Abstract
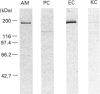
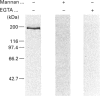
Upon intravenous injection into rats, the plant toxin ricin was rapidly cleared from the circulation by the liver. Among the different liver cell populations, most of the injected ricin associated with the sinusoidal endothelial cells (EC), whereas the liver parenchymal cells (PC) and Kupffer cells (KC) yielded minor contributions to the total liver uptake in vivo. Co-injection of mannan strongly inhibited ricin uptake by the EC, showing that it was mediated by mannose receptors. On the other hand, co-injection of lactose, which inhibits the galactose-specific association of ricin with cells, enhanced ricin uptake by the EC. The carbohydrate-dependency of the EC contribution to the uptake of ricin in vivo was reflected in the carbohydrate-dependency of the uptake in vivo by whole liver. In vitro, the EC also endocytosed ricin more efficiently than did the PC or KC. Whereas uptake in vitro in the EC was mainly mannose-specific, uptake in the two other cell types was mainly galactose-specific. Western blotting showed that the mannose receptors of liver non-parenchymal cells are identical with the mannose receptor previously isolated from alveolar macrophages. The mannose receptors are expressed at a higher level in EC than in KC. Ligand blotting showed that, in the presence of lactose, the mannose receptor is the only protein in the EC that binds ricin, and the binding is mannose-specific and Ca(2+)-dependent.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baenziger J. U., Fiete D. Structural determinants of Ricinus communis agglutinin and toxin specificity for oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9795–9799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingen A., Creppy E. E., Gut J. P., Dirheimer G., Kirn A. The Kupffer cell is the first target in ricin-induced hepatitis. J Submicrosc Cytol. 1987 Apr;19(2):247–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakey D. C., Skilleter D. N., Price R. J., Thorpe P. E. Uptake of native and deglycosylated ricin A-chain immunotoxins by mouse liver parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells in vitro and in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 22;968(2):172–178. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakey D. C., Watson G. J., Knowles P. P., Thorpe P. E. Effect of chemical deglycosylation of ricin A chain on the in vivo fate and cytotoxic activity of an immunotoxin composed of ricin A chain and anti-Thy 1.1 antibody. Cancer Res. 1987 Feb 15;47(4):947–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomhoff R., Helgerud P., Rasmussen M., Berg T., Norum K. R. In vivo uptake of chylomicron [3H]retinyl ester by rat liver: evidence for retinol transfer from parenchymal to nonparenchymal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7326–7330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourrie B. J., Casellas P., Blythman H. E., Jansen F. K. Study of the plasma clearance of antibody--ricin-A-chain immunotoxins. Evidence for specific recognition sites on the A chain that mediate rapid clearance of the immunotoxin. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 17;155(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09451.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decastel M., Haentjens G., Aubery M., Goussault Y. Differential entry of ricin into malignant and normal rat hepatocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Feb;180(2):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derenzini M., Bonetti E., Marionozzi V., Stirpe F. Toxic effects of ricin: studies on the pathogenesis of liver lesions. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1976 Feb 11;20(1):15–28. doi: 10.1007/BF02890323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K. RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectin ricin on eukaryotic ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8128–8130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekowitz R. A., Stahl P. D. The structure and function of vertebrate mannose lectin-like proteins. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1988;9:121–133. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1988.supplement_9.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodstad O., Olsnes S., Pihl A. Toxicity, distribution and elimination of the cancerostatic lectins abrin and ricin after parenteral injection into mice. Br J Cancer. 1976 Oct;34(4):418–425. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1976.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foxwell B. M., Donovan T. A., Thorpe P. E., Wilson G. The removal of carbohydrates from ricin with endoglycosidases H, F and D and alpha-mannosidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 18;840(2):193–203. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90119-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frénoy J. P., Turpin E., Janicot M., Gehin-Fouque F., Desbuquois B. Uptake of injected 125I-ricin by rat liver in vivo. Subcellular distribution and characterization of the internalized ligand. Biochem J. 1992 May 15;284(Pt 1):249–257. doi: 10.1042/bj2840249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furbish F. S., Steer C. J., Krett N. L., Barranger J. A. Uptake and distribution of placental glucocerebrosidase in rat hepatic cells and effects of sequential deglycosylation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 3;673(4):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90474-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltiwanger R. S., Hill R. L. The isolation of a rat alveolar macrophage lectin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7440–7444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltiwanger R. S., Hill R. L. The ligand binding specificity and tissue localization of a rat alveolar macrophage lectin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15696–15702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe C. A., Lee Y. C. The binding and processing of mannose-bovine serum albumin derivatives by rabbit alveolar macrophages. Effect of the sugar density. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14193–14199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L., Wilson G., Ashwell G., Stukenbrok H. An electron microscope autoradiographic study of the carbohydrate recognition systems in rat liver. I. Distribution of 125I-ligands among the liver cell types. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):47–64. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen R. W., Molema G., Ching T. L., Oosting R., Harms G., Moolenaar F., Hardonk M. J., Meijer D. K. Hepatic endocytosis of various types of mannose-terminated albumins. What is important, sugar recognition, net charge, or the combination of these features. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3343–3348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindberg G. M., Magnusson S., Berg T., Smedsrød B. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of ovalbumin by two carbohydrate-specific receptors in rat liver cells. The intracellular transport of ovalbumin to lysosomes is faster in liver endothelial cells than in parenchymal cells. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 15;270(1):197–203. doi: 10.1042/bj2700197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennartz M. R., Wileman T. E., Stahl P. D. Isolation and characterization of a mannose-specific endocytosis receptor from rabbit alveolar macrophages. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):705–711. doi: 10.1042/bj2450705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson S., Berg T. Extremely rapid endocytosis mediated by the mannose receptor of sinusoidal endothelial rat liver cells. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 1;257(3):651–656. doi: 10.1042/bj2570651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson S., Berg T., Turpin E., Frénoy J. P. Interactions of ricin with sinusoidal endothelial rat liver cells. Different involvement of two distinct carbohydrate-specific mechanisms in surface binding and internalization. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 1;277(Pt 3):855–861. doi: 10.1042/bj2770855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Blaustein J. The interaction of Ricinus communis agglutinin with normal and tumor cell surfaces. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 9;266(2):543–547. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niesen T. E., Alpers D. H., Stahl P. D., Rosenblum J. L. Metabolism of glycosylated human salivary amylase: in vivo plasma clearance by rat hepatic endothelial cells and in vitro receptor mediated pinocytosis by rat macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Sep;36(3):307–320. doi: 10.1002/jlb.36.3.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opresko L. K., Wiley H. S. Receptor-mediated endocytosis in Xenopus oocytes. I. Characterization of the vitellogenin receptor system. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4109–4115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. C., Carew T. E., Glass C. K., Green S. R., Taylor C. A., Jr, Attie A. D. A radioiodinated, intracellularly trapped ligand for determining the sites of plasma protein degradation in vivo. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):791–800. doi: 10.1042/bj2120791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press O. W. Immunotoxins. Biotherapy. 1991;3(1):65–76. doi: 10.1007/BF02175100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsden C. S., Drayson M. T., Bell E. B. The toxicity, distribution and excretion of ricin holotoxin in rats. Toxicology. 1989 Apr;55(1-2):161–171. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(89)90183-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Tønnessen T. I., Olsnes S. Ability of inhibitors of glycosylation and protein synthesis to sensitize cells to abrin, ricin, Shigella toxin, and Pseudomonas toxin. Cancer Res. 1986 Dec;46(12 Pt 1):6418–6422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger P. H., Doebber T. W., Mandell B. F., White R., DeSchryver C., Rodman J. S., Miller M. J., Stahl P. Plasma clearance of glycoproteins with terminal mannose and N-acetylglucosamine by liver non-parenchymal cells. Studies with beta-glucuronidase, N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase, ribonuclease B and agalacto-orosomucoid. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 15;176(1):103–109. doi: 10.1042/bj1760103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons B. M., Stahl P. D., Russell J. H. In vivo depletion of mannose receptor bearing cells from rat liver by ricin A chain: effects on clearance of beta-glucuronidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 31;146(2):849–854. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90608-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons B. M., Stahl P. D., Russell J. H. Mannose receptor-mediated uptake of ricin toxin and ricin A chain by macrophages. Multiple intracellular pathways for a chain translocation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7912–7920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skilleter D. N., Foxwell B. M. Enzymic deglycosylation of ricin lowers its uptake by rat liver non-parenchymal cells. Arch Toxicol Suppl. 1987;11:257–260. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-72558-6_46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skilleter D. N., Paine A. J., Stirpe F. A comparison of the accumulation of ricin by hepatic parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells and its inhibition of protein synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 5;677(3-4):495–500. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90264-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skilleter D. N., Price R. J., Thorpe P. E. Modification of the carbohydrate in ricin with metaperiodate and cyanoborohydride mixtures: effect on binding, uptake and toxicity to parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 27;842(1):12–21. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90287-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl P. D., Wileman T. E., Diment S., Shepherd V. L. Mannose-specific oligosaccharide recognition by mononuclear phagocytes. Biol Cell. 1984;51(2):215–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1984.tb00301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. D., Shepherd V. L. Purification of the human alveolar macrophage mannose receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 29;148(2):883–889. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90958-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summerfield J. A., Vergalla J., Jones E. A. Modulation of a glycoprotein recognition system on rat hepatic endothelial cells by glucose and diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jun;69(6):1337–1347. doi: 10.1172/JCI110573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe P. E., Detre S. I., Foxwell B. M., Brown A. N., Skilleter D. N., Wilson G., Forrester J. A., Stirpe F. Modification of the carbohydrate in ricin with metaperiodate-cyanoborohydride mixtures. Effects on toxicity and in vivo distribution. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 15;147(1):197–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08737.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolleshaug H., Berg T., Nilsson M., Norum K. R. Uptake and degradation of 125I-labelled asialo-fetuin by isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 25;499(1):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. M., Kaplan J. The rate of internalization of different receptor-ligand complexes in alveolar macrophages is receptor-specific. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 1;270(2):369–374. doi: 10.1042/bj2700369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley H. S., Cunningham D. D. The endocytotic rate constant. A cellular parameter for quantitating receptor-mediated endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4222–4229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worrell N. R., Skilleter D. N., Cumber A. J., Price R. J. Mannose receptor dependent uptake of a ricin A chain--antibody conjugate by rat liver non-parenchymal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 13;137(2):892–896. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91163-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youle R. J., Colombatti M. Hybridoma cells containing intracellular anti-ricin antibodies show ricin meets secretory antibody before entering the cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4676–4682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenilman M. E., Fiani M., Stahl P. D., Brunt E. M., Flye M. W. Selective depletion of Kupffer cells in mice by intact ricin. Transplantation. 1989 Jan;47(1):200–203. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198901000-00043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deurs B., Petersen O. W., Olsnes S., Sandvig K. Delivery of internalized ricin from endosomes to cisternal Golgi elements is a discontinuous, temperature-sensitive process. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Jul;171(1):137–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90257-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]