Abstract
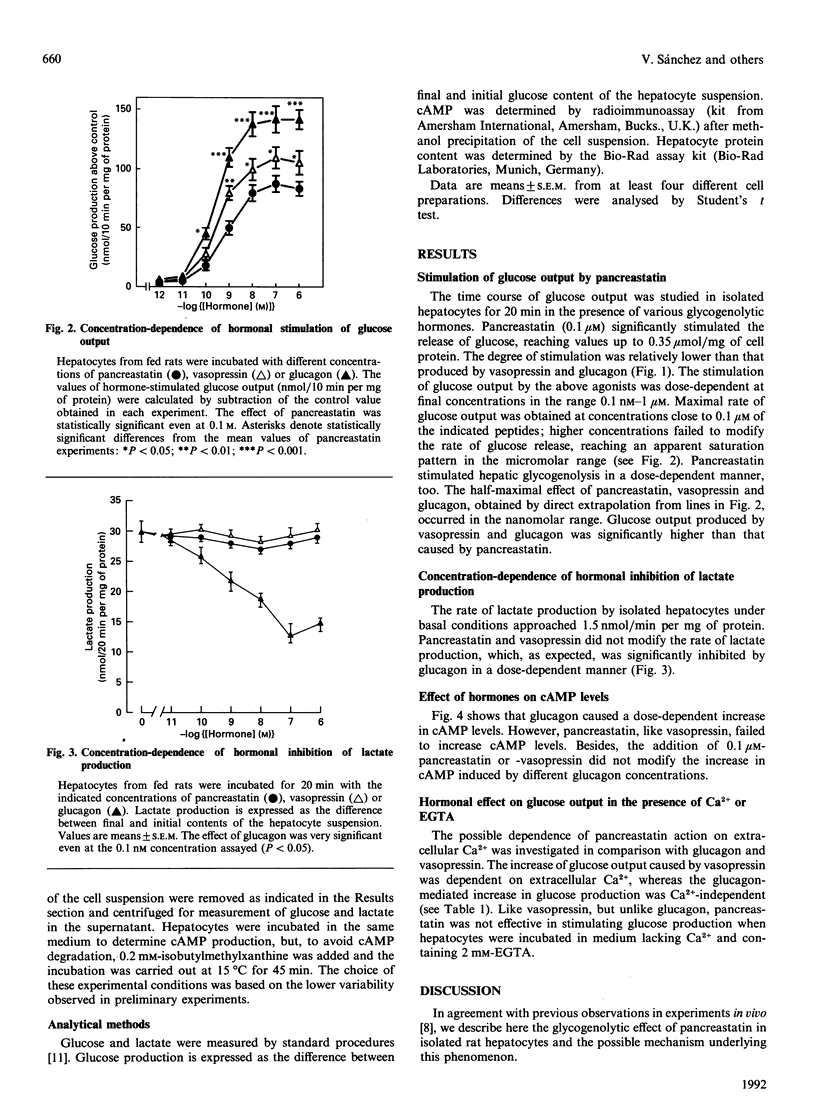
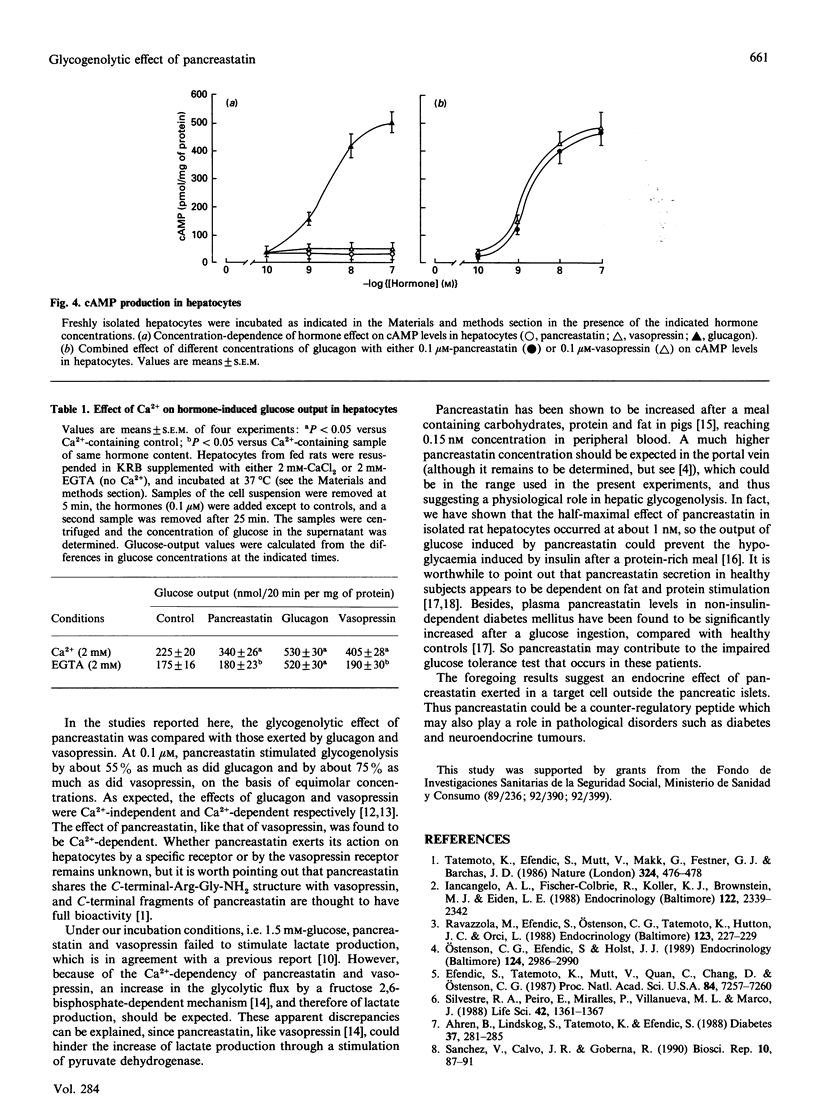
We have studied the effect of pig pancreastatin on glucose and lactate production in freshly isolated rat hepatocytes. Pancreastatin stimulated the rate of glucose output, whereas, in contrast with glucagon, it failed to modify the rate of lactate production. The effective concentration of pancreastatin was in the range 0.1-100 nM, with half-maximal rate close to 1 nM. The ability of pancreastatin to increase glucose output was abolished by chelation of the calcium in the medium. By itself, pancreastatin did not increase cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels and had no influence on cAMP levels in glucagon-stimulated hepatocytes. Our results point out a possible role of pancreastatin in glycogenolysis. This appears to be mediated by a cAMP-independent Ca(2+)-dependent mechanism.
Full text
PDF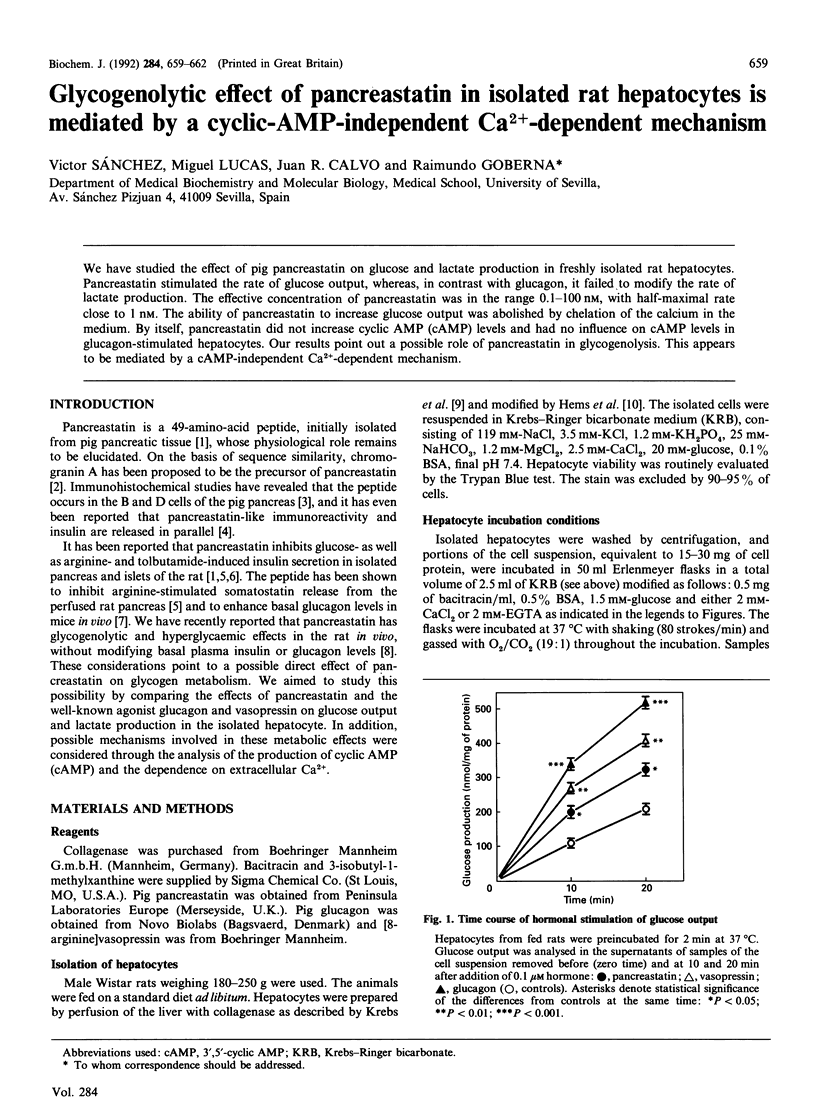

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahrén B., Lindskog S., Tatemoto K., Efendić S. Pancreastatin inhibits insulin secretion and stimulates glucagon secretion in mice. Diabetes. 1988 Mar;37(3):281–285. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.3.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretherton-Watt D., Ghatei M. A., Bishop A. E., Facer P., Fahey M., Hedges M., Williams G., Valentino K. L., Tatemoto K., Roth K. Pancreastatin distribution and plasma levels in the pig. Peptides. 1988 Sep-Oct;9(5):1005–1014. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(88)90081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington A. D., Vranic M. Effect of arginine on glucose turnover and plasma free fatty acids in normal dogs. Diabetes. 1973 Jul;22(7):537–543. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.7.