Abstract
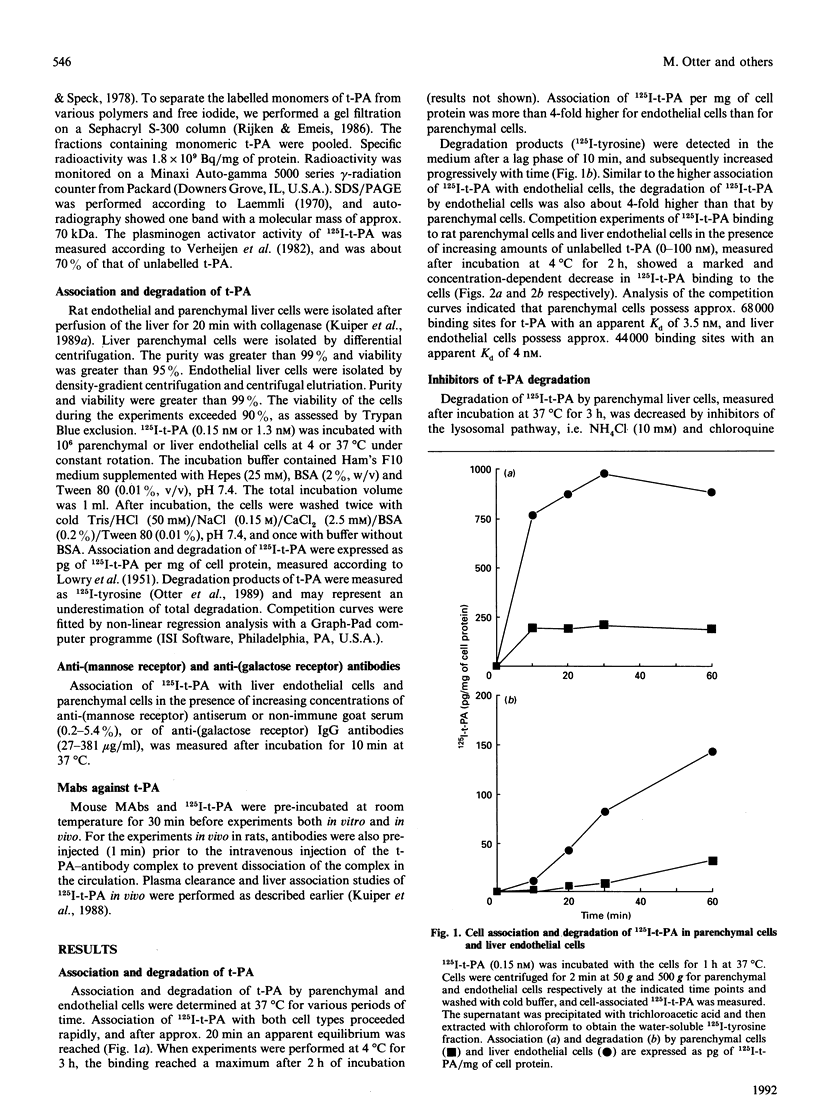
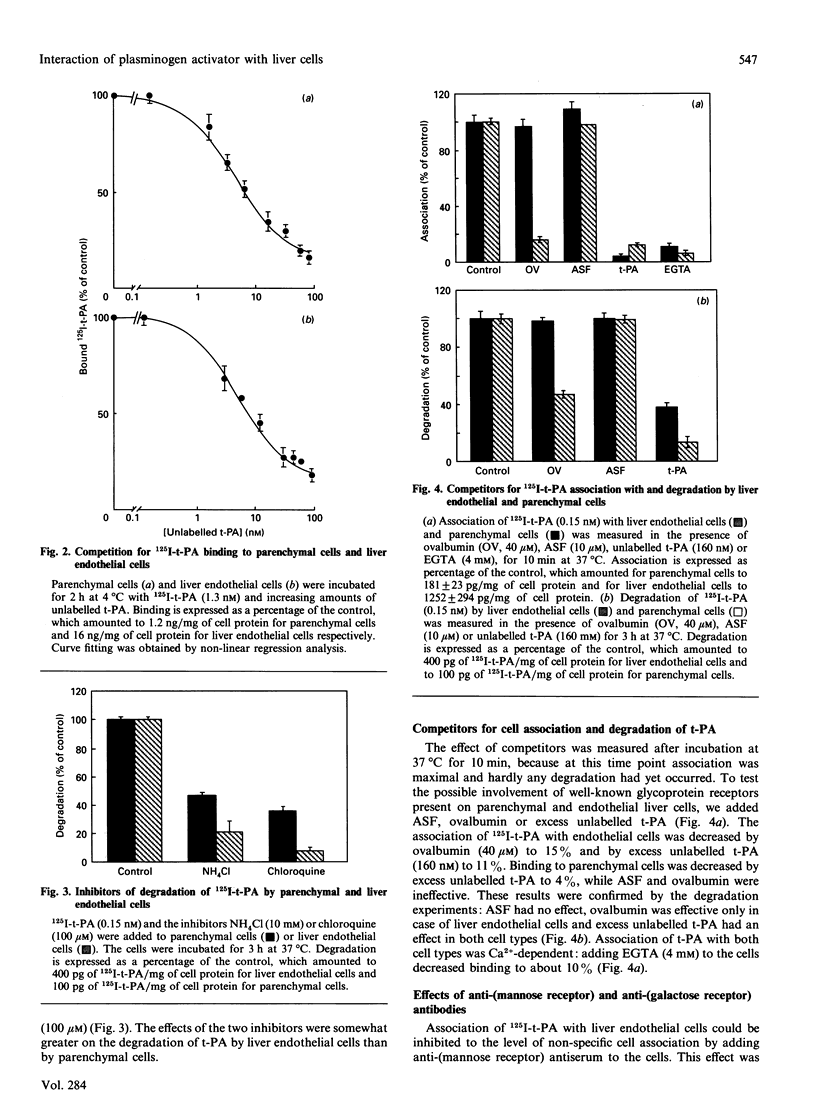
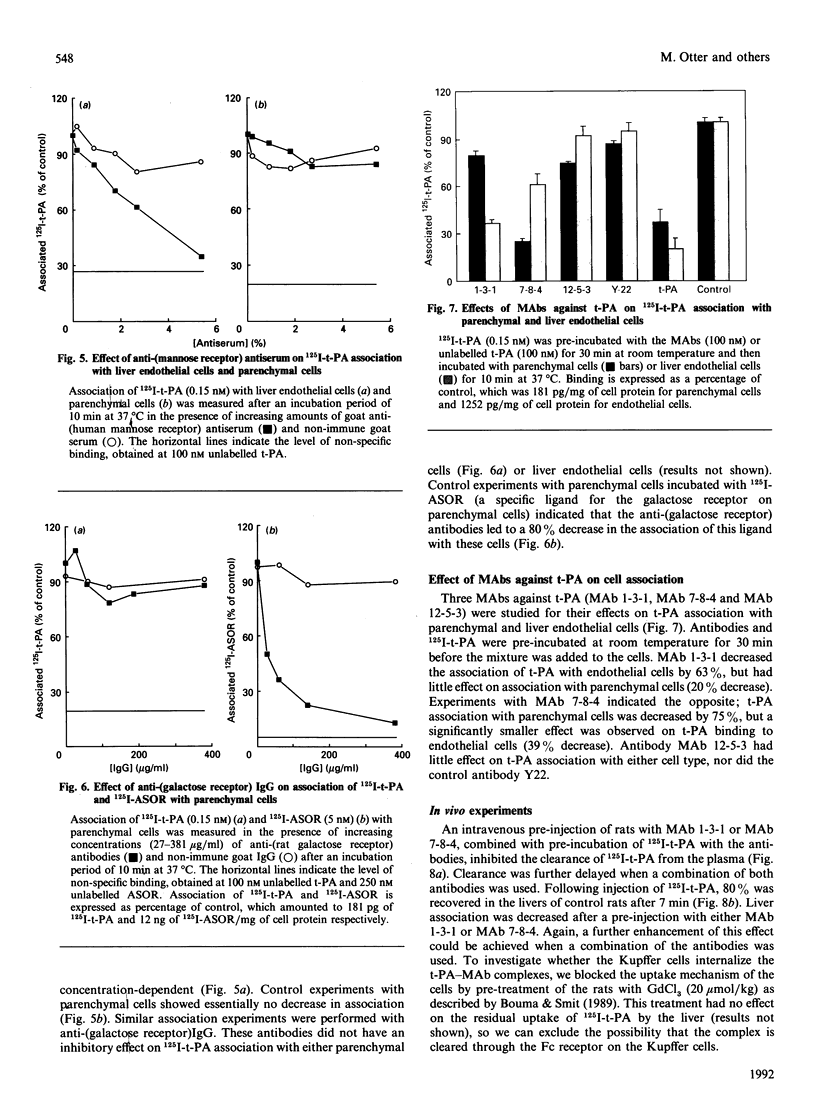
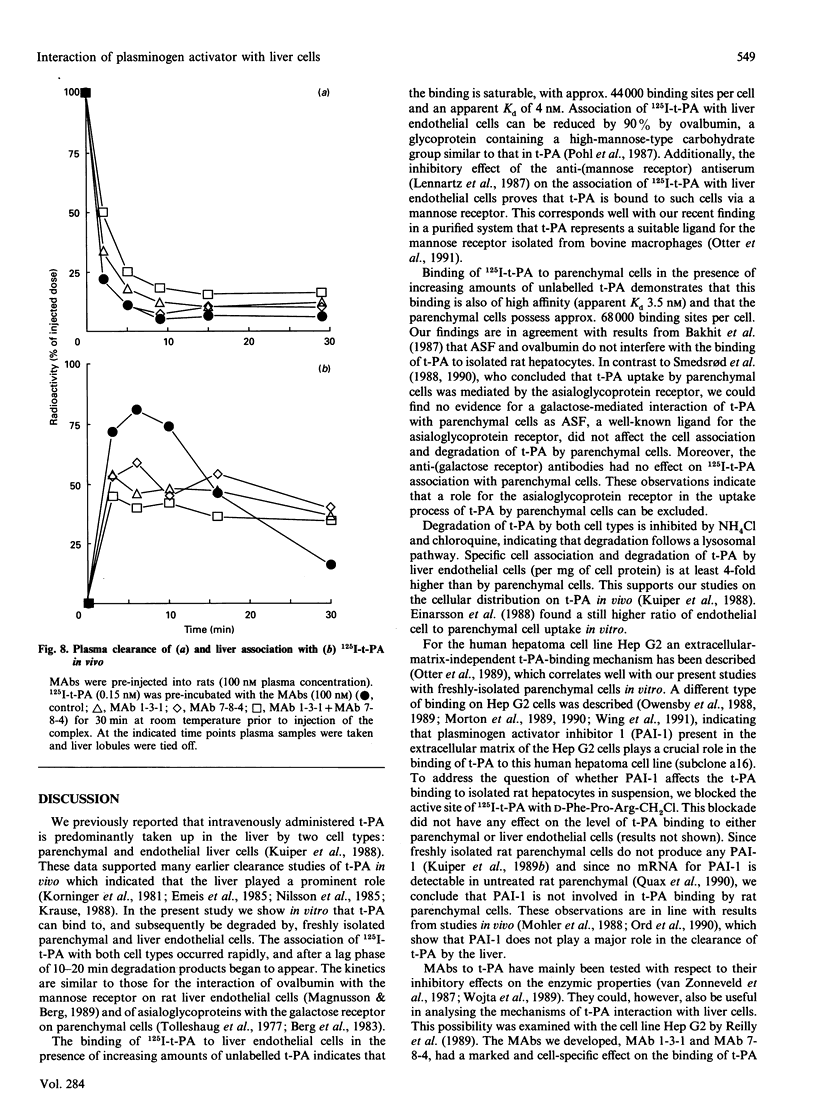
The interaction of 125I-labelled tissue-type plasminogen activator (125I-t-PA) with freshly isolated rat parenchymal and endothelial liver cells was studied. Binding experiments at 4 degrees C with parenchymal cells and endothelial liver cells indicated the presence of 68,000 and 44,000 high-affinity t-PA-binding sites, with an apparent Kd of 3.5 and 4 nM respectively. Association of 125I-t-PA with parenchymal cells was Ca(2+)-dependent and was not influenced by asialofetuin, a known ligand for the galactose receptor. Association of 125I-t-PA with liver endothelial cells was Ca(2+)-dependent and mannose-specific, since ovalbumin (a mannose-terminated glycoprotein) inhibited the cell association of t-PA. Association of 125I-t-PA with liver endothelial cells was inhibited by anti-(human mannose receptor) antiserum. Anti-(galactose receptor) IgG had no effect on 125I-t-PA association with either cell type. Degradation of 125I-t-PA at 37 degrees C by both cell types was inhibited by chloroquine or NH4Cl, indicating that t-PA is degraded lysosomally. in vitro experiments with three monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) demonstrated that anti-t-PA MAb 1-3-1 specifically decreased association of 125I-t-PA with the endothelial cells, and anti-t-PA Mab 7-8-4 inhibited association with the parenchymal cells. Results of competition experiments in rats in vivo with these antibodies were in agreement with findings in vitro. Both antibodies decreased the liver uptake of 125I-t-PA, while a combination of the two antibodies was even more effective in reducing the liver association of 125I-t-PA and increasing its plasma half-life. We conclude from these data that clearance of t-PA by the liver is regulated by at least two pathways, one on parenchymal cells (not galactose/mannose-mediated) and another on liver endothelial cells (mediated by a mannose receptor). Results with the MAbs imply that two distinct sites on the t-PA molecule are involved in binding to parenchymal cells and liver endothelial cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann F., Kruithof I. E. Tissue plasminogen activator: chemical and physiological aspects. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1984 Jan;10(1):6–17. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakhit C., Lewis D., Billings R., Malfroy B. Cellular catabolism of recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator. Identification and characterization of a novel high affinity uptake system on rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8716–8720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg T., Blomhoff R., Naess L., Tolleshaug H., Drevon C. A. Monensin inhibits receptor-mediated endocytosis of asialoglycoproteins in rat hepatocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Oct 15;148(2):319–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90156-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugelski P. J., Fong K. L., Klinkner A., Sowinski J., Rush G., Morgan D. G. Uptake of human recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator by rat hepatocytes in vivo: an electron microscope autoradiographic study. Thromb Res. 1989 Feb 1;53(3):287–303. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90104-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchill S. A., Virden R., Fuller B. B., Thody A. J. Regulation of tyrosinase synthesis by alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone in hair follicular melanocytes of the mouse. J Endocrinol. 1988 Jan;116(1):17–23. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1160017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D. On the regulation and control of fibrinolysis. Edward Kowalski Memorial Lecture. Thromb Haemost. 1980 Jun 18;43(2):77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarsson M., Smedsrød B., Pertoft H. Uptake and degradation of tissue plasminogen activator in rat liver. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Jun 16;59(3):474–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeis J. J., van den Hoogen C. M., Jense D. Hepatic clearance of tissue-type plasminogen activator in rats. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Oct 30;54(3):661–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs H. E., Berger H., Jr, Pizzo S. V. Catabolism of human tissue plasminogen activator in mice. Blood. 1985 Mar;65(3):539–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korninger C., Stassen J. M., Collen D. Turnover of human extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator in rabbits. Thromb Haemost. 1981 Oct;46(3):658–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause J., Seydel W., Heinzel G., Tanswell P. Different receptors mediate the hepatic catabolism of tissue-type plasminogen activator and urokinase. Biochem J. 1990 May 1;267(3):647–652. doi: 10.1042/bj2670647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuiper J., Kamps J. A., Van Berkel T. J. Identification of the inhibitor of