Abstract
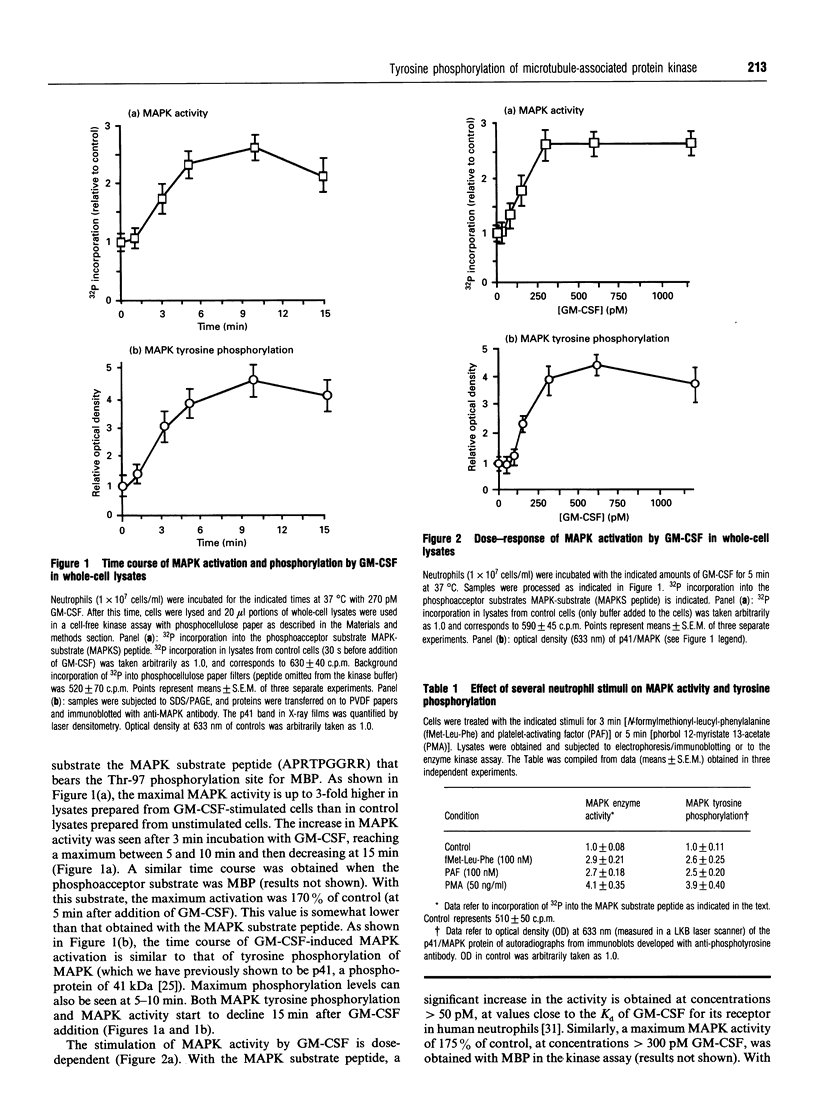
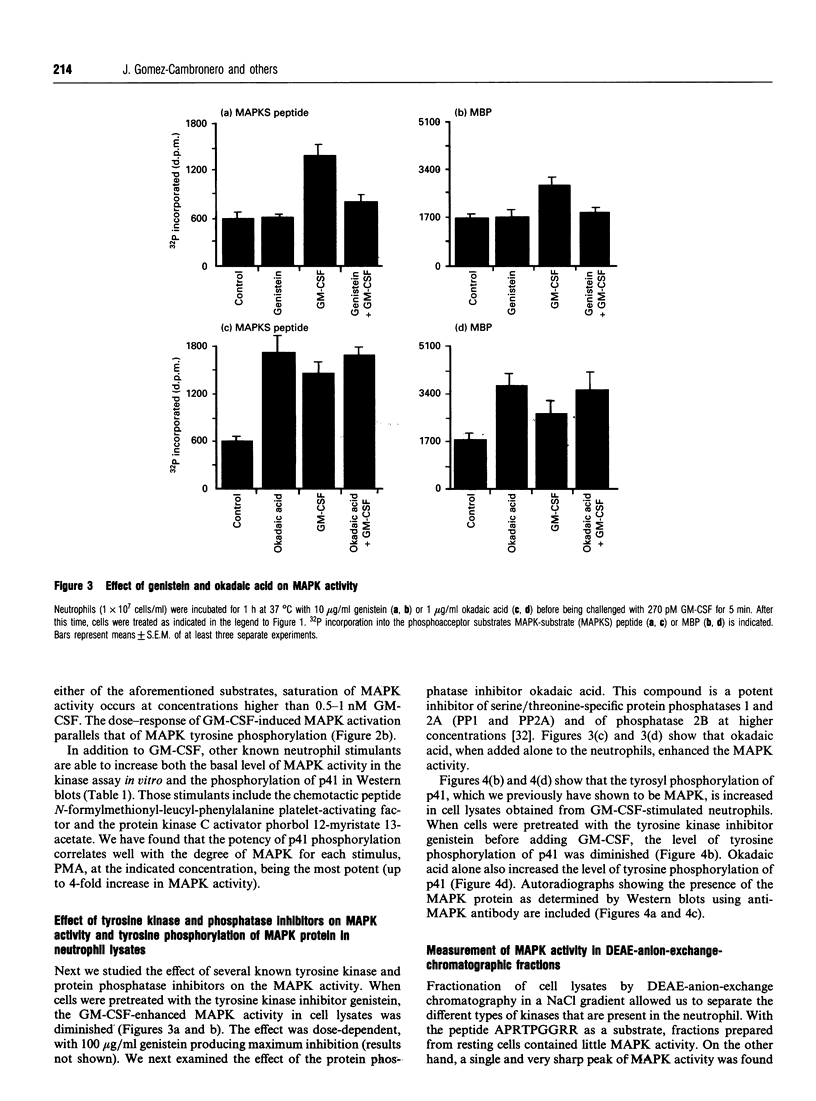
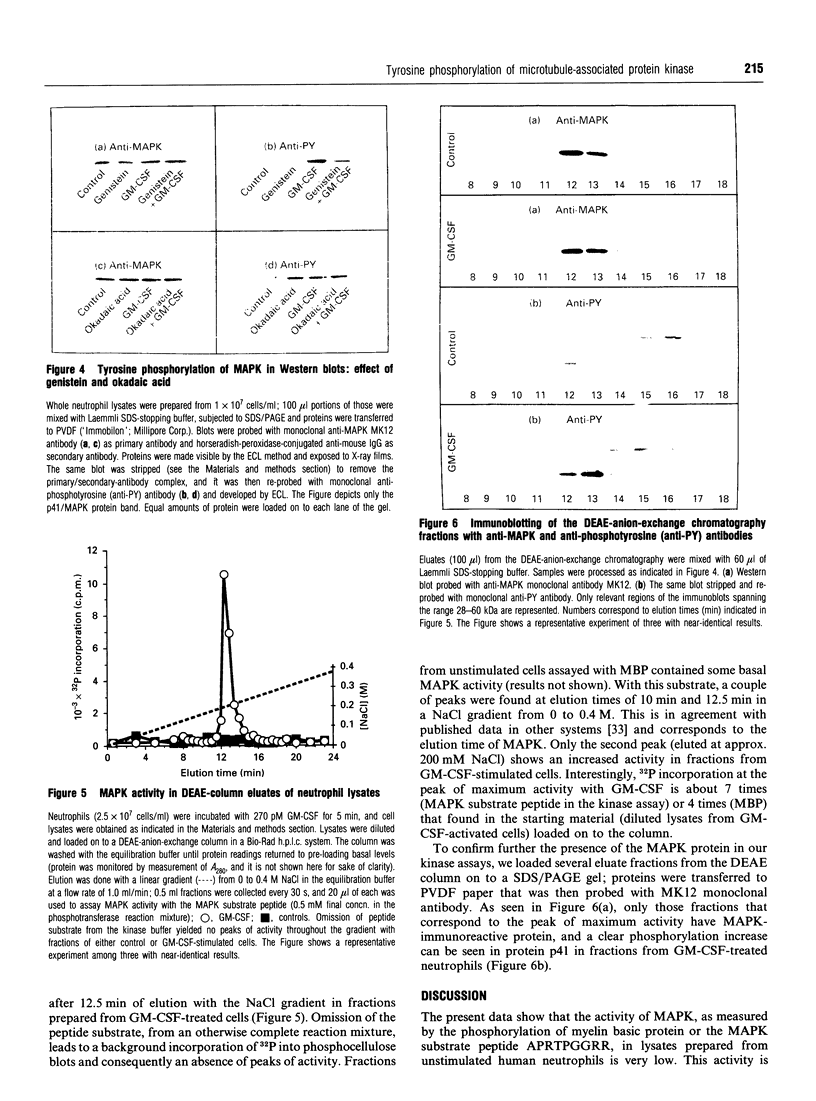
Human polymorphonuclear neutrophils exhibit a low level of the microtubule-associated protein kinase (MAPK) activity. This enzymic activity is enhanced up to 3-fold upon cell stimulation with the human haematopoietic hormone granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). This is demonstrated both in whole-cell lysates and in DEAE-anion-exchange semi-purified fractions prepared from GM-CSF-stimulated neutrophils, by assaying the kinase activity against either myelin basic protein or a phosphoacceptor peptide that bears the specific phosphorylation site of the MAPK natural substrate. Similarly, phosphorylation of MAPK in tyrosine residues, as found in immunoblots using anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies, follows similar time- and dose-response curves as the kinase activation. Pretreatment of the cells with the tyrosine kinase inhibitor genistein abrogates the above-mentioned effect, whereas the phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid enhances both the basal and the GM-CSF-stimulated kinase activities. Likewise, MAPK tyrosine phosphorylation is diminished in genistein-treated neutrophils, and enhanced in okadaic acid-treated cells. We conclude that MAPK activity is present in human neutrophils, and that it is stimulated by GM-CSF. This stimulation of the activity is most likely due to the phosphorylation of MAPK in tyrosine residues triggered upon binding of GM-CSF to its receptors.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn N. G., Weiel J. E., Chan C. P., Krebs E. G. Identification of multiple epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein serine/threonine kinases from Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11487–11494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama T., Ishida J., Nakagawa S., Ogawara H., Watanabe S., Itoh N., Shibuya M., Fukami Y. Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5592–5595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Li P., Marsden L. A., Williams N., Roberts T. M., Sturgill T. W. Raf-1 is a potential substrate for mitogen-activated protein kinase in vivo. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 15;277(Pt 2):573–576. doi: 10.1042/bj2770573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Maller J. L., Tonks N. K., Sturgill T. W. Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):651–653. doi: 10.1038/343651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkow R. L., Dodson R. W. Tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation during activation of human neutrophils. Blood. 1990 Jun 15;75(12):2445–2452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Gregory J. S., Cobb M. H. Purification and properties of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1, an insulin-stimulated microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 8;30(1):278–286. doi: 10.1021/bi00215a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Yancopoulos G. D., Gregory J. S., Slaughter C., Moomaw C., Hsu J., Cobb M. H. An insulin-stimulated protein kinase similar to yeast kinases involved in cell cycle control. Science. 