Abstract
Two sapecin homologues were purified from the culture medium of NIH-Sape-4, an embryonic cell line of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly). These homologues contained six cysteine residues with exactly the same disulphide pairings as those in sapecin. The amino acid sequence of one of them, sapecin C, was also very similar to that of sapecin. The other homologue, sapecin B, was less similar to sapecin but showed significant similarity to charybdotoxin, an inhibitor of K+ channels isolated from a scorpion venom. Like sapecin, these homologues repressed the growth of various Gram-positive bacteria.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bontems F., Roumestand C., Gilquin B., Ménez A., Toma F. Refined structure of charybdotoxin: common motifs in scorpion toxins and insect defensins. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1521–1523. doi: 10.1126/science.1720574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimarcq J. L., Keppi E., Dunbar B., Lambert J., Reichhart J. M., Hoffmann D., Rankine S. M., Fothergill J. E., Hoffmann J. A. Insect immunity. Purification and characterization of a family of novel inducible antibacterial proteins from immunized larvae of the dipteran Phormia terranovae and complete amino-acid sequence of the predominant member, diptericin A. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):17–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara S., Imai J., Fujiwara M., Yaeshima T., Kawashima T., Kobayashi K. A potent antibacterial protein in royal jelly. Purification and determination of the primary structure of royalisin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11333–11337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullmer C. S. Identification of cysteine-containing peptides in protein digests by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1984 Nov 1;142(2):336–339. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90473-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimenez-Gallego G., Navia M. A., Reuben J. P., Katz G. M., Kaczorowski G. J., Garcia M. L. Purification, sequence, and model structure of charybdotoxin, a potent selective inhibitor of calcium-activated potassium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3329–3333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanzawa H., Shimada I., Kuzuhara T., Komano H., Kohda D., Inagaki F., Natori S., Arata Y. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance study of the solution conformation of an antibacterial protein, sapecin. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 3;269(2):413–420. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81206-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai A., Natori S. Analysis of a gene cluster for sarcotoxin II, a group of antibacterial proteins of Sarcophaga peregrina. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6114–6122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai A., Natori S. Cloning of gene cluster for sarcotoxin I, antibacterial proteins of Sarcophaga peregrina. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 4;258(2):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81652-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komano H., Homma K., Natori S. Involvement of sapecin in embryonic cell proliferation of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly). FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 9;289(2):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81061-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komano H., Kasama E., Nagasawa Y., Nakanishi Y., Matsuyama K., Ando K., Natori S. Purification of Sarcophaga (fleshfly) lectin and detection of sarcotoxins in the culture medium of NIH-Sape-4, an embryonic cell line of Sarcophaga peregrina. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):217–222. doi: 10.1042/bj2480217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzuhara T., Nakajima Y., Matsuyama K., Natori S. Determination of the disulfide array in sapecin, an antibacterial peptide of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly). J Biochem. 1990 Apr;107(4):514–518. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzuhara T., Nakajima Y., Matsuyama K., Natori S. Determination of the disulfide array in sapecin, an antibacterial peptide of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly). J Biochem. 1990 Apr;107(4):514–518. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert J., Keppi E., Dimarcq J. L., Wicker C., Reichhart J. M., Dunbar B., Lepage P., Van Dorsselaer A., Hoffmann J., Fothergill J. Insect immunity: isolation from immune blood of the dipteran Phormia terranovae of two insect antibacterial peptides with sequence homology to rabbit lung macrophage bactericidal peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):262–266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama K., Natori S. Molecular cloning of cDNA for sapecin and unique expression of the sapecin gene during the development of Sarcophaga peregrina. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):17117–17121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
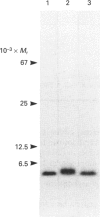
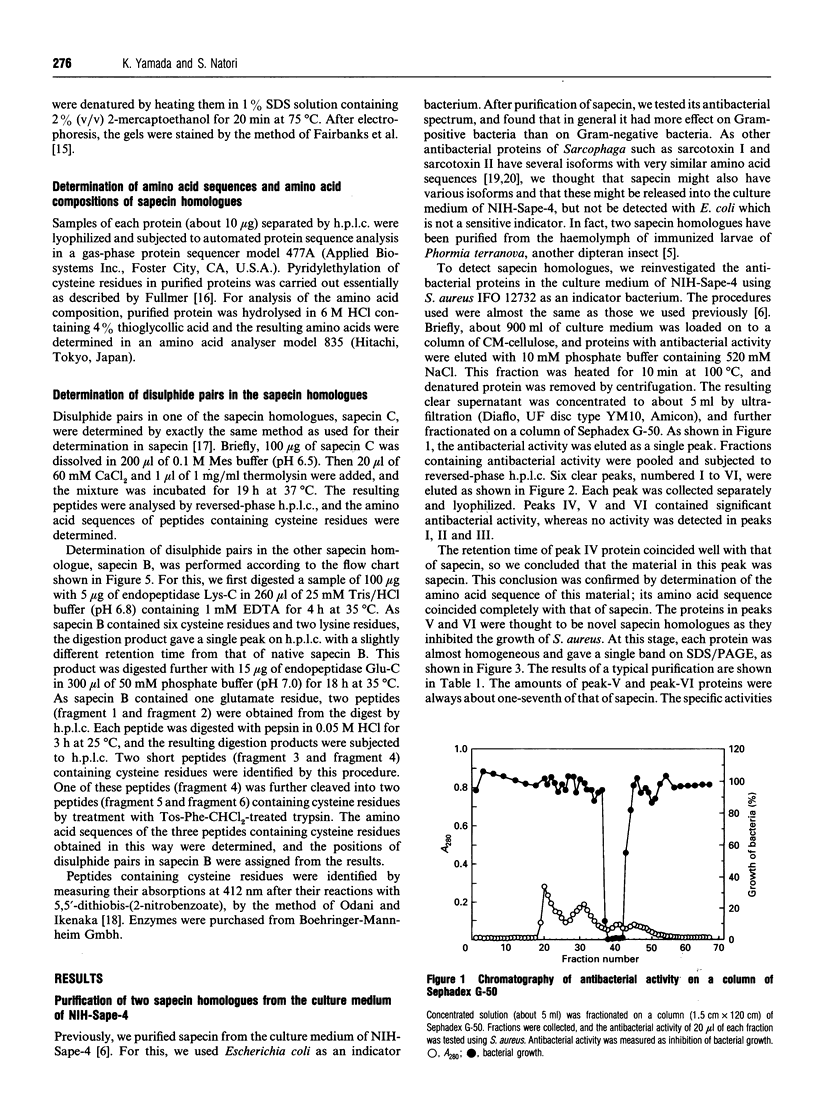
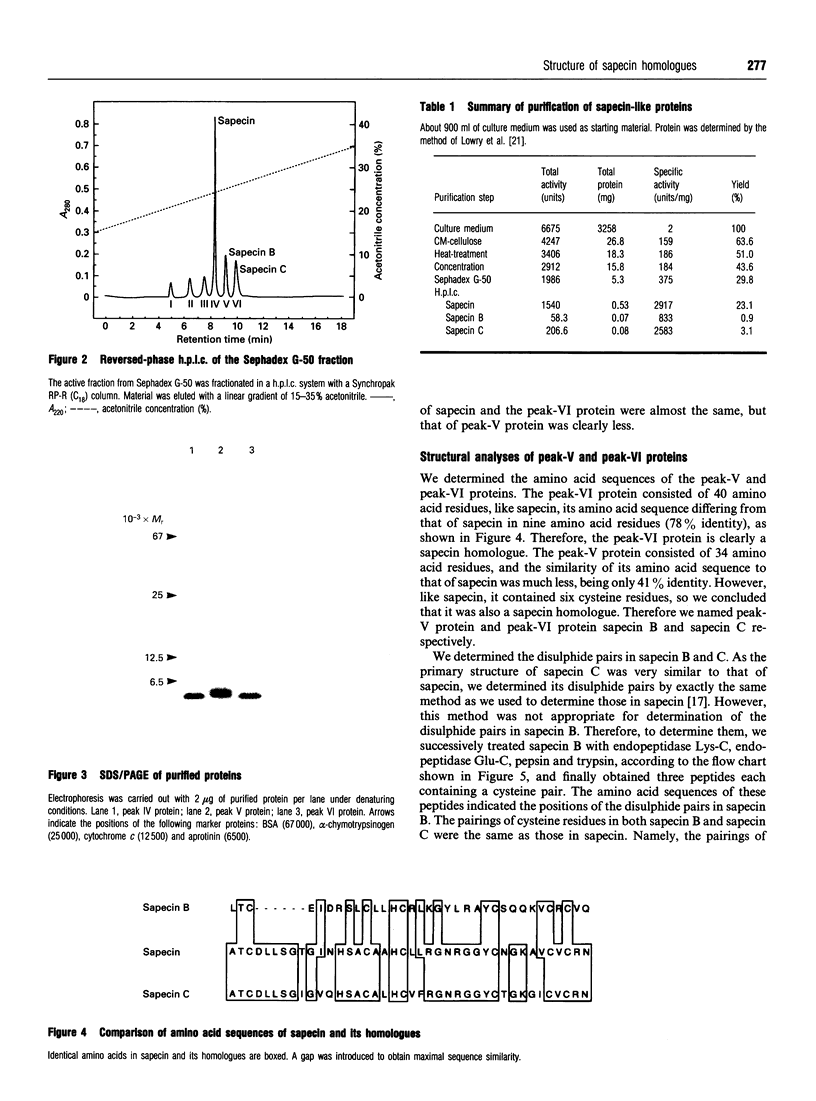
- Matsuyama K., Natori S. Purification of three antibacterial proteins from the culture medium of NIH-Sape-4, an embryonic cell line of Sarcophaga peregrina. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):17112–17116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Moczydlowski E., Latorre R., Phillips M. Charybdotoxin, a protein inhibitor of single Ca2+-activated K+ channels from mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):316–318. doi: 10.1038/313316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Nomura K., Doi M., Yoshida T. Production of low-affinity penicillin-binding protein by low- and high-resistance groups of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1307–1311. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odani S., Ikenaka T. Studies on soybean trypsin inhibitors. 8. Disulfide bridges in soybean Bowman-Birk proteinase inhibitor. J Biochem. 1973 Oct;74(4):697–715. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Natori S. Primary structure of sarcotoxin I, an antibacterial protein induced in the hemolymph of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly) larvae. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7174–7177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Natori S. Primary structure of sarcotoxin I, an antibacterial protein induced in the hemolymph of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly) larvae. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7174–7177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Natori S. Purification and characterization of an antibacterial protein from haemolymph of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh-fly) larvae. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 1;211(3):727–734. doi: 10.1042/bj2110727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]