the plasminogen activator as the major protein secreted by endothelial rat liver cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):229–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80227-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuiper J., Kamps J. A., Van Berkel T. J. Induction of ornithine decarboxylase in rat liver by phorbol ester is mediated by prostanoids from Kupffer cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6874–6878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuiper J., Otter M., Rijken D. C., van Berkel T. J. Characterization of the interaction in vivo of tissue-type plasminogen activator with liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18220–18224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennartz M. R., Cole F. S., Shepherd V. L., Wileman T. E., Stahl P. D. Isolation and characterization of a mannose-specific endocytosis receptor from human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):9942–9944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson S., Berg T. Extremely rapid endocytosis mediated by the mannose receptor of sinusoidal endothelial rat liver cells. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 1;257(3):651–656. doi: 10.1042/bj2570651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton P. A., Owensby D. A., Sobel B. E., Schwartz A. L. Catabolism of tissue-type plasminogen activator by the human hepatoma cell line Hep G2. Modulation by plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7228–7235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton P. A., Owensby D. A., Wun T. C., Billadello J. J., Schwartz A. L. Identification of determinants involved in binding of tissue-type plasminogen activator-plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 complexes to HepG2 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14093–14099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson S., Einarsson M., Ekvärn S., Häggroth L., Mattsson C. Turnover of tissue plasminogen activator in normal and hepatectomized rabbits. Thromb Res. 1985 Aug 15;39(4):511–521. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90174-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otter M., Barrett-Bergshoeff M. M., Rijken D. C. Binding of tissue-type plasminogen activator by the mannose receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13931–13935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otter M., Van Berkel T. J., Rijken D. C. Binding and degradation of tissue-type plasminogen activator by the human hepatoma cell line Hep G2. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Sep 29;62(2):667–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owensby D. A., Morton P. A., Schwartz A. L. Interactions between tissue-type plasminogen activator and extracellular matrix-associated plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 in the human hepatoma cell line HepG2. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18180–18187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owensby D. A., Sobel B. E., Schwartz A. L. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of tissue-type plasminogen activator by the human hepatoma cell line Hep G2. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10587–10594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl G., Kenne L., Nilsson B., Einarsson M. Isolation and characterization of three different carbohydrate chains from melanoma tissue plasminogen activator. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 30;170(1-2):69–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13668.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax P. H., van den Hoogen C. M., Verheijen J. H., Padro T., Zeheb R., Gelehrter T. D., van Berkel T. J., Kuiper J., Emeis J. J. Endotoxin induction of plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 mRNA in rat tissues in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15560–15563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly T. M., Knabb R. M., Chiu A. T., Bradfute D. L., Timmermans P. B. Monoclonal antibodies to tissue-type plasminogen activator which prolong its clearance in vivo. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Apr 25;61(2):259–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Collen D. Purification and characterization of the plasminogen activator secreted by human melanoma cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):7035–7041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Emeis J. J. Clearance of the heavy and light polypeptide chains of human tissue-type plasminogen activator in rats. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 15;238(3):643–646. doi: 10.1042/bj2380643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Otter M., Kuiper J., van Berkel T. J. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) by liver cells. Thromb Res Suppl. 1990;10:63–71. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(90)90379-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smedsrød B., Einarsson M. Clearance of tissue plasminogen activator by mannose and galactose receptors in the liver. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Feb 19;63(1):60–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smedsrød B., Einarsson M., Pertoft H. Tissue plasminogen activator is endocytosed by mannose and galactose receptors of rat liver cells. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Jun 16;59(3):480–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Pricer W. E., Jr, Ashwell G. Subcellular membrane topology and turnover of a rat hepatic binding protein specific for asialoglycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1038–1043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolleshaug H., Berg T., Nilsson M., Norum K. R. Uptake and degradation of 125I-labelled asialo-fetuin by isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 25;499(1):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheijen J. H., Mullaart E., Chang G. T., Kluft C., Wijngaards G. A simple, sensitive spectrophotometric assay for extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator applicable to measurements in plasma. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Dec 27;48(3):266–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasser M. N., Koppert P. W., Arndt J. W., Emeis J. J., Feitsma R. I., Pauwels E. K., Nieuwenhuizen W. An antifibrin monoclonal antibody useful in immunoscintigraphic detection of thrombi. Blood. 1989 Aug 1;74(2):708–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead P. H., Sammons H. G. A simple technique for the isolation of orosomucoid from normal and pathological sera. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jul 27;124(1):209–211. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing L. R., Bennett B., Booth N. A. The receptor for tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) in complex with its inhibitor, PAI-1, on human hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jan 14;278(1):95–97. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80092-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojta J., Beckmann R., Turcu L., Wagner O. F., van Zonneveld A. J., Binder B. R. Functional characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed against fibrin binding domains of tissue-type plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7957–7961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zonneveld A. J., Veerman H., Brakenhoff J. P., Aarden L. A., Cajot J. F., Pannekoek H. Mapping of epitopes on human tissue-type plasminogen activator with recombinant deletion mutant proteins. Thromb Haemost. 1987 Feb 3;57(1):82–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


