Abstract
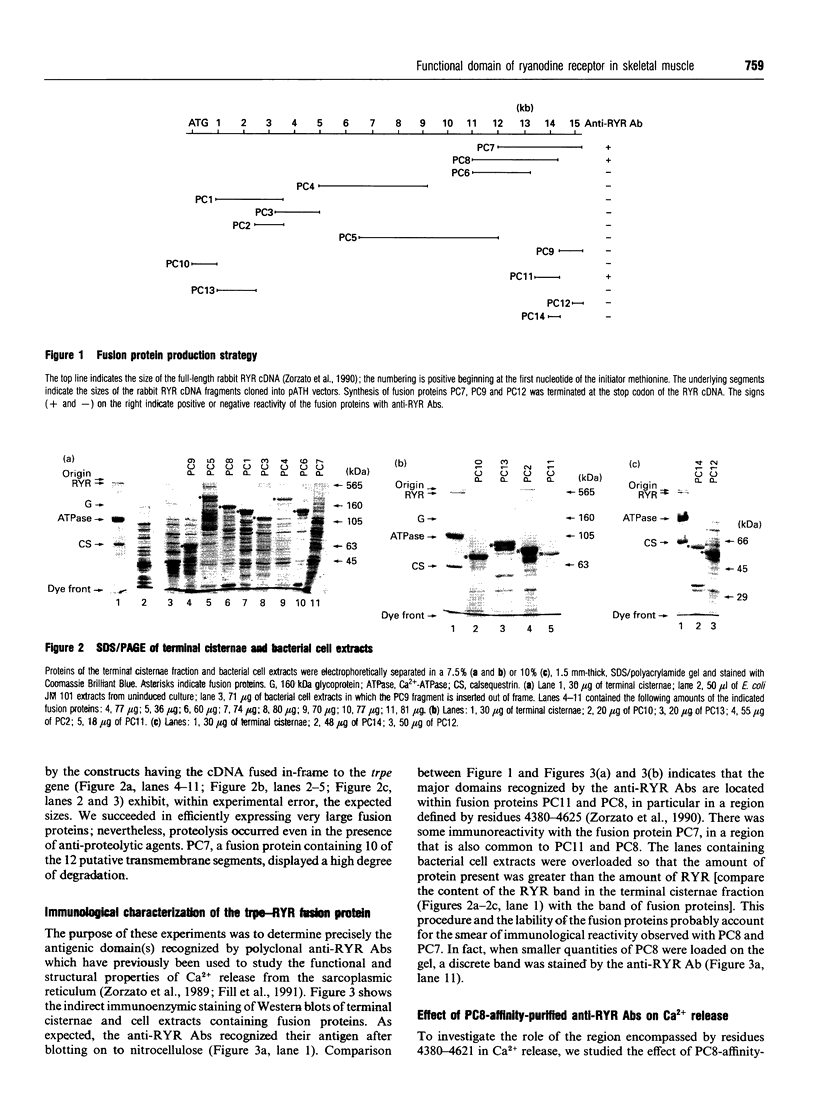
In the present paper we have defined putative functional domains of the ryanodine receptor Ca2+ channel. cDNA fragments of the skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor were fused in-frame with the Escherichia coli trpe protein and the resulting fusion proteins were evaluated for their ability to react with anti-(ryanodine receptor) antibodies, which are known to block Ca(2+)-dependent activation of the Ca(2+)-release channel. Anti-(ryanodine receptor) antibodies react with epitopes lying within a 245-amino-acid-long polypeptide which is located in a region (residues 4380-4625) encompassing most of myoplasmic loop 2, the predicted transmembrane segment M5 and part of the next lumenal loop (45 residues). Purification of the anti-(ryanodine receptor) antibodies by affinity chromatography led to the isolation of a population of antibodies which was capable of decreasing (by > 30%) the doxorubicin-induced Ca2+ release from isolated terminal cisternae. Polyclonal antibodies raised against a ryanodine receptor fusion encompassing part (198 out of 245 residues) of the immunopositive polypeptide decreased by 2-fold the first-order rate constant of Ca(2+)-induced 45Ca2+ efflux from isolated terminal cisternae. These results suggest strongly that the Ca(2+)-activating domain of the skeletal muscle Ca(2+)-release channel is close to, or associated with, myoplasmic loop 2.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson J. J., Buck E., Salama G., Casida J. E., Pessah I. N. Mechanism of anthraquinone-induced calcium release from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18750–18758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisson R., Schiavo G. Two different forms of cytochrome c oxidase can be purified from the slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4373–4376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Computer programs for calculating total from specified free or free from specified total ionic concentrations in aqueous solutions containing multiple metals and ligands. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:378–417. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fill M., Mejia-Alvarez R., Zorzato F., Volpe P., Stefani E. Antibodies as probes for ligand gating of single sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2(+)-release channels. Biochem J. 1991 Jan 15;273(Pt 2):449–457. doi: 10.1042/bj2730449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzini-Armstrong C. Structure of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Fed Proc. 1980 May 15;39(7):2403–2409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii J., Otsu K., Zorzato F., de Leon S., Khanna V. K., Weiler J. E., O'Brien P. J., MacLennan D. H. Identification of a mutation in porcine ryanodine receptor associated with malignant hyperthermia. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):448–451. doi: 10.1126/science.1862346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Davis F. E., Palade G. E. Protein blotting in uniform or gradient electric fields. Anal Biochem. 1985 Jan;144(1):32–40. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90080-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hymel L., Inui M., Fleischer S., Schindler H. Purified ryanodine receptor of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum forms Ca2+-activated oligomeric Ca2+ channels in planar bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):441–445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa T., Smith J. S., Coronado R., Campbell K. P. Purified ryanodine receptor from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum is the Ca2+-permeable pore of the calcium release channel. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16636–16643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inui M., Saito A., Fleischer S. Purification of the ryanodine receptor and identity with feet structures of junctional terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum from fast skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1740–1747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto R. M., Brunschwig J. P., Kim K. C., Caswell A. H. Isolation, characterization, and localization of the spanning protein from skeletal muscle triads. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1405–1414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson C. M., Mickelson J. R., Louis C. F., Campbell K. P. Distinct immunopeptide maps of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release channel in malignant hyperthermia. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2421–2424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner T. J., Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A. High-expression vectors with multiple cloning sites for construction of trpE fusion genes: pATH vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:477–490. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94036-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Erickson H. P., Rousseau E., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Purification and reconstitution of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):315–319. doi: 10.1038/331315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks A. R., Fleischer S., Tempst P. Surface topography analysis of the ryanodine receptor/junctional channel complex based on proteolysis sensitivity mapping. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13143–13149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai J., Imagawa T., Hakamat Y., Shigekawa M., Takeshima H., Numa S. Primary structure and functional expression from cDNA of the cardiac ryanodine receptor/calcium release channel. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 1;271(1-2):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80399-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Kobayashi J., Gilmore J., Mascal M., Rinehart K. L., Jr, Nakamura H., Ohizumi Y. Bromo-eudistomin D, a novel inducer of calcium release from fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum that causes contractions of skinned muscle fibers. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4139–4142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLANS E., ROSE M. E., MARRACK J. R. Fowl antibody. I. Some physical and immunochemical properties. Immunology. 1961 Jul;4:262–277. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu K., Willard H. F., Khanna V. K., Zorzato F., Green N. M., MacLennan D. H. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of rabbit cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13472–13483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade P. Drug-induced Ca2+ release from isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum. I. Use of pyrophosphate to study caffeine-induced Ca2+ release. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6135–6141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessah I. N., Francini A. O., Scales D. J., Waterhouse A. L., Casida J. E. Calcium-ryanodine receptor complex. Solubilization and partial characterization from skeletal muscle junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8643–8648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ríos E., Pizarro G. Voltage sensor of excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev. 1991 Jul;71(3):849–908. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.3.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Coronado R., Meissner G. Single-channel calcium and barium currents of large and small conductance from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biophys J. 1986 Nov;50(5):921–928. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83533-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Imagawa T., Ma J., Fill M., Campbell K. P., Coronado R. Purified ryanodine receptor from rabbit skeletal muscle is the calcium-release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jul;92(1):1–26. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., McClellan G., Gonzalez-Serratos H., Somlyo A. P. Electron probe X-ray microanalysis of post-tetanic Ca2+ and Mg2+ movements across the sarcoplasmic reticulum in situ. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6801–6807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshima H., Nishimura S., Matsumoto T., Ishida H., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Matsuo H., Ueda M., Hanaoka M., Hirose T. Primary structure and expression from complementary DNA of skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):439–445. doi: 10.1038/339439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe P., Bravin M., Zorzato F., Margreth A. Isolation of terminal cisternae of frog skeletal muscle. Calcium storage and release properties. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9901–9907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Bloom B. R., Grosskinsky C. M., Ivanyi J., Thomas D., Davis R. W. Dissection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens using recombinant DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2583–2587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzato F., Chu A., Volpe P. Antibodies to junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum proteins: probes for the Ca2+-release channel. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 1;261(3):863–870. doi: 10.1042/bj2610863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzato F., Fujii J., Otsu K., Phillips M., Green N. M., Lai F. A., Meissner G., MacLennan D. H. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding human and rabbit forms of the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2244–2256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzato F., Margreth A., Volpe P. Direct photoaffinity labeling of junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum with [14C]doxorubicin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13252–13257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]