Abstract
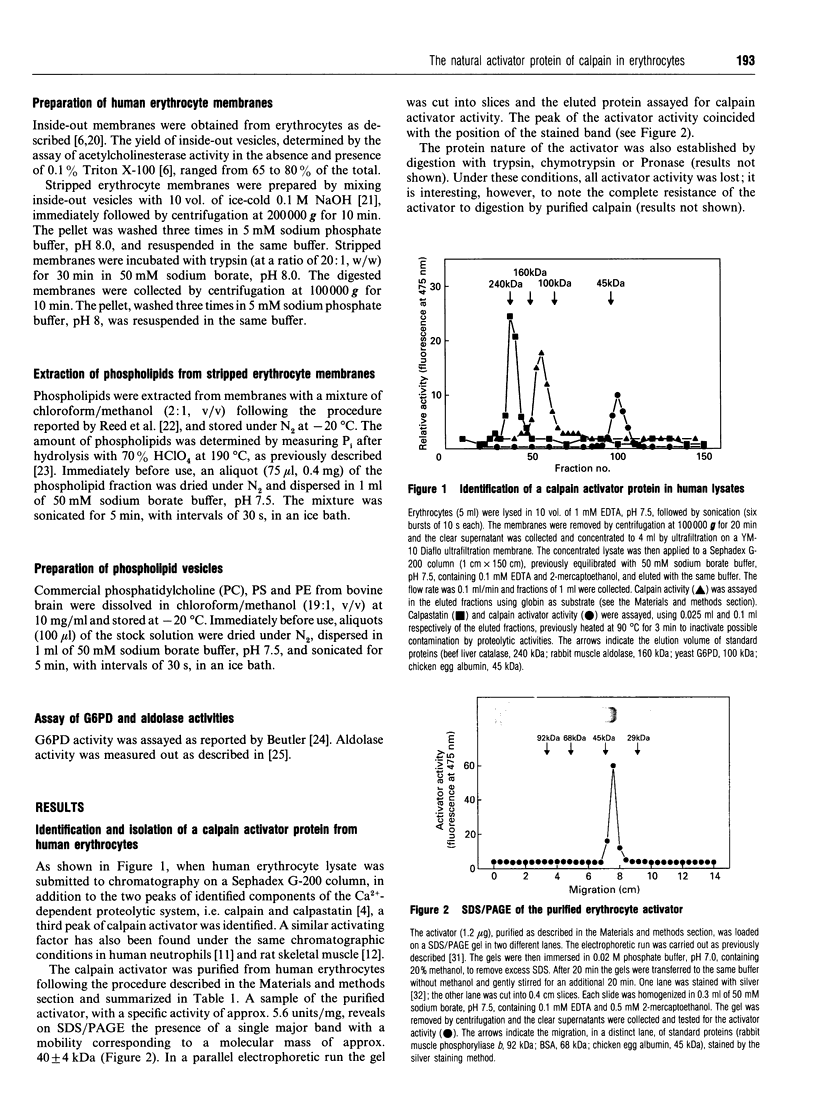
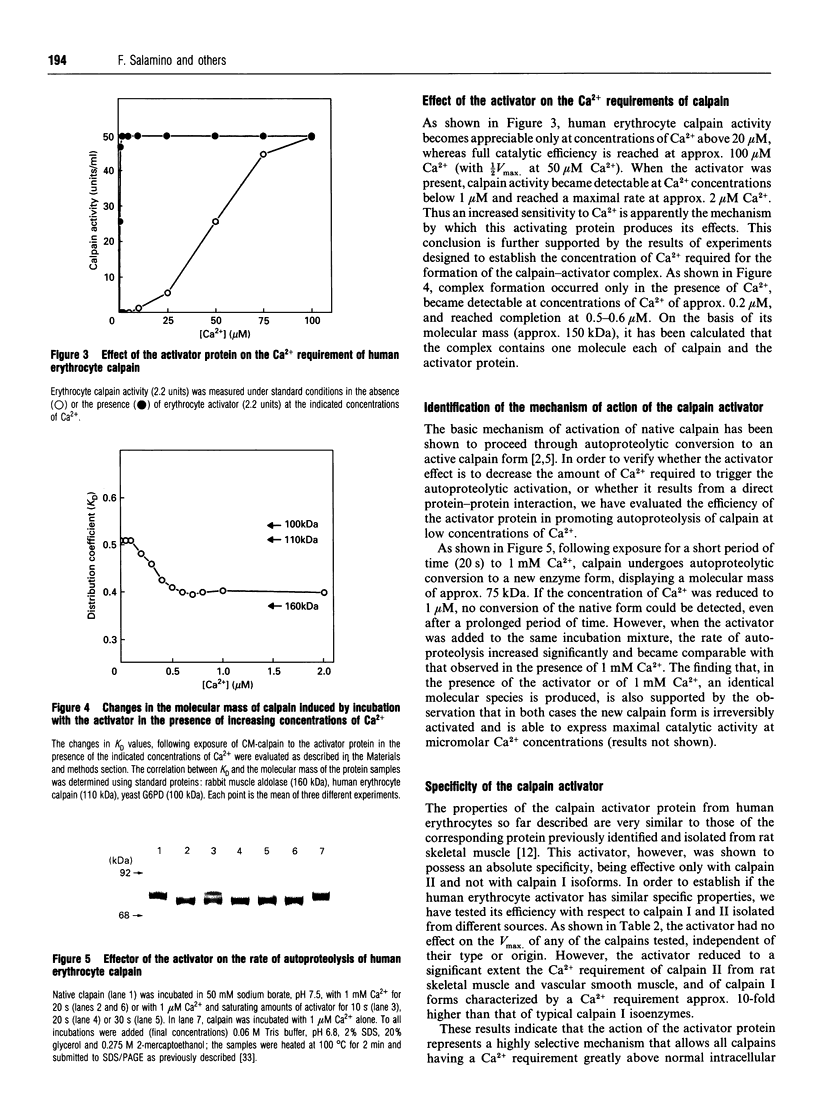
Human erythrocytes contain a calpain activator protein with a molecular mass of approx. 40 kDa. The activator is present in association with the plasma membrane and promotes expression of calpain activity at a concentration of Ca2+ close to physiological values. The initial step of the activating mechanism involves association of the activator with calpain, followed by autoproteolytic activation of the proteinase in the presence of 1 microM Ca2+, at a rate identical to that induced by 1 mM Ca2+. In a reconstituted system, the activator binds to erythrocyte membranes, but not to phospholipid vesicles, suggesting the participation of an intrinsic membrane protein(s). In its membrane-associated form the activator selectively binds calpain, thus favouring interaction of the proteinase with the inner surface of plasma membranes. These results further confirm the importance of a natural activator protein in promoting intracellular activation of calpain under physiological conditions through a site-directed mechanism, which explains the high specificity of the proteinase for membrane of cytoskeletal proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACKERS G. K. MOLECULAR EXCLUSION AND RESTRICTED DIFFUSION PROCESSES IN MOLECULAR-SIEVE CHROMATOGRAPHY. Biochemistry. 1964 May;3:723–730. doi: 10.1021/bi00893a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croall D. E., DeMartino G. N. Calcium-activated neutral protease (calpain) system: structure, function, and regulation. Physiol Rev. 1991 Jul;71(3):813–847. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.3.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMartino G. N., Blumenthal D. K. Identification and partial purification of a factor that stimulates calcium-dependent proteases. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 31;21(18):4297–4303. doi: 10.1021/bi00261a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(5):463–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb M., Chavko M. Silver staining of native and denatured eucaryotic DNA in agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1987 Aug 15;165(1):33–37. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melloni E., Pontremoli S., Salamino F., Sparatore B., Michetti M., Horecker B. L. Characterization of three rabbit liver lysosomal proteinases with fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase converting enzyme activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Apr 15;208(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melloni E., Pontremoli S. The calpains. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Nov;12(11):438–444. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melloni E., Salamino F., Sparatore B., Michetti M., Pontremoli S. Ca2+-dependent neutral proteinase from human erythrocytes: activation by Ca2+ ions and substrate and regulation by the endogenous inhibitor. Biochem Int. 1984 Apr;8(4):477–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melloni E., Salamino F., Sparatore B. The calpain-calpastatin system in mammalian cells: properties and possible functions. Biochimie. 1992 Mar;74(3):217–223. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(92)90120-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melloni E., Sparatore B., Salamino F., Michetti M., Pontremoli S. Cytosolic calcium dependent neutral proteinase of human erythrocytes: the role of calcium ions on the molecular and catalytic properties of the enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):1053–1059. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90628-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michetti M., Viotti P. L., Melloni E., Pontremoli S. Mechanism of action of the calpain activator protein in rat skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 18;202(3):1177–1180. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murachi T. Intracellular regulatory system involving calpain and calpastatin. Biochem Int. 1989 Feb;18(2):263–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontremoli S., Melloni E., Michetti M., Salamino F., Sparatore B., Horecker B. L. An endogenous activator of the Ca2+-dependent proteinase of human neutrophils that increases its affinity for Ca2+. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1740–1743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontremoli S., Melloni E., Salamino F., Sparatore B., Michetti M., Benatti U., Morelli A., De Flora A. Identification of proteolytic activities in the cytosolic compartment of mature human erythrocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Sep;110(2):421–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontremoli S., Melloni E., Sparatore B., Salamino F., Michetti M., Sacco O., Horecker B. L. Binding to erythrocyte membrane is the physiological mechanism for activation of Ca2+-dependent neutral proteinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 16;128(1):331–338. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91683-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontremoli S., Melloni E., Viotti P. L., Michetti M., Di Lisa F., Siliprandi N. Isovalerylcarnitine is a specific activator of the high calcium requiring calpain forms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Feb 28;167(1):373–380. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91775-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontremoli S., Salamino F., Sparatore B., Michetti M., Sacco O., Melloni E. Following association to the membrane, human erythrocyte procalpain is converted and released as fully active calpain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Oct 18;831(3):335–339. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90116-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontremoli S., Viotti P. L., Michetti M., Sparatore B., Salamino F., Melloni E. Identification of an endogenous activator of calpain in rat skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 14;171(2):569–574. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91184-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REED C. F., SWISHER S. N., MARINETTI G. V., ENEN E. G. Studies of the lipids of the erythrocyte. I. Quantitative analysis of the lipids of normal human red blood cells. J Lab Clin Med. 1960 Aug;56:281–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiba E., Ariyoshi H., Yano Y., Kawasaki T., Sakon M., Kambayashi J., Mori T. Purification and characterization of a calpain activator from human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jan 31;182(2):461–465. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91754-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Kant J. A. Preparation of impermeable ghosts and inside-out vesicles from human erythrocyte membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:172–180. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Ramos B., Strapazon E. Proteolytic dissection of band 3, the predominant transmembrane polypeptide of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 9;15(5):1153–1161. doi: 10.1021/bi00650a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeyama Y., Nakanishi H., Uratsuji Y., Kishimoto A., Nishizuka Y. A calcium-protease activator associated with brain microsomal-insoluble elements. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 1;194(1):110–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80060-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINTERHALTER K. H., HUEHNS E. R. PREPARATIONS, PROPERTIES, AND SPECIFIC RECOMBINATION OF ALPHA-BETA-GLOBIN SUBUNITS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3699–3705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




