Abstract
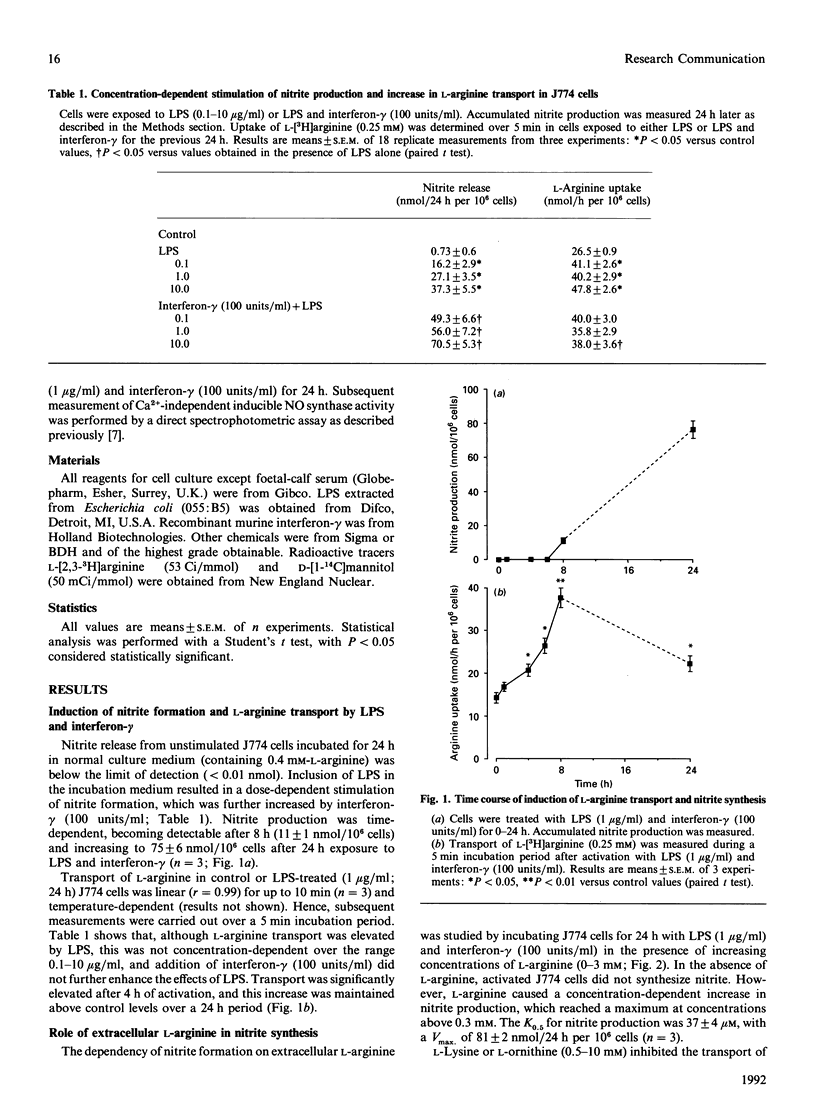
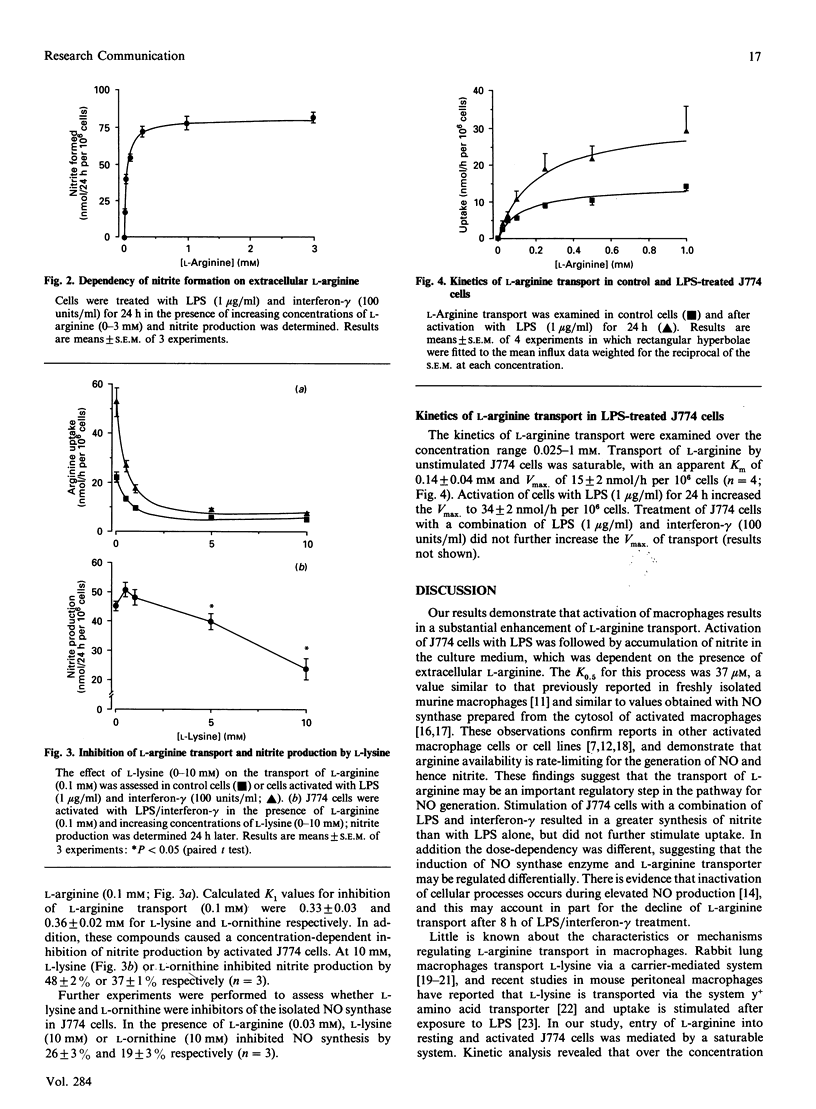
Transport of L-arginine and nitrite production were examined in the murine macrophage cell line J774. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced a dose- and time-dependent stimulation of nitrite production, which was further increased in the presence of interferon-gamma. Nitrite synthesis was absolutely dependent on extracellular L-arginine and inhibited in the presence of L-lysine or L-ornithine. In unactivated J774 cells L-arginine transport was saturable, with an apparent Km of 0.14 +/- 0.04 mM and Vmax. of 15 +/- 2 nmol/h per 10(6) cells. LPS (1 microgram/ml) induced a time-dependent stimulation of L-arginine transport, and after 24 h the Vmax. increased to 34 +/- 2 nmol/h per 10(6) cells. These findings indicate that activation of J774 cells with LPS produces an increase in both L-arginine transport and nitrite synthesis. The elevated rate of L-arginine transport in activated J774 cells may provide a mechanism for sustained substrate supply during enhanced utilization of L-arginine for the generation of NO.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O., Hamilton T. A. The cell biology of macrophage activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:283–318. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albina J. E., Caldwell M. D., Henry W. L., Jr, Mills C. D. Regulation of macrophage functions by L-arginine. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):1021–1029. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albina J. E., Mills C. D., Barbul A., Thirkill C. E., Henry W. L., Jr, Mastrofrancesco B., Caldwell M. D. Arginine metabolism in wounds. Am J Physiol. 1988 Apr;254(4 Pt 1):E459–E467. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.4.E459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannai S., Sato H., Ishii T., Taketani S. Enhancement of glutathione levels in mouse peritoneal macrophages by sodium arsenite, cadmium chloride and glucose/glucose oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 17;1092(2):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90153-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Straus D., Baughn R. E., Imhoff J. Enhancement of carrier-mediated transport after immunologic activation of peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1827–1835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie G. A. Activated macrophages kill tumour cells by releasing arginase. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):758–759. doi: 10.1038/273758a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie G. A., Gyure L., Cifuentes L. Microenvironmental arginine depletion by macrophages in vivo. Br J Cancer. 1979 Jun;39(6):613–620. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1979.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Rosa M., Radomski M., Carnuccio R., Moncada S. Glucocorticoids inhibit the induction of nitric oxide synthase in macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1246–1252. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91583-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger D. L., Hibbs J. B., Jr, Perfect J. R., Durack D. T. Metabolic fate of L-arginine in relation to microbiostatic capability of murine macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):264–273. doi: 10.1172/JCI114422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti G. G., Gazzola G. C., Borghetti A. F., Franchi-Gazzola R. Adaptive regulation of amino acid transport across the cell membrane in avian and mammalian tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 6;406(2):264–279. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschildt S., Lückhoff A., Mülsch A., Kohler J., Bessler W., Busse R. Induction and activity of NO synthase in bone-marrow-derived macrophages are independent of Ca2+. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 1;270(2):351–356. doi: 10.1042/bj2700351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hevel J. M., White K. A., Marletta M. A. Purification of the inducible murine macrophage nitric oxide synthase. Identification as a flavoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):22789–22791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Vavrin Z., Rachlin E. M. Nitric oxide: a cytotoxic activated macrophage effector molecule. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Vavrin Z., Taintor R. R. L-arginine is required for expression of the activated macrophage effector mechanism causing selective metabolic inhibition in target cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):550–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorens P. G., Van Overveld F. J., Bult H., Vermeire P. A., Herman A. G. L-arginine-dependent production of nitrogen oxides by rat pulmonary macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug 6;200(2-3):205–209. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90573-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R., Geiges M., Keist R. L-arginine-dependent reactive nitrogen intermediates as mediators of tumor cell killing by activated macrophages. Cancer Res. 1990 Mar 1;50(5):1421–1425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A., Yoon P. S., Iyengar R., Leaf C. D., Wishnok J. S. Macrophage oxidation of L-arginine to nitrite and nitrate: nitric oxide is an intermediate. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8706–8711. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Secretory products of macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):319–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI112815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Meister A. The gamma-glutamyl cycle: a possible transport system for amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1248–1255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pofit J. F., Strauss P. R. Membrane transport by macrophages in suspension and adherent to glass. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Aug;92(2):249–255. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040920213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouzer C. A., Scott W. A., Griffith O. W., Hamill A. L., Cohn Z. A. Glutathione metabolism in resting and phagocytizing peritoneal macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):2002–2008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Ishii T., Sugita Y., Bannai S. Changes in neutral amino acid transport activity in myeloid leukemia cells differentiated by lipopolysaccharide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Aug 7;983(2):259–263. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90242-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Ishii T., Sugita Y., Bannai S. Induction of cationic amino acid transport activity in mouse peritoneal macrophages by lipopolysaccharide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Oct 14;1069(1):46–52. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90102-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss P. R., Berlin R. D. Effects of serum on membrane transport. I. Separation and preliminary characterization of factors which depress lysine or stimulate adenosine transport in rabbit alveolar macrophages. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):359–368. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Marletta M. A. Mammalian nitrate biosynthesis: mouse macrophages produce nitrite and nitrate in response to Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7738–7742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Marletta M. A. Synthesis of nitrite and nitrate in murine macrophage cell lines. Cancer Res. 1987 Nov 1;47(21):5590–5594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Nathan C. F. Nitric oxide. A macrophage product responsible for cytostasis and respiratory inhibition in tumor target cells. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1543–1555. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsan M. F., Berlin R. D. Membrane transport in the rabbit alveolar macrophage. The specificity and characteristics of amino acid transport systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 6;241(1):155–169. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90313-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Bannai S. Induction of cystine transport activity in mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):628–640. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F. The transport of cationic amino acids across the plasma membrane of mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 9;822(3-4):355–374. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(85)90015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yui Y., Hattori R., Kosuga K., Eizawa H., Hiki K., Kawai C. Purification of nitric oxide synthase from rat macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12544–12547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


