Abstract
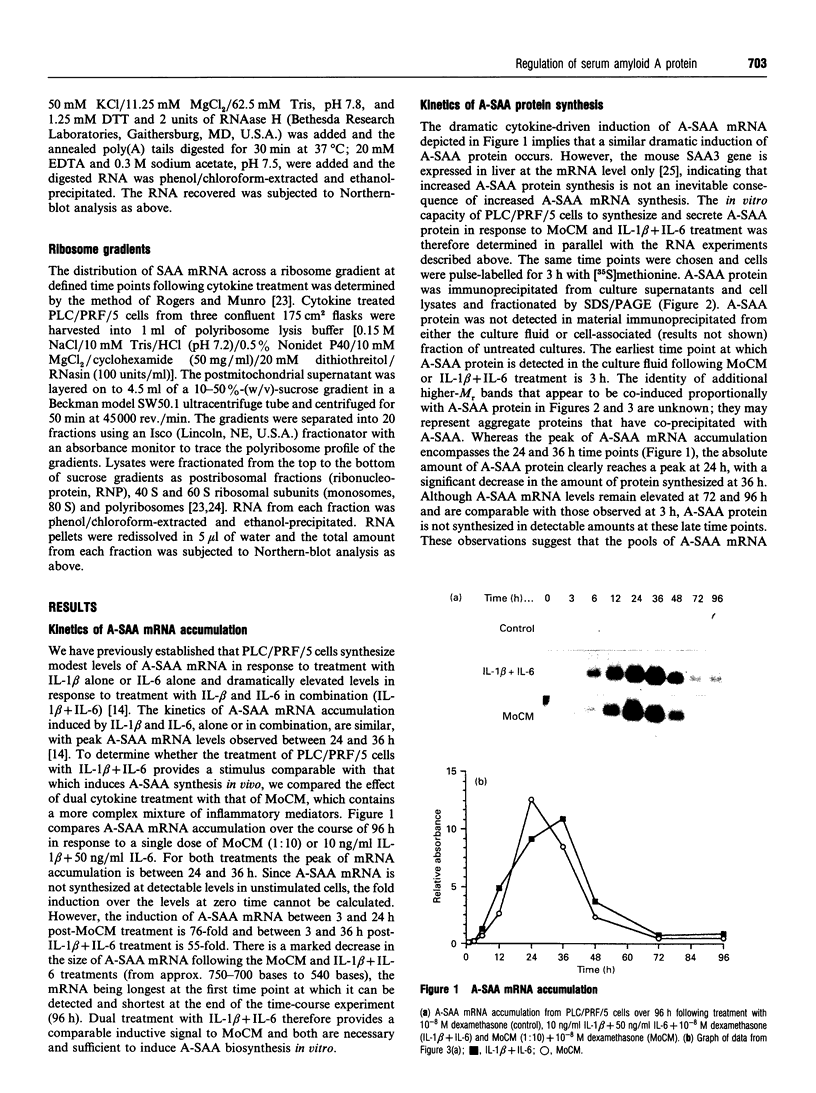
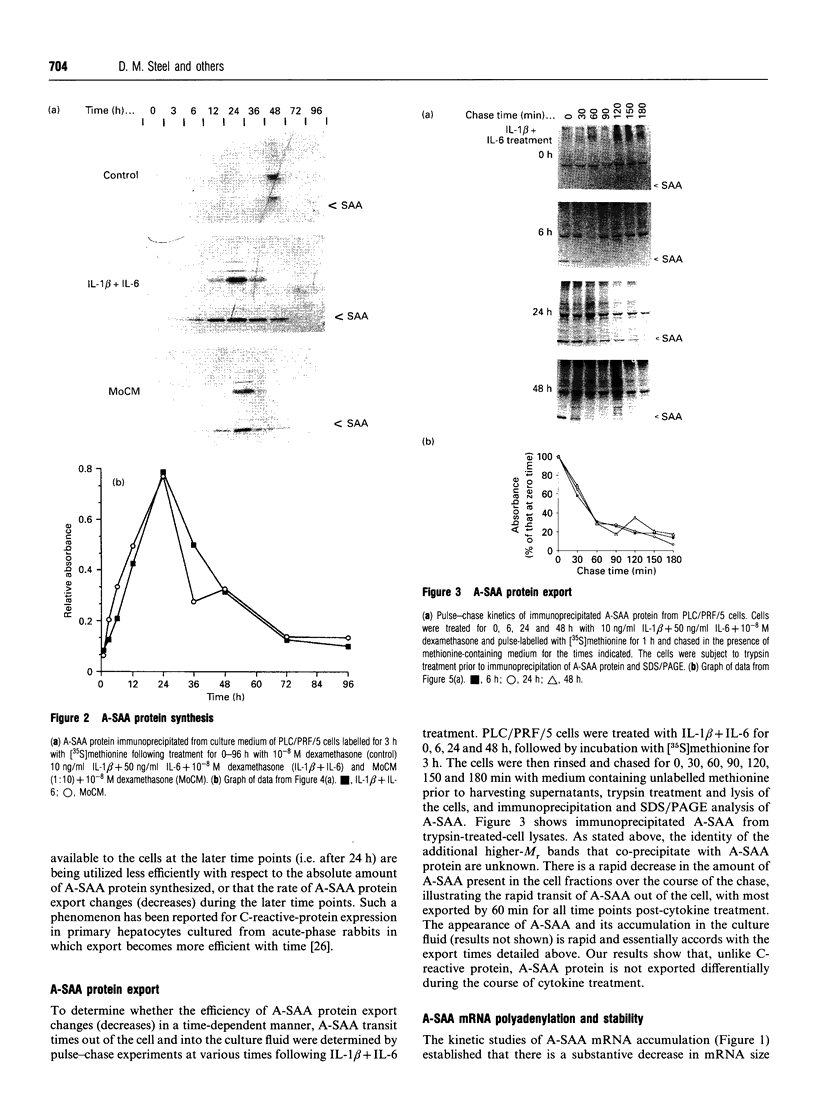
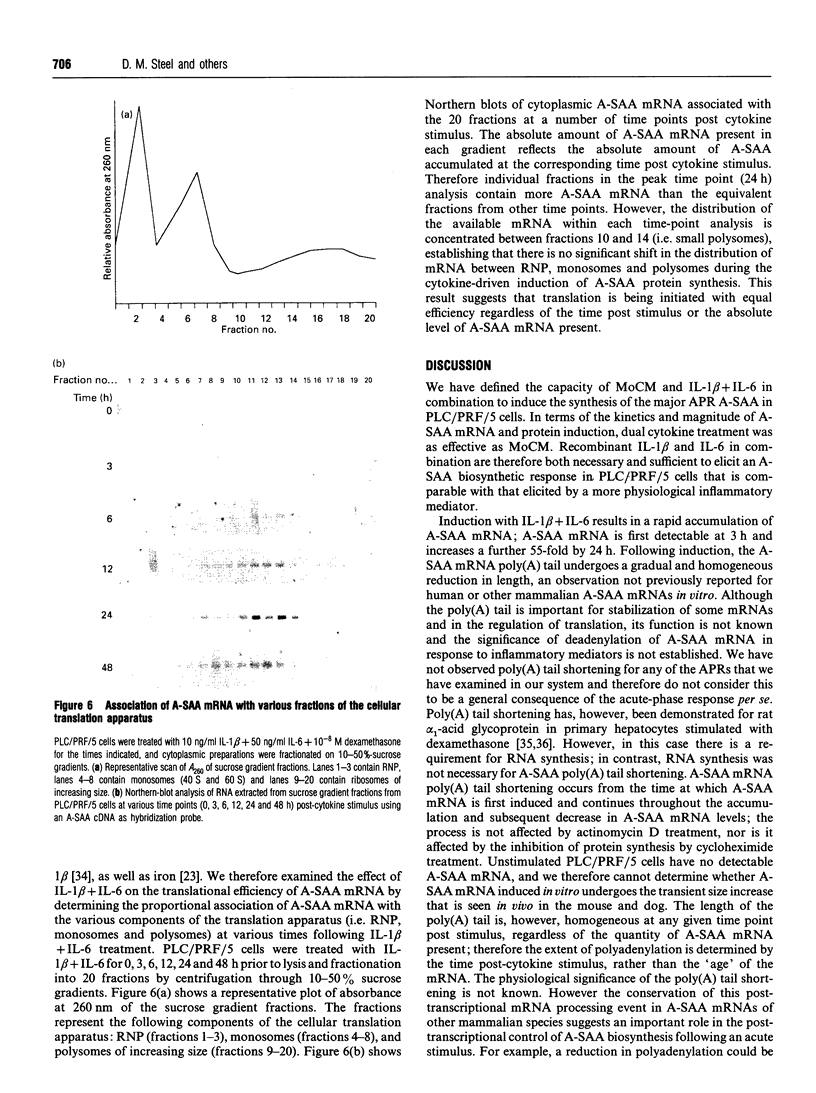
Human 'acute-phase' serum amyloid A protein (A-SAA) is a major acute-phase reactant (APR) and an apolipoprotein of high density lipoprotein 3 (HDL3). We have examined several parameters of A-SAA biosynthesis in PLC/PRF/5 hepatoma cells in response to monocyte conditioned medium (MoCM) and dual treatment with interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-6 (IL-1 beta + IL-6). Treatment of PLC/PRF/5 cells with MoCM or IL-1 beta + IL-6 caused a dramatic and rapid increase in A-SAA mRNA and protein synthesis; A-SAA mRNA was first detectable at 3 h, with peak levels reached by 24 h. A-SAA mRNA accumulation is accompanied by a gradual and homogeneous decrease in the length of the A-SAA poly(A) tail; the poly(A) tail shortening does not apparently affect the intrinsic stability of A-SAA mRNA. Analysis of RNA isolated from the ribonucleoprotein, monosome and polysome fractions of cytokine-treated PLC/PRF/5 cells showed that most A-SAA mRNA was associated with small polyribosomes, regardless of time post-stimulus, suggesting that the translational efficiency of A-SAA mRNA is constant throughout cytokine-driven induction. Moreover, the transit time of A-SAA protein out of the cell is also constant throughout the time course of induction. These data provide evidence of a paradox with regard to the transcriptional upregulation of A-SAA by IL-1 beta + IL-6 and the relative synthesis of A-SAA protein and suggest a role for post-transcriptional control of A-SAA biosynthesis during the acute phase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aziz N., Munro H. N. Both subunits of rat liver ferritin are regulated at a translational level by iron induction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):915–927. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballinger D. G., Pardue M. L. The control of protein synthesis during heat shock in Drosophila cells involves altered polypeptide elongation rates. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90339-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brissette L., Young I., Narindrasorasak S., Kisilevsky R., Deeley R. Differential induction of the serum amyloid A gene family in response to an inflammatory agent and to amyloid-enhancing factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19327–19332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock M. L., Shapiro D. J. Estrogen stabilizes vitellogenin mRNA against cytoplasmic degradation. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):207–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrazana E. J., Pasieka K. B., Majzoub J. A. The vasopressin mRNA poly(A) tract is unusually long and increases during stimulation of vasopressin gene expression in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2267–2274. