Abstract
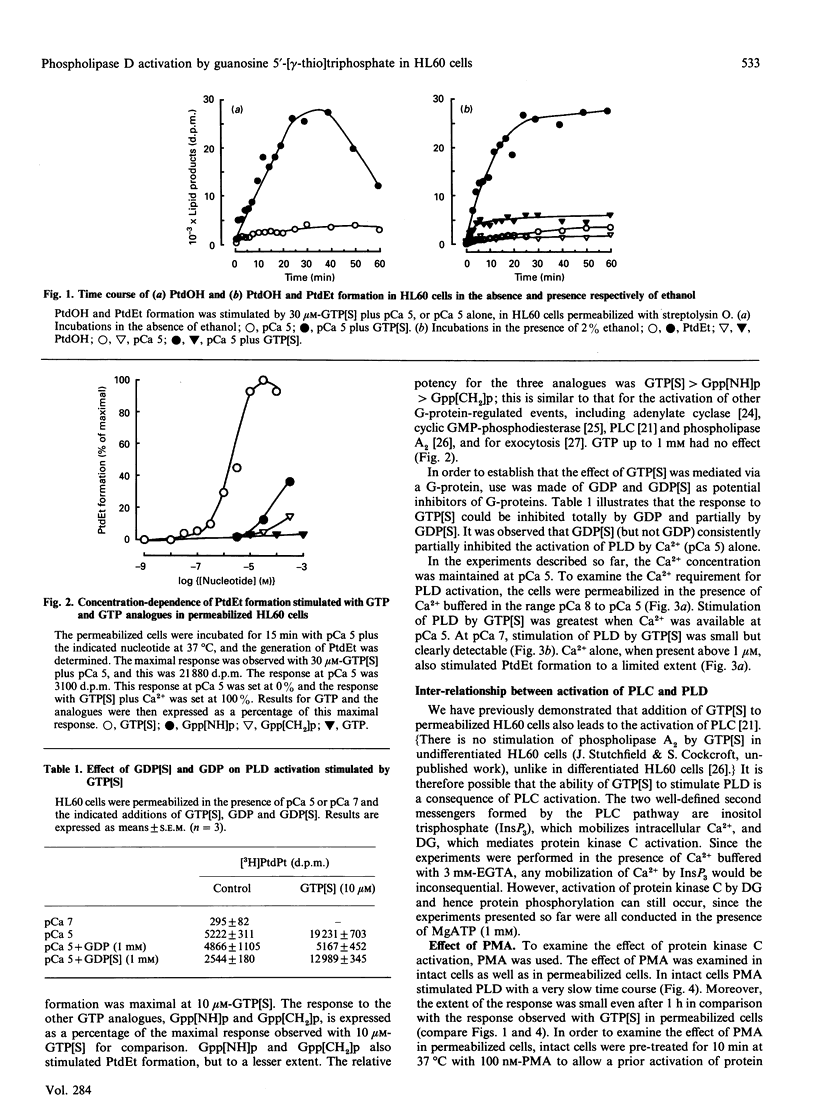
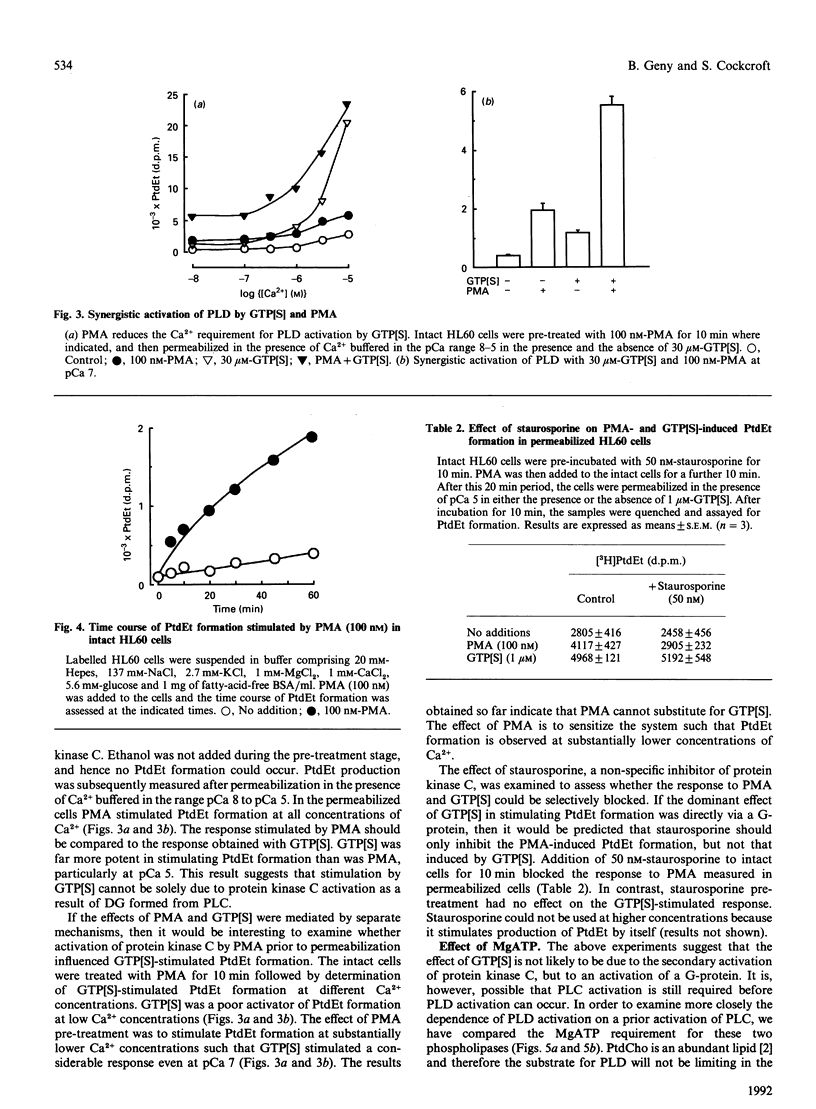
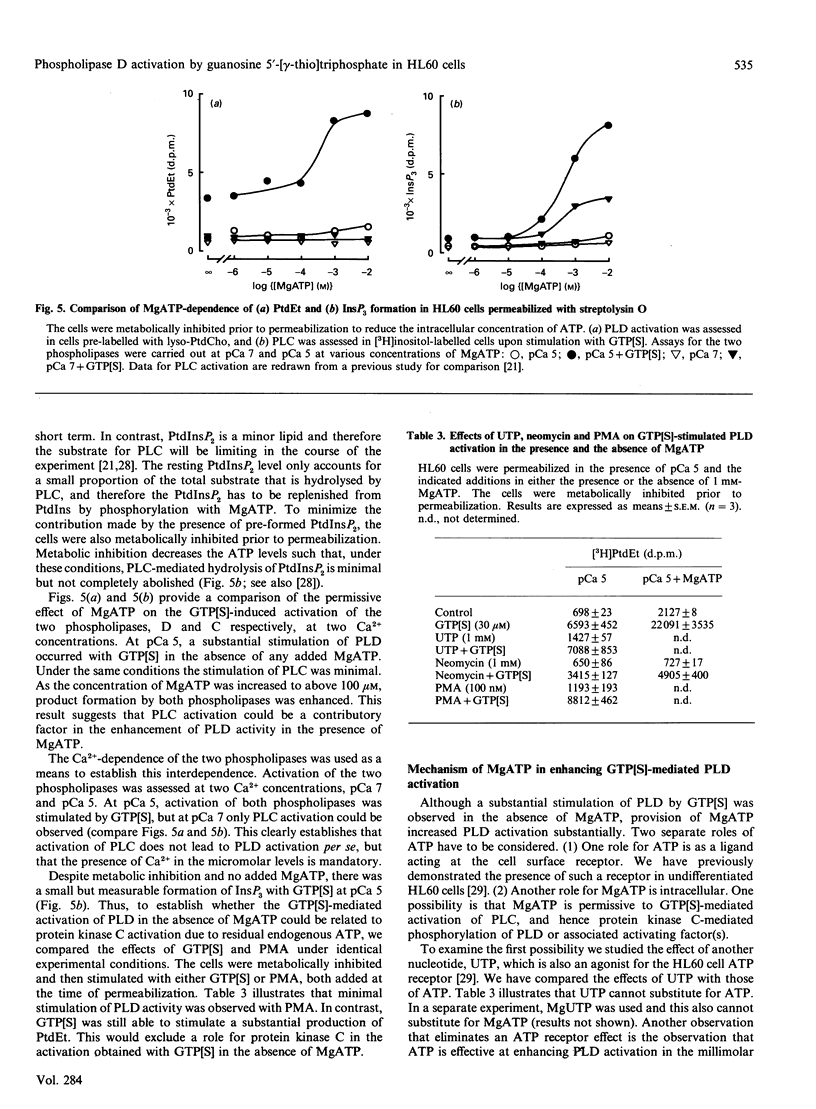
Stimulation of phospholipase D (PLD) by cell surface receptors has been observed in many cell types. We have investigated the mechanism of activation of this enzyme in undifferentiated HL60 cells. GTP analogues and Ca2+ (buffered in the nanomolar to micromolar range) were introduced into HL60 cells in the presence of the permeabilizing agent, streptolysin O. We report that guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP[S]) is a potent activator of phospholipase D when Ca2+ is available at micromolar levels. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate or Ca2+ alone can also stimulate PLD, but to a limited extent. The activation of PLD by GTP[S] can be partially dissociated from GTP[S]-stimulated phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C, suggesting that a G-protein may be directly involved in regulating PLD. However, maximal activation of PLD only occurs under conditions that are permissive to phospholipase C stimulation. We conclude that PLD activation is under dual control, i.e. protein kinase C- as well as G-protein-mediated regulation. Synergistic activation occurs when both pathways are simultaneously stimulated. We conclude that full activation of PLD requires protein kinase C, increased Ca2+ and a GTP-binding protein. Evidence for cytosolic components that may also be involved in obtaining full activation of PLD is also presented.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthes J. C., Wang P., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Billah M. M. Granulocyte phospholipase D is activated by a guanine nucleotide dependent protein factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 28;175(1):236–243. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81225-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Av P., Liscovitch M. Phospholipase D activation by the mitogens platelet-derived growth factor and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate in NIH-3T3 cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):64–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81495-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benistant C., Rubin R. Ethanol inhibits thrombin-induced secretion by human platelets at a site distinct from phospholipase C or protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):489–497. doi: 10.1042/bj2690489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Pai J. K., Mullmann T. J., Egan R. W., Siegel M. I. Regulation of phospholipase D in HL-60 granulocytes. Activation by phorbol esters, diglyceride, and calcium ionophore via protein kinase- independent mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9069–9076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocckino S. B., Blackmore P. F., Wilson P. B., Exton J. H. Phosphatidate accumulation in hormone-treated hepatocytes via a phospholipase D mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15309–15315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollag W. B., Barrett P. Q., Isales C. M., Liscovitch M., Rasmussen H. A potential role for phospholipase-D in the angiotensin-II-induced stimulation of aldosterone secretion from bovine adrenal glomerulosa cells. Endocrinology. 