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efendić S., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Quan C., Chang D., Ostenson C. G. Pancreastatin and islet hormone release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7257–7260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Role of phosphoinositides in the regulation of liver function. Hepatology. 1988 Jan-Feb;8(1):152–166. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funakoshi A., Tateishi K., Shinozaki H., Matsumoto M., Wakasugi H. Elevated plasma levels of pancreastatin (PST) in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). Regul Pept. 1990 Sep 10;30(2):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(90)90056-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funakoshi A., Tateishi K., Shinozaki H., Miyasaka K., Ito T., Wakasugi H. Plasma pancreastatin responses after intrajejunal infusion of liquid meal in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1990 Jun;35(6):721–725. doi: 10.1007/BF01540174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hems D. A., Rodrigues L. M., Whitton P. D. Rapid stimulation by vasopressin, oxytocin and angiotensin II of glycogen degradation in hepatocyte suspensions. Biochem J. 1978 May 15;172(2):311–317. doi: 10.1042/bj1720311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hue L., Rider M. H. Role of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in the control of glycolysis in mammalian tissues. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):313–324. doi: 10.1042/bj2450313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacangelo A. L., Fischer-Colbrie R., Koller K. J., Brownstein M. J., Eiden L. E. The sequence of porcine chromogranin A messenger RNA demonstrates chromogranin A can serve as the precursor for the biologically active hormone, pancreastatin. Endocrinology. 