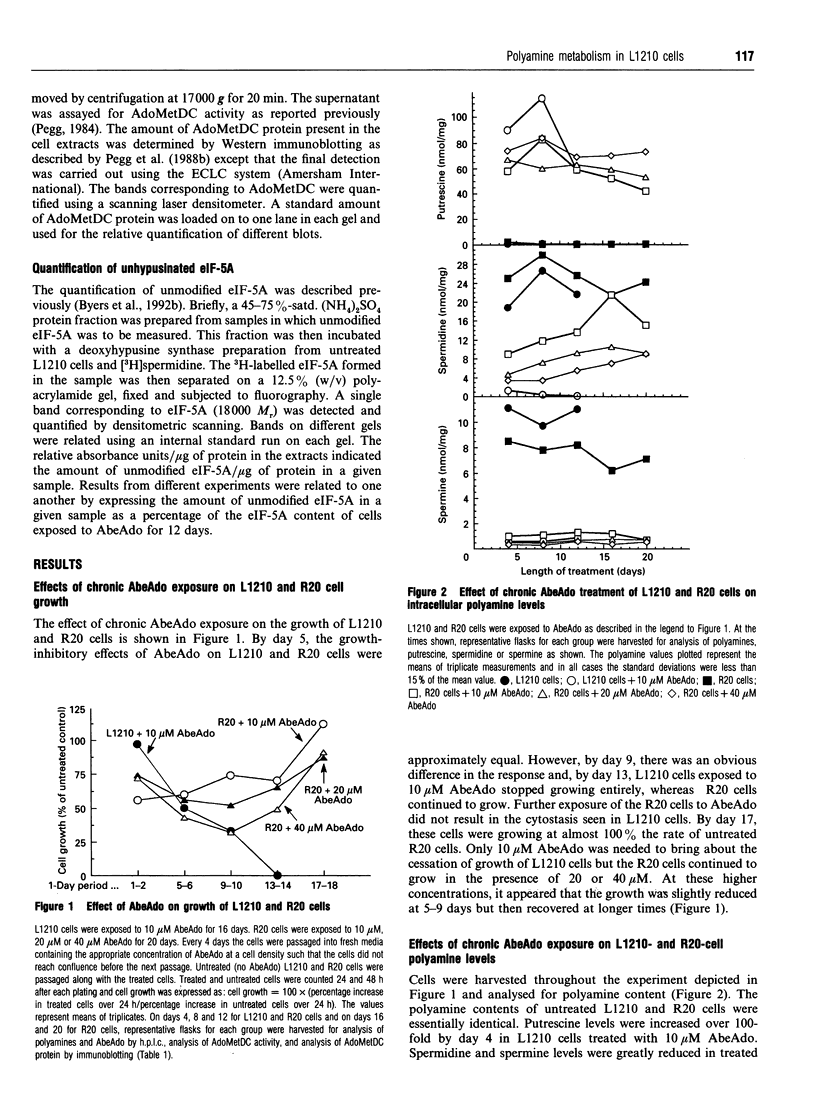
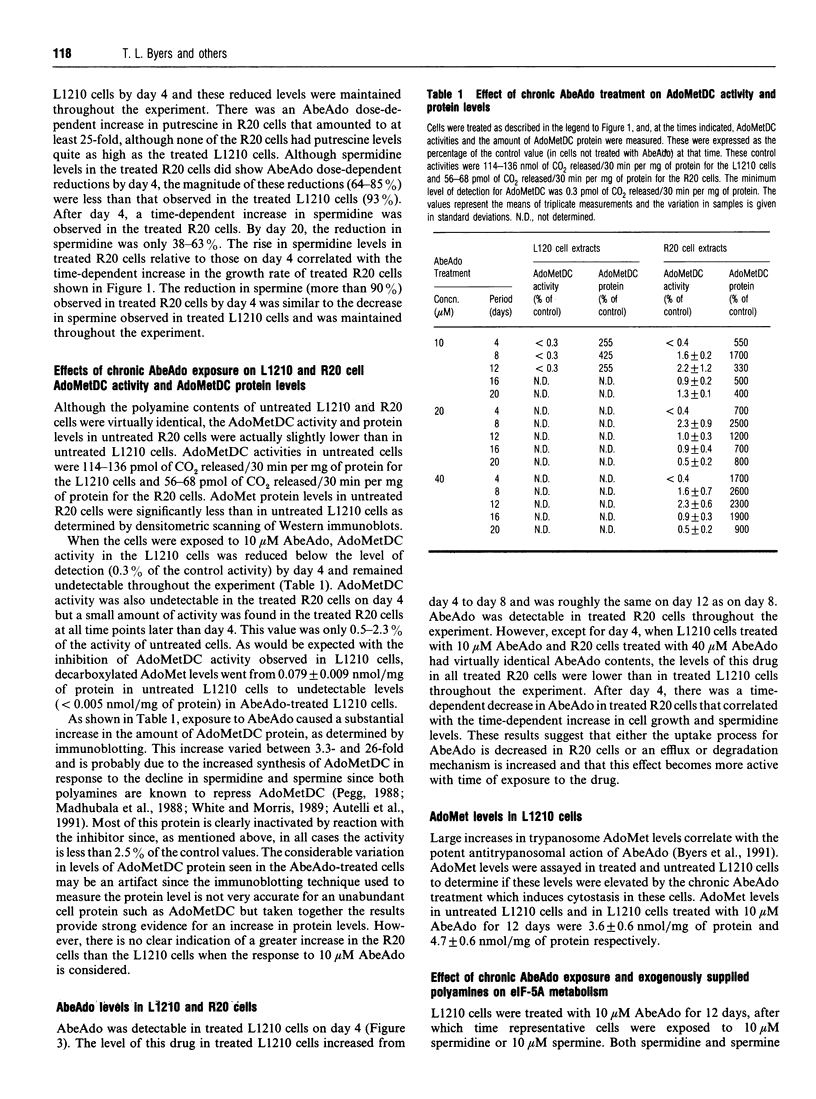
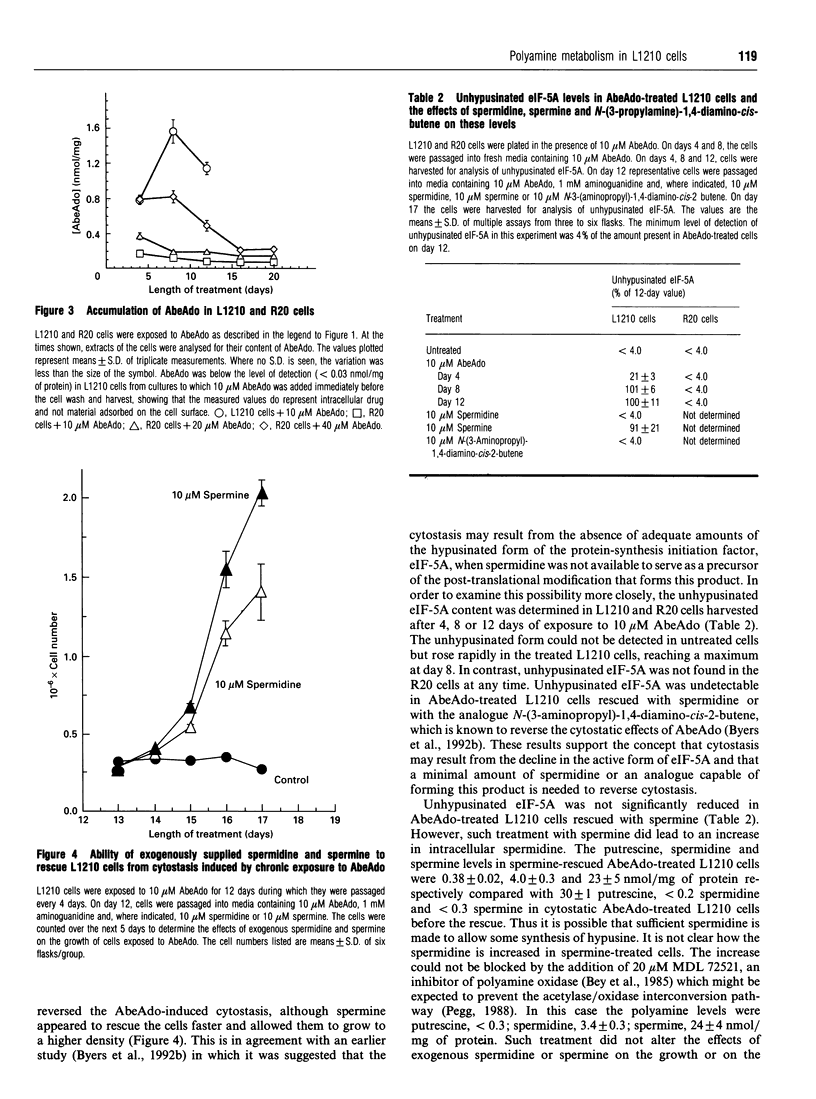
We have previously reported that prolonged chronic exposure to the S-adenosyl-L-methionine decarboxylase (AdoMetDC) inhibitor, 5'-([(Z)-4-amino-2-butenyl]methylamino)-5'-deoxy-adenosine (MDL 73811, AbeAdo), leads to cytostasis of L1210 cells [Byers, Ganem and Pegg (1992) Biochem. J. 287, 717-724]. Further studies to investigate the mechanism by which these effects are brought about were carried out by comparing an L1210-derived cell line (R20) that is resistant to AbeAdo with the parent cells. The R20 cells were derived by two rounds of AbeAdo-induced cytostasis followed by rescue with exogenous polyamines. Cytostasis was induced in L1210 cells treated for 12 days with 10 microM AbeAdo; however, exposure to up to 40 microM AbeAdo did not induce cytostasis in R20 cells. Putrescine levels were elevated and spermine levels were depleted in both treated L1210 and treated R20 cells. Spermidine was depleted in treated L1210 cells but was only partly reduced in treated R20 cells. AdoMetDC activity was below the limit of detection in treated L1210 cells but, although greatly reduced, could be measured in the treated R20 cells. The resistance of the R20 cells to the effects of AbeAdo on cell growth and spermidine depletion correlated with reduced AbeAdo accumulation by R20 cells. In the absence of spermidine synthesis, unhypusinated eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (eIF-5A) accumulated in AbeAdo-treated L1210 cells. There was no detectable accumulation of unhypusinated eIF-5A in R20 cells. Unhypusinated eIF-5A accumulated during AbeAdo treatment was depleted in L1210 cells rescued by exogenous spermidine. These findings are consistent with the hypothesis that AbeAdo-induced cytostasis is due to the loss of hypusinated eIF-5A. However, spermine was able to rescue AbeAdo-treated L1210 cells without significantly reducing the unhypusinated eIF-5A accumulated during AbeAdo treatment, suggesting that only a small amount of the unmodified protein must be hypusinated to restore cell growth.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Autelli R., Stjernborg L., Khomutov A. R., Khomutov R. M., Persson L. Regulation of S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase in L1210 leukemia cells. Studies using an irreversible inhibitor of the enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Mar 28;196(3):551–556. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck W. T. The cell biology of multiple drug resistance. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Sep 15;36(18):2879–2887. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bey P., Bolkenius F. N., Seiler N., Casara P. N-2,3-Butadienyl-1,4-butanediamine derivatives: potent irreversible inactivators of mammalian polyamine oxidase. J Med Chem. 1985 Jan;28(1):1–2. doi: 10.1021/jm00379a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitonti A. J., Byers T. L., Bush T. L., Casara P. J., Bacchi C. J., Clarkson A. B., Jr, McCann P. P., Sjoerdsma A. Cure of Trypanosoma brucei brucei and Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense infections in mice with an irreversible inhibitor of S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Aug;34(8):1485–1490. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.8.1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers T. L., Bush T. L., McCann P. P., Bitonti A. J. Antitrypanosomal effects of polyamine biosynthesis inhibitors correlate with increases in Trypanosoma brucei brucei S-adenosyl-L-methionine. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 1;274(Pt 2):527–533. doi: 10.1042/bj2740527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers T. L., Ganem B., Pegg A. E. Cytostasis induced in L1210 murine leukaemia cells by the S-adenosyl-L-methionine decarboxylase inhibitor 5'-([(Z)-4-amino-2-butenyl]methylamino)-5'-deoxyadenosine may be due to hypusine depletion. Biochem J. 1992 Nov 1;287(Pt 3):717–724. doi: 10.1042/bj2870717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers T. L., Pegg A. E. Properties and physiological function of the polyamine transport system. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 1):C545–C553. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.3.C545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer D. L., Khomutov R. M., Bukin Y. V., Khomutov A. R., Porter C. W. Cellular characterization of a new irreversible inhibitor of S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase and its use in determining the relative abilities of individual polyamines to sustain growth and viability of L1210 cells. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 15;259(2):325–331. doi: 10.1042/bj2590325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhubala R., Secrist J. A., 3rd, Pegg A. E. Effect of inhibitors of S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase on the contents of ornithine decarboxylase and S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase in L1210 cells. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 15;254(1):45–50. doi: 10.1042/bj2540045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamont P. S., Duchesne M. C., Grove J., Bey P. Anti-proliferative properties of DL-alpha-difluoromethyl ornithine in cultured cells. A consequence of the irreversible inhibition of ornithine decarboxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Mar 15;81(1):58–66. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91630-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M. H., Cooper H. L., Folk J. E. Identification of hypusine, an unusual amino acid, in a protein from human lymphocytes and of spermidine as its biosynthetic precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2869–2873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M. H. The essential role of hypusine in eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4D (eIF-4D). Purification of eIF-4D and its precursors and comparison of their activities. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18531–18535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M. H. The identification of an eukaryotic initiation factor 4D precursor in spermidine-depleted Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7447–7449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M. H., Wolff E. C., Abbruzzese A., Folk J. E. Biosynthesis of hypusine in eIF-4D precursors. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1988;250:435–447. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5637-0_38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegg A. E., Coward J. K. Growth of mammalian cells in the absence of the accumulation of spermine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Nov 27;133(1):82–89. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91844-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegg A. E., Jones D. B., Secrist J. A., 3rd Effect of inhibitors of S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase on polyamine content and growth of L1210 cells. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 8;27(5):1408–1415. doi: 10.1021/bi00405a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegg A. E., McCann P. P. Polyamine metabolism and function. Am J Physiol. 1982 Nov;243(5):C212–C221. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.243.5.C212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegg A. E. Polyamine metabolism and its importance in neoplastic growth and a target for chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 1988 Feb 15;48(4):759–774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegg A. E., Tang K. C., Coward J. K. Effects of S-adenosyl-1,8-diamino-3-thiooctane on polyamine metabolism. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 28;21(20):5082–5089. doi: 10.1021/bi00263a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegg A. E. The role of polyamine depletion and accumulation of decarboxylated S-adenosylmethionine in the inhibition of growth of SV-3T3 cells treated with alpha-difluoromethylornithine. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 15;224(1):29–38. doi: 10.1042/bj2240029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegg A. E., Wiest L., Pajunen A. Detection of proenzyme form of S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase in extracts from rat prostate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 29;150(2):788–793. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90460-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohjanpelto P., Hölttä E., Jänne O. A. Mutant strain of Chinese hamster ovary cells with no detectable ornithine decarboxylase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1385–1390. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohjanpelto P., Virtanen I., Hölttä E. Polyamine starvation causes disappearance of actin filaments and microtubules in polyamine-auxotrophic CHO cells. Nature. 1981 Oct 8;293(5832):475–477. doi: 10.1038/293475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter C. W., Bergeron R. J. Spermidine requirement for cell proliferation in eukaryotic cells: structural specificity and quantitation. Science. 1983 Mar 4;219(4588):1083–1085. doi: 10.1126/science.6823570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnier J., Schwelberger H. G., Smit-McBride Z., Kang H. A., Hershey J. W. Translation initiation factor 5A and its hypusine modification are essential for cell viability in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3105–3114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit-McBride Z., Dever T. E., Hershey J. W., Merrick W. C. Sequence determination and cDNA cloning of eukaryotic initiation factor 4D, the hypusine-containing protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1578–1583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steglich C., Scheffler I. E. An ornithine decarboxylase-deficient mutant of Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4603–4609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff E. C., Park M. H., Folk J. E. Cleavage of spermidine as the first step in deoxyhypusine synthesis. The role of NAD. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):4793–4799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