1990 Jul 6;249(4964):64–67. doi: 10.1126/science.2164259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H. C., Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B., Smith A. J., Misconi L., Van Patten S. M., Walsh D. A. A potent synthetic peptide inhibitor of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):989–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicirelli M. F., Pelech S. L., Krebs E. G. Activation of multiple protein kinases during the burst in protein phosphorylation that precedes the first meiotic cell division in Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):2009–2019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Sanghera J. S., Pelech S. L. Definition of a consensus sequence for peptide substrate recognition by p44mpk, the meiosis-activated myelin basic protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15180–15184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A. Related proteins are phosphorylated at tyrosine in response to mitogenic stimuli and at meiosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3143–3147. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPersio J., Billing P., Kaufman S., Eghtesady P., Williams R. E., Gasson J. C. Characterization of the human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1834–1841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely C. M., Oddie K. M., Litz J. S., Rossomando A. J., Kanner S. B., Sturgill T. W., Parsons S. J. A 42-kD tyrosine kinase substrate linked to chromaffin cell secretion exhibits an associated MAP kinase activity and is highly related to a 42-kD mitogen-stimulated protein in fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):731–742. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. Purification and characterization of a protein kinase from Xenopus eggs highly specific for ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):350–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ettehadieh E., Sanghera J. S., Pelech S. L., Hess-Bienz D., Watts J., Shastri N., Aebersold R. Tyrosyl phosphorylation and activation of MAP kinases by p56lck. Science. 1992 Feb 14;255(5046):853–855. doi: 10.1126/science.1311128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Cambronero J., Huang C. K., Bonak V. A., Wang E., Casnellie J. E., Shiraishi T., Sha'afi R. I. Tyrosine phosphorylation in human neutrophil. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):1478–1485. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90841-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Cambronero J., Huang C. K., Gomez-Cambronero T. M., Waterman W. H., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-induced protein tyrosine phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein kinase in human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7551–7555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Cambronero J., Sha'afi R. I. