Abstract
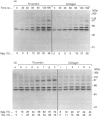
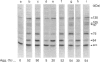
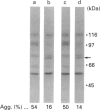
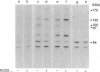
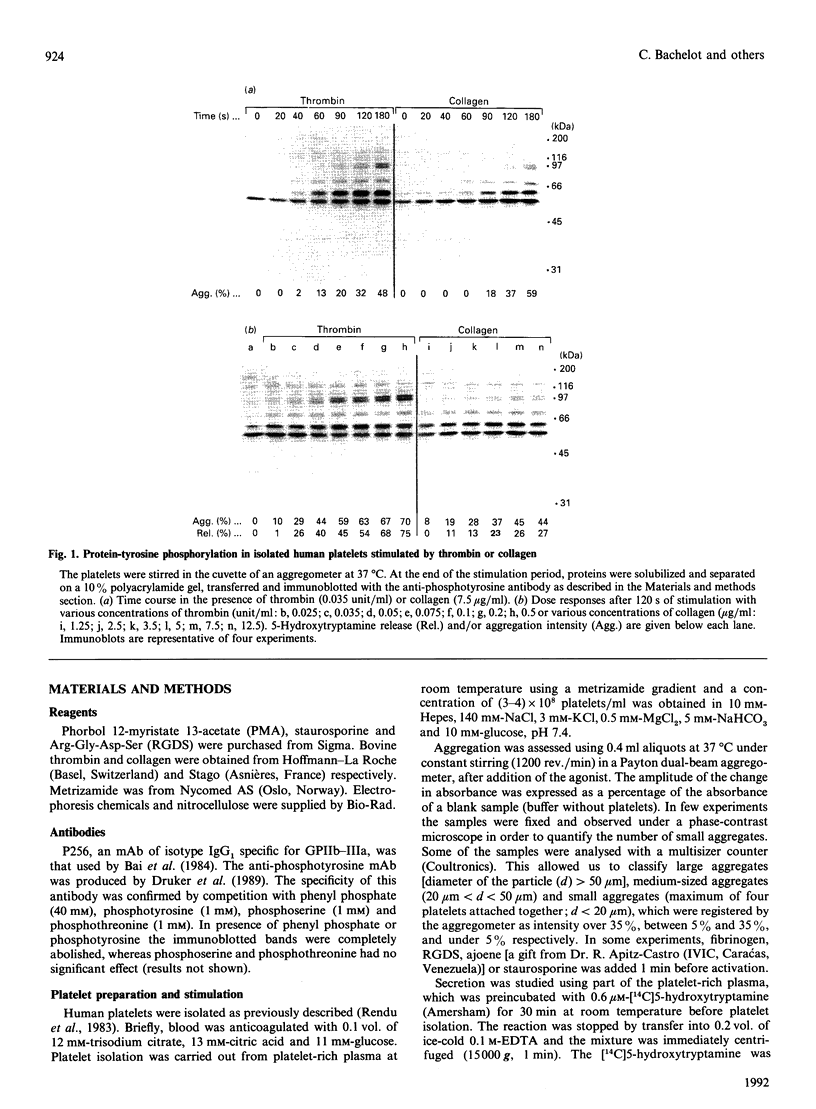
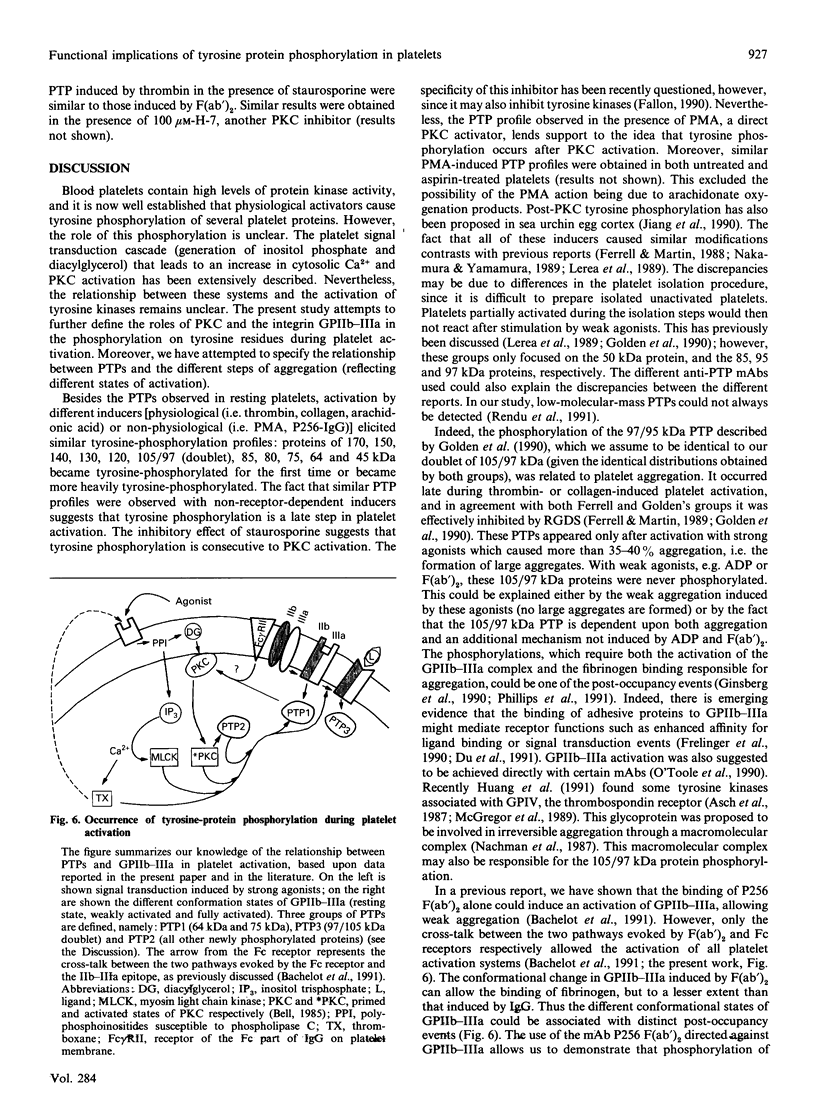
During activation of platelets by agonists, a number of proteins become phosphorylated at tyrosine residues. Using immunoblotting with a monoclonal anti-phosphotyrosine antibody, we have compared the different phosphotyrosine-protein (PTP) profiles of platelets stimulated with thrombin, collagen, ADP, arachidonic acid, phorbol myristate acetate and P256, an anti-glycoprotein-IIb-IIIa (GPIIb-IIIa) monoclonal antibody (mAb). Only a few PTPs were observed in resting platelets, of molecular masses 130, 64, 56-60 and 36 kDa. After stimulation by different agonists these proteins were more intensely phosphorylated and additional PTPs appeared with molecular masses of 170, 150, 140, 120, 105/97 (doublet), 85, 80, 75 and 45 kDa. The kinetics of phosphorylation differed from one agonist to another, but no significant differences in the overall patterns were detected, except in presence of ADP and P256-F(ab')2, which induced only the additional tyrosine phosphorylation of the 64 kDa protein and to a lesser extent that of a 75 kDa protein. The use of various agonists and the inhibitors (staurosporine, ajoene and RGDS) permitted a better characterization of the relationship between the different steps of activation and phosphorylation on tyrosine residues. The studies suggest the following conclusions: (i) stimulation of tyrosine phosphorylation occurs after activation of protein kinase C; (ii) there is a relationship between ligand binding to GPIIb-IIIa and the tyrosine phosphorylation of the 64 kDa protein; and (iii) there is a close relationship between PTP formation and the intensity of platelet activation and aggregation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asch A. S., Barnwell J., Silverstein R. L., Nachman R. L. Isolation of the thrombospondin membrane receptor. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1054–1061. doi: 10.1172/JCI112918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachelot C., Rendu F., Boucheix C., Hogg N., Levy-Toledano S. Activation of platelets induced by mAb P256 specific for glycoprotein IIb-IIIa. Possible evidence for a role for IIb-IIIa in membrane signal transduction. Eur J Biochem. 1990 May 31;190(1):177–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachelot C., Sulpice J. C., Giraud F., Rendu F. Mechanisms involved in platelet activation induced by a monoclonal antibody anti glycoprotein IIb-IIIa: inositol phosphate production is not the primary event. Cell Signal. 1991;3(6):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(91)90030-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bai Y., Durbin H., Hogg N. Monoclonal antibodies specific for platelet glycoproteins react with human monocytes. Blood. 1984 Jul;64(1):139–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. M. Protein kinase C activation by diacylglycerol second messengers. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):631–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90774-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Druker B. J., Mamon H. J., Roberts T. M. Oncogenes, growth factors, and signal transduction. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 16;321(20):1383–1391. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911163212007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du X. P., Plow E. F., Frelinger A. L., 3rd, O'Toole T. E., Loftus J. C., Ginsberg M. H. Ligands "activate" integrin alpha IIb beta 3 (platelet GPIIb-IIIa). Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):409–416. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90458-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon R. J. Staurosporine inhibits a tyrosine protein kinase in human hepatoma cell membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Aug 16;170(3):1191–1196. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90519-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Martin G. S. Platelet tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation is regulated by thrombin. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3603–3610. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Martin G. S. Tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation is regulated by glycoprotein IIb-IIIa in platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2234–2238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frelinger A. L., 3rd, Cohen I., Plow E. F., Smith M. A., Roberts J., Lam S. C., Ginsberg M. H. Selective inhibition of integrin function by antibodies specific for ligand-occupied receptor conformers. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6346–6352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. H., Frelinger A. L., Lam S. C., Forsyth J., McMillan R., Plow E. F., Shattil S. J. Analysis of platelet aggregation disorders based on flow cytometric analysis of membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa with conformation-specific monoclonal antibodies. Blood. 1990 Nov 15;76(10):2017–2023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Brugge J. S., Shattil S. J. Role of platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa in agonist-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of platelet proteins. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):3117–3127. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.3117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Brugge J. S. Thrombin treatment induces rapid changes in tyrosine phosphorylation in platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):901–905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. M., Bolen J. B., Barnwell J. W., Shattil S. J., Brugge J. S. Membrane glycoprotein IV (CD36) is physically associated with the Fyn, Lyn, and Yes protein-tyrosine kinases in human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7844–7848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang W. P., Gottlieb R. A., Lennarz W. J., Kinsey W. H. Phorbol ester treatment stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of a sea urchin egg cortex protein. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):1049–1053. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerea K. M., Tonks N. K., Krebs E. G., Fischer E. H., Glomset J. A. Vanadate and molybdate increase tyrosine phosphorylation in a 50-kilodalton protein and stimulate secretion in electropermeabilized platelets. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 28;28(24):9286–9292. doi: 10.1021/bi00450a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor J. L., Catimel B., Parmentier S., Clezardin P., Dechavanne M., Leung L. L. Rapid purification and partial characterization of human platelet glycoprotein IIIb. Interaction with thrombospondin and its role in platelet aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):501–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Yamamura H. Thrombin and collagen induce rapid phosphorylation of a common set of cellular proteins on tyrosine in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7089–7091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole T. E., Loftus J. C., Du X. P., Glass A. A., Ruggeri Z. M., Shattil S. J., Plow E. F., Ginsberg M. H. Affinity modulation of the alpha IIb beta 3 integrin (platelet GPIIb-IIIa) is an intrinsic property of the receptor. Cell Regul. 