1990 Sep;127(3):1436–1443. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-3-1436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalifa V., Möhn H., Liscovitch M. A neutral phospholipase D activity from rat brain synaptic plasma membranes. Identification and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17512–17519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalifour R. J., Kanfer J. N. Microsomal phospholipase D of rat brain and lung tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Sep 30;96(2):742–747. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91417-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Allan D. The fatty acid composition of phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidate and 1,2-diacylglycerol in stimulated human neutrophils. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 1;222(2):557–559. doi: 10.1042/bj2220557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S. Ca2+-dependent conversion of phosphatidylinositol to phosphatidate in neutrophils stimulated with fMet-Leu-Phe or ionophore A23187. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Aug 15;795(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Nielson C. P., Stutchfield J. Is phospholipase A2 activation regulated by G-proteins? Biochem Soc Trans. 1991 Apr;19(2):333–336. doi: 10.1042/bst0190333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Stutchfield J. Effect of pertussis toxin and neomycin on G-protein-regulated polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. A comparison between HL60 membranes and permeabilized HL60 cells. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 1;256(2):343–350. doi: 10.1042/bj2560343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Stutchfield J. G-proteins, the inositol lipid signalling pathway, and secretion. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 26;320(1199):247–265. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Stutchfield J. The receptors for ATP and fMetLeuPhe are independently coupled to phospholipases C and A2 via G-protein(s). Relationship between phospholipase C and A2 activation and exocytosis in HL60 cells and human neutrophils. Biochem J. 1989 Nov 1;263(3):715–723. doi: 10.1042/bj2630715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabev E., Kasianowicz J., Abbott T., McLaughlin S. Binding of neomycin to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 13;979(1):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90529-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruchalla R. S., Dinh T. T., Kennerly D. A. An indirect pathway of receptor-mediated 1,2-diacylglycerol formation in mast cells. I. IgE receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase D. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2334–2342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell T. W., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Essential synergy between Ca2+ and guanine nucleotides in exocytotic secretion from permeabilized rat mast cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):191–197. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. F., Cabot M. C. Phorbol diesters stimulate the accumulation of phosphatidate, phosphatidylethanol, and diacylglycerol in three cell types. Evidence for the indirect formation of phosphatidylcholine-derived diacylglycerol by a phospholipase D pathway and direct formation of diacylglycerol by a phospholipase C pathway. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14858–14863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. F., Cabot M. C. Vasopressin-induced polyphosphoinositide and phosphatidylcholine degradation in fibroblasts. Temporal relationship for formation of phospholipase C and phospholipase D hydrolysis products. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17468–17473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst K. M., Hughes B. P., Barritt G. J. The roles of phospholipase D and a GTP-binding protein in guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate-stimulated hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine in rat liver plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 15;272(3):749–753. doi: 10.1042/bj2720749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss Z., Anderson W. B. ATP stimulates the hydrolysis of phosphatidylethanolamine in NIH 3T3 cells. Potentiating effects of guanosine triphosphates and sphingosine. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7345–7350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin P. Y., Wiggan G. A., Gilfillan A. M. Activation of phospholipase D in a rat mast (RBL 2H3) cell line. A possible unifying mechanism for IgE-dependent degranulation and arachidonic acid metabolite release. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 1;146(5):1609–1616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscovitch M., Amsterdam A. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone activates phospholipase D in ovarian granulosa cells. Possible role in signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11762–11767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscovitch M., Chalifa V., Danin M., Eli Y. Inhibition of neural phospholipase D activity by aminoglycoside antibiotics. Biochem J. 1991 Oct 1;279(Pt 1):319–321. doi: 10.1042/bj2790319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. W. Formation of diacylglycerol by a phospholipase D-phosphatidate phosphatase pathway specific for phosphatidylcholine in endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Oct 14;962(3):282–296. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90258-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. W., Michaelis K. C. Bradykinin stimulates phosphodiesteratic cleavage of phosphatidylcholine in cultured endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 30;157(3):1271–1279. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. W., Michaelis K. P2-purinergic agonists stimulate phosphodiesteratic cleavage of phosphatidylcholine in endothelial cells. Evidence for activation of phospholipase D. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8847–8856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinson E. A., Goldstein D., Brown J. H. Muscarinic receptor activation of phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis. Relationship to phosphoinositide hydrolysis and diacylglycerol metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14748–14754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A., Dunlop M. Stimulation of insulin release by phospholipase D. A potential role for endogenous phosphatidic acid in pancreatic islet function. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 1;270(2):427–435. doi: 10.1042/bj2700427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielson C. P., Stutchfield J., Cockcroft S. Chemotactic peptide stimulation of arachidonic acid release in HL60 cells, an interaction between G protein and phospholipase C mediated signal transduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Oct 16;1095(1):83–89. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson S. C., Bowman E. P., Lambeth J. D. Phospholipase D activation in a cell-free system from human neutrophils by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and guanosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate). Activation is calcium dependent and requires protein factors in both the plasma membrane and cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17236–17242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai J. K., Pachter J. A., Weinstein I. B., Bishop W. R. Overexpression of protein kinase C beta 1 enhances phospholipase D activity and diacylglycerol formation in phorbol ester-stimulated rat fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):598–602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai J. K., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Billah M. M. Phospholipase D catalyzes phospholipid metabolism in chemotactic peptide-stimulated HL-60 granulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12472–12477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepitoni S., Mallon R. G., Pai J. K., Borkowski J. A., Buck M. A., McQuade R. D. Phospholipase D activity and phosphatidylethanol formation in stimulated HeLa cells expressing the human m1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 15;176(1):453–458. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90945-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeuffer T., Eckstein F. Topology of the GTP-binding site of adenylyl cyclase from pigeon erythrocytes. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 1;67(3):354–358. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80563-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Z., Drewes L. R. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor regulates phosphatidylcholine phospholipase D in canine brain. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21720–21724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Z., Reddy P. V., Drewes L. R. Guanine nucleotide-binding protein regulation of microsomal phospholipase D activity of canine cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1990 May;54(5):1632–1638. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold S. L., Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A., McIntyre T. M. Activation of human neutrophil phospholipase D by three separable mechanisms. FASEB J. 1990 Feb 1;4(2):208–214. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.2.2105252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandmann J., Peralta E. G., Wurtman R. J. Coupling of transfected muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes to phospholipase D. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6031–6034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacht J. Purification of polyphosphoinositides by chromatography on immobilized neomycin. J Lipid Res. 1978 Nov;19(8):1063–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shukla S. D., Halenda S. P. Phospholipase D in cell signalling and its relationship to phospholipase C. Life Sci. 1991;48(9):851–866. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutchfield J., Cockcroft S. Guanine nucleotides stimulate polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase and exocytotic secretion from HL60 cells permeabilized with streptolysin O. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 1;250(2):375–382. doi: 10.1042/bj2500375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutchfield J., Cockcroft S. Undifferentiated HL60 cells respond to extracellular ATP and UTP by stimulating phospholipase C activation and exocytosis. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 26;262(2):256–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80204-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tettenborn C. S., Mueller G. C. 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate activates phosphatidylethanol and phosphatidylglycerol synthesis by phospholipase D in cell lysates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 30;155(1):249–255. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81076-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. M., Geny B., Cockcroft S. Identification of a novel cytosolic poly-phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C (PLC-86) as the major G-protein-regulated enzyme. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2507–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07790.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Meulen J., Haslam R. J. Phorbol ester treatment of intact rabbit platelets greatly enhances both the basal and guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate-stimulated phospholipase D activities of isolated platelet membranes. Physiological activation of phospholipase D may be secondary to activation of phospholipase C. Biochem J. 1990 Nov 1;271(3):693–700. doi: 10.1042/bj2710693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P., Anthes J. C., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Billah M. M. Existence of cytosolic phospholipase D. Identification and comparison with membrane-bound enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):14877–14880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka G., Eckstein F., Stryer L. Interaction of retinal transducin with guanosine triphosphate analogues: specificity of the gamma-phosphate binding region. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 7;25(20):6149–6153. doi: 10.1021/bi00368a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. F., Freer S., Benson A. A. Transphosphatidylation by phospholipase D. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 10;242(3):477–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuli I., Tomonaga A., Synderman R. Chemoattractant receptor functions in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes are divergently altered by membrane fluidizers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5906–5910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