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and the neutrophil: mechanisms of action. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;314:35–71. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-6024-7_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Cambronero J., Wang E., Johnson G., Huang C. K., Sha'afi R. I. Platelet-activating factor induces tyrosine phosphorylation in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6240–6245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Cambronero J., Yamazaki M., Metwally F., Molski T. F., Bonak V. A., Huang C. K., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and human neutrophils: role of guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3569–3573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. A. Use of vanadate as protein-phosphotyrosine phosphatase inhibitor. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:477–482. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Furuya W. Chemoattractant-induced tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of microtubule-associated protein kinase in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):18122–18125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutkind J. S., Robbins K. C. Translocation of the FGR protein-tyrosine kinase as a consequence of neutrophil activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8783–8787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez N., Cohen P. Dissection of the protein kinase cascade by which nerve growth factor activates MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):170–173. doi: 10.1038/353170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haystead T. A., Sim A. T., Carling D., Honnor R. C., Tsukitani Y., Cohen P., Hardie D. G. Effects of the tumour promoter okadaic acid on intracellular protein phosphorylation and metabolism. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):78–81. doi: 10.1038/337078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haystead T. A., Weiel J. E., Litchfield D. W., Tsukitani Y., Fischer E. H., Krebs E. G. Okadaic acid mimics the action of insulin in stimulating protein kinase activity in isolated adipocytes. The role of protein phosphatase 2a in attenuation of the signal. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16571–16580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinze H., Arnold H. H., Fischer D., Kruppa J. The primary structure of the human ribosomal protein S6 derived from a cloned cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4139–4144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Her J. H., Wu J., Rall T. B., Sturgill T. W., Weber M. J. Sequence of pp42/MAP kinase, a serine/threonine kinase regulated by tyrosine phosphorylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3743–3743. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanakura Y., Druker B., Cannistra S. A., Furukawa Y., Torimoto Y., Griffin J. D. Signal transduction of the human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-3 receptors involves tyrosine phosphorylation of a common set of cytoplasmic proteins. Blood. 1990 Aug 15;76(4):706–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Berkow R. L. Tyrosine kinase and phosphotyrosine phosphatase activity in human promyelocytic leukemia cells and human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Blood. 1987 Aug;70(2):356–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McColl S. R., DiPersio J. F., Caon A. C., Ho P., Naccache P. H. Involvement of tyrosine kinases in the activation of human peripheral blood neutrophils by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Blood. 1991 Oct 1;78(7):1842–1852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. The granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factors. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):16–22. doi: 10.1126/science.2990035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda K., Sanghera J. S., Pelech S. L., Kanakura Y., Hallek M., Griffin J. D., Druker B. J. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, interleukin-3, and steel factor induce rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of p42 and p44 MAP kinase. Blood. 1992 Jun 1;79(11):2880–2887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter R. M., Marth J. D., Ziegler S. F., Garvin A. M., Pawar S., Cooke M. P., Abraham K. M. Specialized protein tyrosine kinase proto-oncogenes in hematopoietic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb;948(3):245–262. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines M. A., Golde D. W., Daeipour M., Nel A. E. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor activates microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase in neutrophils via a tyrosine kinase-dependent pathway. Blood. 1992 Jun 15;79(12):3350–3354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Rapid stimulation by insulin of a serine/threonine kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 2 in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1502–1506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossomando A. J., Payne D. M., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Evidence that pp42, a major tyrosine kinase target protein, is a mitogen-activated serine/threonine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6940–6943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Wu J. Recent progress in characterization of protein kinase cascades for phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 17;1092(3):350–357. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(97)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarup G., Cohen S., Garbers D. L. Inhibition of membrane phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase activity by vanadate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):1104–1109. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90635-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