1988 May;122(5):2339–2341. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-5-2339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostenson C. G., Efendic S., Holst J. J. Pancreastatin-like immunoreactivity and insulin are released in parallel from the perfused porcine pancreas. Endocrinology. 1989 Jun;124(6):2986–2990. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-6-2986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravazzola M., Efendic S., Ostenson C. G., Tatemoto K., Hutton J. C., Orci L. Localization of pancreastatin immunoreactivity in porcine endocrine cells. Endocrinology. 1988 Jul;123(1):227–229. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-1-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez V., Calvo J. R., Goberna R. Glycogenolytic effect of pancreastatin in the rat. Biosci Rep. 1990 Feb;10(1):87–91. doi: 10.1007/BF01116856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvestre R. A., Peiró E., Miralles P., Villanueva M. L., Marco J. Effects of pancreastatin on insulin, glucagon and somatostatin secretion by the perfused rat pancreas. Life Sci. 1988;42(14):1361–1367. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Efendić S., Mutt V., Makk G., Feistner G. J., Barchas J. D. Pancreastatin, a novel pancreatic peptide that inhibits insulin secretion. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):476–478. doi: 10.1038/324476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Cooper R. H., Hoek J. B. Role of calcium in the hormonal regulation of liver metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 30;639(3-4):243–295. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(81)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


