Abstract
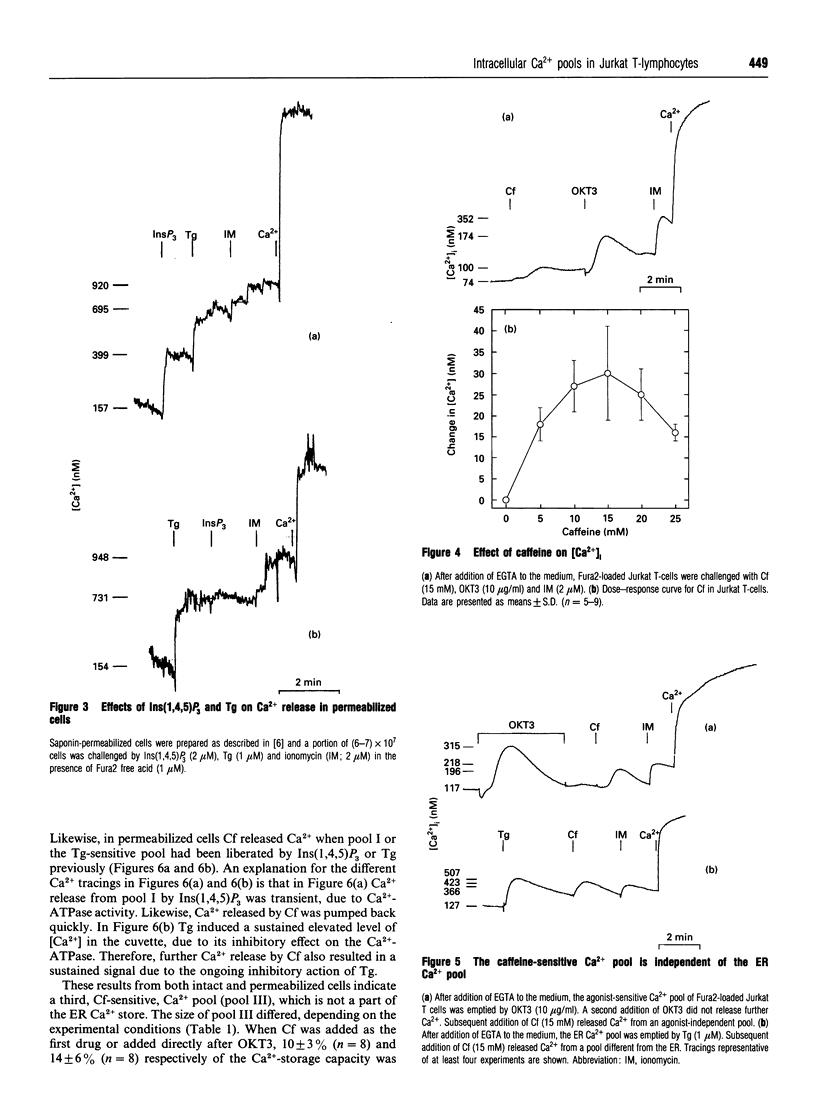
Jurkat T-lymphocytes comprise at least four intracellular Ca2+ pools. Pool I was agonist-sensitive and contained 23 +/- 8% (n = 18) of the total Ca(2+)-storage capacity, as shown in intact cells in the presence of EGTA. The time courses of the agonist-induced formation of Ins(1,4,5)P3 and of the Ca2+ release from pool I were nearly superimposable, indicating that the agonist-sensitive pool I is emptied by Ins(1,4,5)P3. Likewise, in permeabilized cells, the size of the Ins(1,4,5)P3-sensitive Ca2+ pool I was 27 +/- 11% (n = 14). Pool II contained 26 +/- 5% (n = 9) of intracellularly stored Ca2+ and was liberated by thapsigargin, an inhibitor of the endoplasmic-reticulum (ER) Ca(2+)-ATPase. Addition of thapsigargin before addition of agonist abolished the agonist-induced Ca2+ release in both intact and permeabilized cells, indicating that pool I is a subcompartment of the ER Ca2+ pool. The content of this ER Ca2+ pool (pools I and II) amounted to 51 +/- 15% (n = 9) in intact cells and 49 +/- 16% (n = 16) in permeabilized cells. Caffeine released Ca2+ even when the ER pool (pools I and II) was emptied by previous addition of thapsigargin, indicating the presence of a third pool independent of pools I and II. Pool III contained 23 +/- 6% (n = 8) in intact cells, but 41 +/- 8% (n = 5) in permeabilized cells. The remaining intracellularly stored Ca2+ was released by addition of the Ca2+ ionophore ionomycin. This fourth pool contained 27 +/- 8% (n = 9) in intact cells, but less than 10% in permeabilized cells. The size of pool III was increased when pools I and II were emptied before addition of caffeine, whereas the size of pool IV was decreased under such conditions. In conclusion, this first comprehensive description of intracellular Ca2+ pools in Jurkat T-lymphocytes demonstrates the presence of four different Ca2+ pools, provides estimates of their sizes and describes relationships between each other. Release of Ca2+ from pool I [Ins(1,4,5)P3-sensitive] has previously been shown to play a major role in T-cell activation, whereas the physiological role of pools II-IV remains to be established.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catt K. J., Hunyady L., Balla T. Second messengers derived from inositol lipids. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1991 Feb;23(1):7–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00768836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek T. R., Barry V. A., Berridge M. J., Missiaen L. Bovine adrenal chromaffin cells contain an inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-insensitive but caffeine-sensitive Ca2+ store that can be regulated by intraluminal free Ca2+. Biochem J. 1991 May 1;275(Pt 3):697–701. doi: 10.1042/bj2750697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasolato C., Zottini M., Clementi E., Zacchetti D., Meldolesi J., Pozzan T. Intracellular Ca2+ pools in PC12 cells. Three intracellular pools are distinguished by their turnover and mechanisms of Ca2+ accumulation, storage, and release. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20159–20167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guse A. H., Emmrich F. T-cell receptor-mediated metabolism of inositol polyphosphates in Jurkat T-lymphocytes. Identification of a D-myo-inositol 1,2,3,4,6-pentakisphosphate-2-phosphomonoesterase activity, a D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate-1/3-phosphatase activity and a D/L-myo-inositol 1,2,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate-1/3-kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24498–24502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guse A. H., Roth E., Emmrich F. D-myo-inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate releases Ca2+ from crude microsomes and enriched vesicular plasma membranes, but not from intracellular stores of permeabilized T-lymphocytes and monocytes. Biochem J. 1992 Dec 1;288(Pt 2):489–495. doi: 10.1042/bj2880489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. A., Steiner J. P., Snyder S. H. Plasma membrane inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor of lymphocytes: selective enrichment in sialic acid and unique binding specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2849–2853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscombe D., Madison D. V., Poenie M., Reuter H., Tsien R. Y., Tsien R. W. Spatial distribution of calcium channels and cytosolic calcium transients in growth cones and cell bodies of sympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2398–2402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lückhoff A., Clapham D. E. Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate activates an endothelial Ca(2+)-permeable channel. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):356–358. doi: 10.1038/355356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malgaroli A., Fesce R., Meldolesi J. Spontaneous [Ca2+]i fluctuations in rat chromaffin cells do not require inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate elevations but are generated by a caffeine- and ryanodine-sensitive intracellular Ca2+ store. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3005–3008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson I. M., Burgoyne R. D. Characterisation of distinct inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive and caffeine-sensitive calcium stores in digitonin-permeabilised adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1991 May;56(5):1587–1593. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier M. F., Bird G. S., Putney J. W., Jr Subcellular distribution of the calcium-storing inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive organelle in rat liver. Possible linkage to the plasma membrane through the actin microfilaments. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 15;274(Pt 3):643–650. doi: 10.1042/bj2740643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Ross C. A., Villa A., Supattapone S., Pozzan T., Snyder S. H., Meldolesi J. The inositol 1,4,5,-trisphosphate receptor in cerebellar Purkinje cells: quantitative immunogold labeling reveals concentration in an ER subcompartment. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):615–624. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauderman K. A., McKinney R. A., Murawsky M. M. The role of caffeine-sensitive Ca2+ stores in agonist- and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release from bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochem J. 1991 Sep 15;278(Pt 3):643–650. doi: 10.1042/bj2780643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):67–69. doi: 10.1038/306067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treves S., Di Virgilio F., Cerundolo V., Zanovello P., Collavo D., Pozzan T. Calcium and inositolphosphates in the activation of T cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):33–42. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Delden C., Favre C., Spät A., Cerny E., Krause K. H., Lew D. P. Purification of an inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-binding calreticulin-containing intracellular compartment of HL-60 cells. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 1;281(Pt 3):651–656. doi: 10.1042/bj2810651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe P., Krause K. H., Hashimoto S., Zorzato F., Pozzan T., Meldolesi J., Lew D. P. "Calciosome," a cytoplasmic organelle: the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ store of nonmuscle cells? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1091–1095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakui M., Osipchuk Y. V., Petersen O. H. Receptor-activated cytoplasmic Ca2+ spiking mediated by inositol trisphosphate is due to Ca2(+)-induced Ca2+ release. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90505-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacchetti D., Clementi E., Fasolato C., Lorenzon P., Zottini M., Grohovaz F., Fumagalli G., Pozzan T., Meldolesi J. Intracellular Ca2+ pools in PC12 cells. A unique, rapidly exchanging pool is sensitive to both inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and caffeine-ryanodine. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20152–20158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


