Abstract
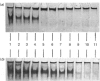
Recently published data [Vorotnikov & Gusev (1990) FEBS Lett. 277, 134-136] indicate that smooth muscle caldesmon interacts with a mixture of soybean phospholipids (azolectin). Continuing this investigation, we found that duck gizzard caldesmon interacts more tightly with acidic (phosphatidylserine) than with neutral (phosphatidylcholine) phospholipids. A high concentration of Ca2+ (50 microM) decreased the interaction of caldesmon with phosphatidylserine. Among chymotryptic peptides of caldesmon, only those having molecular masses of 45, 40, 23, 22 and 20 kDa were able to specifically interact with phospholipids. These peptides, derived from the C-terminal part of caldesmon, contained the sites phosphorylated by Ca2+/phospholipid-dependent protein kinase, and phosphorylation catalysed by this enzyme decreased the affinity of these peptides for phospholipids. In the presence of Ca2+, calmodulin competed with phospholipids for the interaction with the caldesmon peptides. The C-terminal part of caldesmon contains three peptides with a primary structure similar to that of the calmodulin- and phospholipid-binding site of neuromodulin. These sites may be involved in the interaction of caldesmon with calmodulin and phospholipids.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams R. J., Pollard T. D. Binding of myosin I to membrane lipids. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):565–568. doi: 10.1038/340565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazzi M. D., Nelsestuen G. L. Role of substrate in imparting calcium and phospholipid requirements to protein kinase C activation. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 7;26(7):1974–1982. doi: 10.1021/bi00381a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J., Imai M., Lee R., Moore P., Cook R. G., Lin W. G. Cloning and expression of a smooth muscle caldesmon. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13873–13879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Cheek T. R., Norman K. M. Identification of a secretory granule-binding protein as caldesmon. Nature. 1986 Jan 2;319(6048):68–70. doi: 10.1038/319068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D. Control of exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jul 22;1071(2):174–202. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90024-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii T., Imai M., Rosenfeld G. C., Bryan J. Domain mapping of chicken gizzard caldesmon. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2757–2763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard P. R., Mazzei G. J., Kuo J. F. Immunological quantitation of phospholipid/Ca2+-dependent protein kinase and its fragments. Tissue levels, subcellular distribution, and ontogenetic changes in brain and heart. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):370–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Machesky L. M., Baldassare J. J., Pollard T. D. The actin-binding protein profilin binds to PIP2 and inhibits its hydrolysis by phospholipase C. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1575–1578. doi: 10.1126/science.2157283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishna R., Anderson W. B. Ca2+-induced hydrophobic site on calmodulin: application for purification of calmodulin by phenyl-Sepharose affinity chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 29;104(2):830–836. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90712-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graceffa P., Wang C. L., Stafford W. F. Caldesmon. Molecular weight and subunit composition by analytical ultracentrifugation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14196–14202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K., Fujio Y., Kato I., Sobue K. Structural and functional relationships between h- and l-caldesmons. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):355–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden S. M., Wolenski J. S., Mooseker M. S. Binding of brush border myosin I to phospholipid vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):443–451. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houbre D., Duportail G., Deloulme J. C., Baudier J. The interactions of the brain-specific calmodulin-binding protein kinase C substrate, neuromodulin (GAP 43), with membrane phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):7121–7131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikebe M., Hornick T. Determination of the phosphorylation sites of smooth muscle caldesmon by protein kinase C. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Aug 1;288(2):538–542. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90232-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G. Actin binding proteins--lipid interactions. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1991 Apr;12(2):136–144. doi: 10.1007/BF01774032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama E. Assignment of the positions of chymotryptic fragments and cysteinyl groups in the primary structure of caldesmon in relation to a conformational change. J Biochem. 1989 Dec;106(6):988–993. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi R., Tashima Y. Purification, biological properties and partial sequence analysis of 67-kDa calcimedin and its 34-kDa fragment from chicken gizzard. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Mar 10;188(2):447–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15422.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Janmey P. A., Yin H. L. Identification of critical functional and regulatory domains in gelsolin. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1717–1726. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. R., Kapiloff M. S., Durgerian S., Tatemoto K., Russo A. F., Hanson P., Schulman H., Rosenfeld M. G. Molecular cloning of a brain-specific calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5962–5966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marston S. B., Smith C. W. The thin filaments of smooth muscles. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1985 Dec;6(6):669–708. doi: 10.1007/BF00712237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Lim T. K. Equilibria involved in prothrombin- and blood-clotting factor X-membrane binding. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4164–4171. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodaway A. R., Sternberg M. J., Bentley D. L. Similarity in membrane proteins. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):624–624. doi: 10.1038/342624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaub M. C., Perry S. V. The relaxing protein system of striated muscle. Resolution of the troponin complex into inhibitory and calcium ion-sensitizing factors and their relationship to tropomyosin. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(5):993–1004. doi: 10.1042/bj1150993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobue K., Kanda K., Tanaka T., Ueki N. Caldesmon: a common actin-linked regulatory protein in the smooth muscle and nonmuscle contractile system. J Cell Biochem. 1988 Jul;37(3):317–325. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240370306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T. Refinement of the coomassie blue method of protein quantitation. A simple and linear spectrophotometric assay for less than or equal to 0.5 to 50 microgram of protein. Anal Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):142–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szpacenko A., Dabrowska R. Functional domain of caldesmon. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 7;202(2):182–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80683-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi T., Yazawa M., Ueno T., Suzuki S., Yagi K. Amino acid sequence studies on cyanogen bromide peptides of chicken caldesmon which bind to calmodulin. J Biochem. 1989 Nov;106(5):778–783. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi K., Takahashi K., Abe M., Nishida W., Hiwada K., Nabeya T., Maruyama K. Co-localization of immunoreactive forms of calponin with actin cytoskeleton in platelets, fibroblasts, and vascular smooth muscle. J Biochem. 1991 Feb;109(2):311–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Ohta H., Kanda K., Tanaka T., Hidaka H., Sobue K. Phosphorylation of high-Mr caldesmon by protein kinase C modulates the regulatory function of this protein on the interaction between actin and myosin. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Mar 30;188(3):495–500. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15427.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Filburn C. R. Affinity chromatography of protein kinase C-phorbol ester receptor on polyacrylamide-immobilized phosphatidylserine. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12311–12314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorotnikov A. V., Gusev N. B. Interaction of smooth muscle caldesmon with phospholipids. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 17;277(1-2):134–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80827-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorotnikov A. V., Gusev N. B. Some properties of duck gizzard caldesmon. Biochem J. 1991 Jan 1;273(Pt 1):161–163. doi: 10.1042/bj2730161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorotnikov A. V., Shirinsky V. P., Gusev N. B. Phosphorylation of smooth muscle caldesmon by three protein kinases: implication for domain mapping. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 29;236(2):321–324. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80047-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G., Kerrick W. G., Bourguignon L. Y. The role of caldesmon in the regulation of receptor capping in mouse T-lymphoma cell. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):496–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. L., Wang L. W., Xu S. A., Lu R. C., Saavedra-Alanis V., Bryan J. Localization of the calmodulin- and the actin-binding sites of caldesmon. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9166–9172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamakita Y., Yamashiro S., Matsumura F. Microinjection of nonmuscle and smooth muscle caldesmon into fibroblasts and muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2487–2498. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonezawa N., Nishida E., Iida K., Yahara I., Sakai H. Inhibition of the interactions of cofilin, destrin, and deoxyribonuclease I with actin by phosphoinositides. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8382–8386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]