1990 Nov;1(12):883–893. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.12.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Charo I. F., Scarborough R. M. GPIIb-IIIa: the responsive integrin. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):359–362. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90451-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E., Marguerie G., Ginsberg M. H. Arginyl-glycyl-aspartic acid sequences and fibrinogen binding to platelets. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):110–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumiglia K. M., Huang C. K., Feinstein M. B. Elevation of cAMP, but not cGMP, inhibits thrombin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 14;171(2):738–745. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91208-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rendu F., Daveloose D., Debouzy J. C., Bourdeau N., Levy-Toledano S., Jain M. K., Apitz-Castro R. Ajoene, the antiplatelet compound derived from garlic, specifically inhibits platelet release reaction by affecting the plasma membrane internal microviscosity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Apr 15;38(8):1321–1328. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90339-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rendu F., Eldor A., Grelac F., Levy-Toledano S., Levitzki A. Tyrosine kinase blockers: new platelet activation inhibitors. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1990 Dec;1(6):713–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rendu F., Marche P., Maclouf J., Girard A., Levy-Toledano S. Triphosphoinositide breakdown and dense body release as the earliest events in thrombin-induced activation of human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Oct 31;116(2):513–519. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90553-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W. Molecular mechanisms of platelet activation. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jan;69(1):58–178. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuttle A. W., Powling M. J., Ritter J. M., Hardisty R. M. Effects of a monoclonal antibody to glycoprotein IIb/IIIa (P256) and of enzymically derived fragments of P256 on human platelets. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Apr 8;65(4):432–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Packham M. A., Tanoue K., Yamazaki H., Mustard J. F. Immunocytochemical localization of fibrinogen on washed human platelets. Lack of requirement for fibrinogen during adenosine diphosphate-induced responses and enhanced fibrinogen binding in a medium with low calcium levels. Blood. 1988 Apr;71(4):850–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama H., Nakamura T., Yanagi S., Taniguchi T., Nakamura S., Yamamura H. Ionophore A23187-induced protein-tyrosine phosphorylation of human platelets: possible synergism between Ca2+ mobilization and protein kinase C activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 31;174(2):922–927. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91506-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vostal J. G., Jackson W. L., Shulman N. R. Cytosolic and stored calcium antagonistically control tyrosine phosphorylation of specific platelet proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16911–16916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., McNally J., Shipman L. J., Godfrey P. P. The action of the protein kinase C inhibitor, staurosporine, on human platelets. Evidence against a regulatory role for protein kinase C in the formation of inositol trisphosphate by thrombin. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 15;249(2):345–350. doi: 10.1042/bj2490345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]