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter K. C., Bryan S., Gadson P., Papaconstantinou J. Deadenylation of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein mRNA in cultured hepatic cells during stimulation by dexamethasone. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):4112–4119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell J. V., Gómez-Lechón M. J., David M., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Heinrich P. C. Recombinant human interleukin-6 (IL-6/BSF-2/HSF) regulates the synthesis of acute phase proteins in human hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 23;232(2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80766-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edbrooke M. R., Burt D. W., Cheshire J. K., Woo P. Identification of cis-acting sequences responsible for phorbol ester induction of human serum amyloid A gene expression via a nuclear factor kappaB-like transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1908–1916. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksen N., Benditt E. P. Isolation and characterization of the amyloid-related apoprotein (SAA) from human high density lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6860–6864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathi M. K., May L. T., Schultz D., Brabenec A., Weinstein J., Sehgal P. B., Kushner I. Role of interleukin-6 in regulating synthesis of C-reactive protein and serum amyloid A in human hepatoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):271–277. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyette W. A., Matusik R. J., Rosen J. M. Prolactin-mediated transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of casein gene expression. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):1013–1023. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husebekk A., Skogen B., Husby G., Marhaug G. Transformation of amyloid precursor SAA to protein AA and incorporation in amyloid fibrils in vivo. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Mar;21(3):283–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluve-Beckerman B., Long G. L., Benson M. D. DNA sequence evidence for polymorphic forms of human serum amyloid A (SAA). Biochem Genet. 1986 Dec;24(11-12):795–803. doi: 10.1007/BF00554519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird-Offringa I. A., de Wit C. L., Elfferich P., van der Eb A. J. Poly(A) tail shortening is the translation-dependent step in c-myc mRNA degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6132–6140. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macintyre S. S., Kushner I., Samols D. Secretion of C-reactive protein becomes more efficient during the course of the acute phase response. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4169–4173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marhaug G., Sletten K., Husby G. Characterization of amyloid related protein SAA complexed with serum lipoproteins (apoSAA). Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Nov;50(2):382–389. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAdam K. P., Li J., Knowles J., Foss N. T., Dinarello C. A., Rosenwasser L. J., Selinger M. J., Kaplan M. M., Goodman R., Herbert P. N. The biology of SAA: identification of the inducer, in vitro synthesis, and heterogeneity demonstrated with monoclonal antibodies. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:126–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltz S. W., Brewer G., Bernstein P., Hart P. A., Ross J. Regulation of mRNA turnover in eukaryotic cells. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1991;1(2):99–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. T., Bridges K. R., Durmowicz G. P., Glass J., Auron P. E., Munro H. N. Translational control during the acute phase response. Ferritin synthesis in response to interleukin-1. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14572–14578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Munro H. Translation of ferritin light and heavy subunit mRNAs is regulated by intracellular chelatable iron levels in rat hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2277–2281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Davis R. W. The poly(A) binding protein is required for poly(A) shortening and 60S ribosomal subunit-dependent translation initiation. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):857–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90938-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack G. H., Jr, Talbot C. C., Jr The human serum amyloid A (SAA)-encoding gene GSAA1: nucleotide sequence and possible autocrine-collagenase-inducer function. Gene. 1989 Dec 14;84(2):509–515. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90528-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellar G. C., DeBeer M. C., Lelias J. M., Snyder P. W., Glickman L. T., Felsburg P. J., Whitehead A. S. Dog serum amyloid A protein. Identification of multiple isoforms defined by cDNA and protein analyses. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3505–3510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiels B. R., Northemann W., Gehring M. R., Fey G. H. Modified nuclear processing of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein RNA during inflammation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12826–12831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra F., Lichtler A., Marashi F., Rickles R., Van Dyke T., Clark S., Wells J., Stein G., Stein J. Organization of human histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1795–1799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipe J. D., Colten H. R., Goldberger G., Edge M. D., Tack B. F., Cohen A. S., Whitehead A. S. Human serum amyloid A (SAA): biosynthesis and postsynthetic processing of preSAA and structural variants defined by complementary DNA. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 4;24(12):2931–2936. doi: 10.1021/bi00333a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearman R. S., Lowell C. A., Peltzman C. G., Morrow J. F. The sequence and structure of a new serum amyloid A gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):797–809. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel D. M., Whitehead A. S. Heterogeneous modulation of acute-phase-reactant mRNA levels by interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-6 in the human hepatoma cell line PLC/PRF/5. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 15;277(Pt 2):477–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2770477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinkasserer A., Weiss E. H., Schwaeble W., Linke R. P. Heterogeneity of human serum amyloid A protein. Five different variants from one individual demonstrated by cDNA sequence analysis. Biochem J. 1990 May 15;268(1):187–193. doi: 10.1042/bj2680187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimac E., Groppi V. E., Jr, Coffino P. Inhibition of protein synthesis stabilizes histone mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2082–2090. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead A. S., de Beer M. C., Steel D. M., Rits M., Lelias J. M., Lane W. S., de Beer F. C. Identification of novel members of the serum amyloid A protein superfamily as constitutive apolipoproteins of high density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3862–3867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Treisman R. Removal of poly(A) and consequent degradation of c-fos mRNA facilitated by 3' AU-rich sequences. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):396–399. doi: 10.1038/336396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo P., Sipe J., Dinarello C. A., Colten H. R. Structure of a human serum amyloid A gene and modulation of its expression in transfected L cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15790–15795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahedi K., Whitehead A. S. Acute phase induction of mouse serum amyloid P component. Correlation with other parameters of inflammation. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):2880–2886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









