Abstract
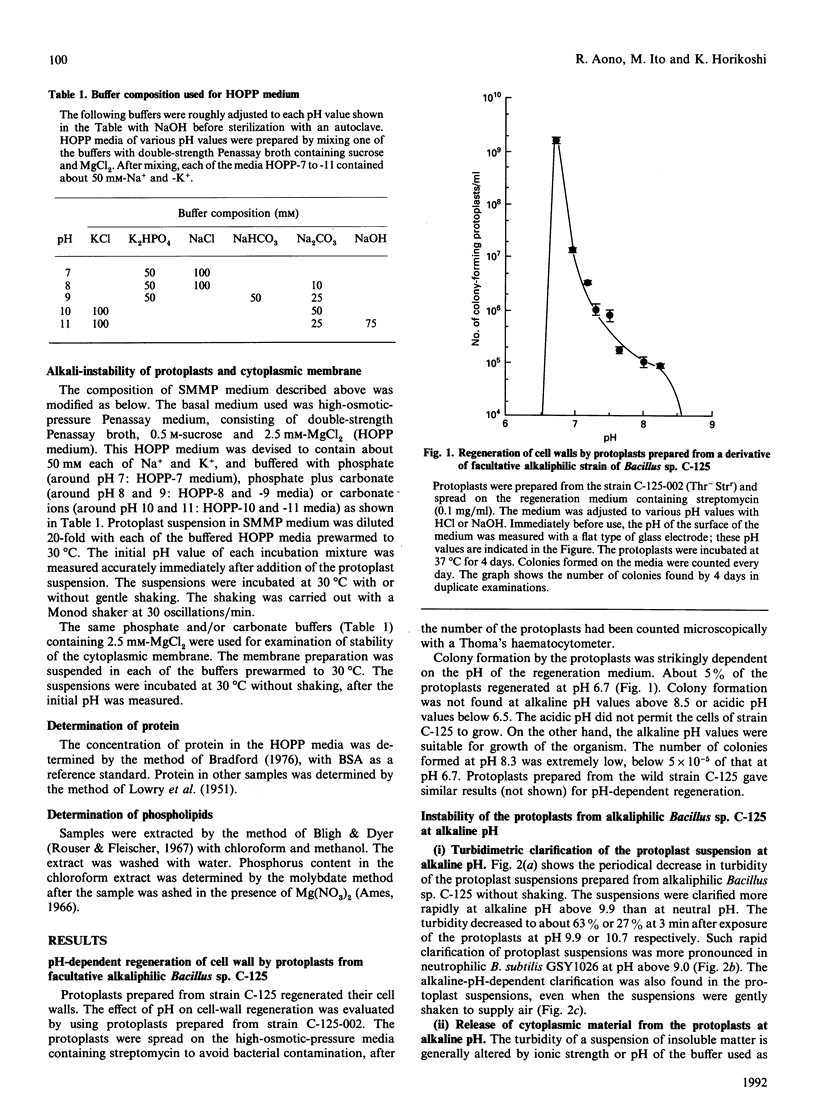
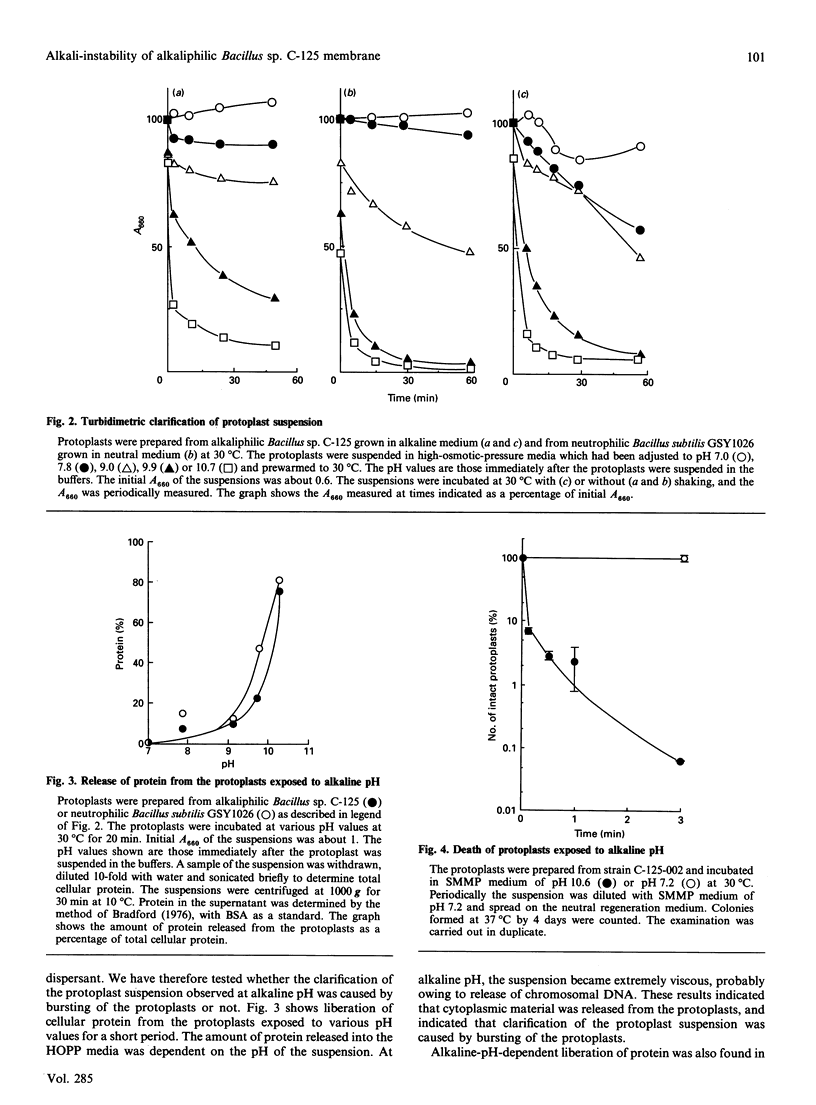
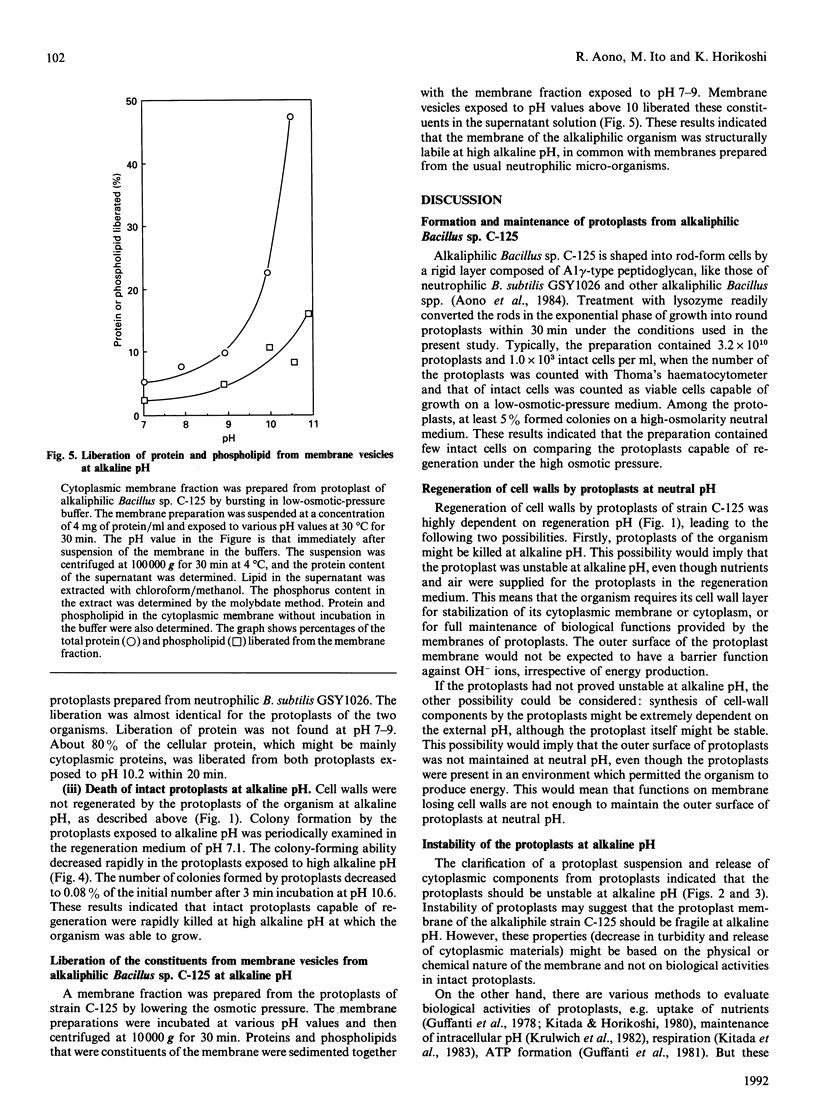
Cell walls of facultative alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. C-125 consist of three polymers (peptidoglycan, teichuronopeptide and teichuronic acid). Protoplasts prepared from the strain with egg-white lysozyme regenerated cell walls at neutral pH, but not at pH above 8.5. The protoplasts were susceptible to lysis at alkaline pH. The protoplasts exposed to alkaline pH rapidly burst and lost ability to regenerate their cell walls. The alkali-instability was similar to that of protoplasts from neutrophilic Bacillus subtilis 168. The membrane vesicles were also labile at alkaline pH. The acidic wall components of strain C-125 may contribute to stabilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of cells growing at alkaline pH, probably by shielding the membrane from direct exposure to an alkaline environment.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aono R. Characterization of structural component of cell walls of alkalophilic strain of Bacillus sp. C-125. Preparation of poly(gamma-L-glutamate) from cell wall component. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):467–472. doi: 10.1042/bj2450467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aono R., Horikoshi K., Goto S. Composition of the peptidoglycan of alkalophilic Bacillus spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):688–689. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.688-689.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aono R., Ohtani M. Loss of alkalophily in cell-wall-component-defective mutants derived from alkalophilic Bacillus C-125. Isolation and partial characterization of the mutants. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 15;266(3):933–936. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aono R., Uramoto M. Presence of fucosamine in teichuronic acid of the alkalophilic Bacillus strain C-125. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 1;233(1):291–294. doi: 10.1042/bj2330291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S., Cohen S. N. High frequency transformation of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts by plasmid DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 5;168(1):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00267940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guffanti A. A., Bornstein R. F., Krulwich T. A. Oxidative phosphorylation by membrane vesicles from Bacillus alcalophilus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 13;635(3):619–630. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(81)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guffanti A. A., Susman P., Blanco R., Krulwich T. A. The protonmotive force and alpha-aminoisobutyric acid transport in an obligately alkalophilic bacterium. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):708–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitada M., Horikoshi K. Sodium-ion stimulated amino acid uptake in membrane vesicles of alkalophilic Bacillus no. 8-1. J Biochem. 1980 Dec;88(6):1757–1764. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitada M., Lewis R. J., Krulwich T. A. Respiratory chain of the alkalophilic bacterium Bacillus firmus RAB and its non-alkalophilic mutant derivative. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):330–335. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.330-335.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Guffanti A. A., Bornstein R. F., Hoffstein J. A sodium requirement for growth, solute transport, and pH homeostasis in Bacillus firmus RAB. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1885–1889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


