Abstract
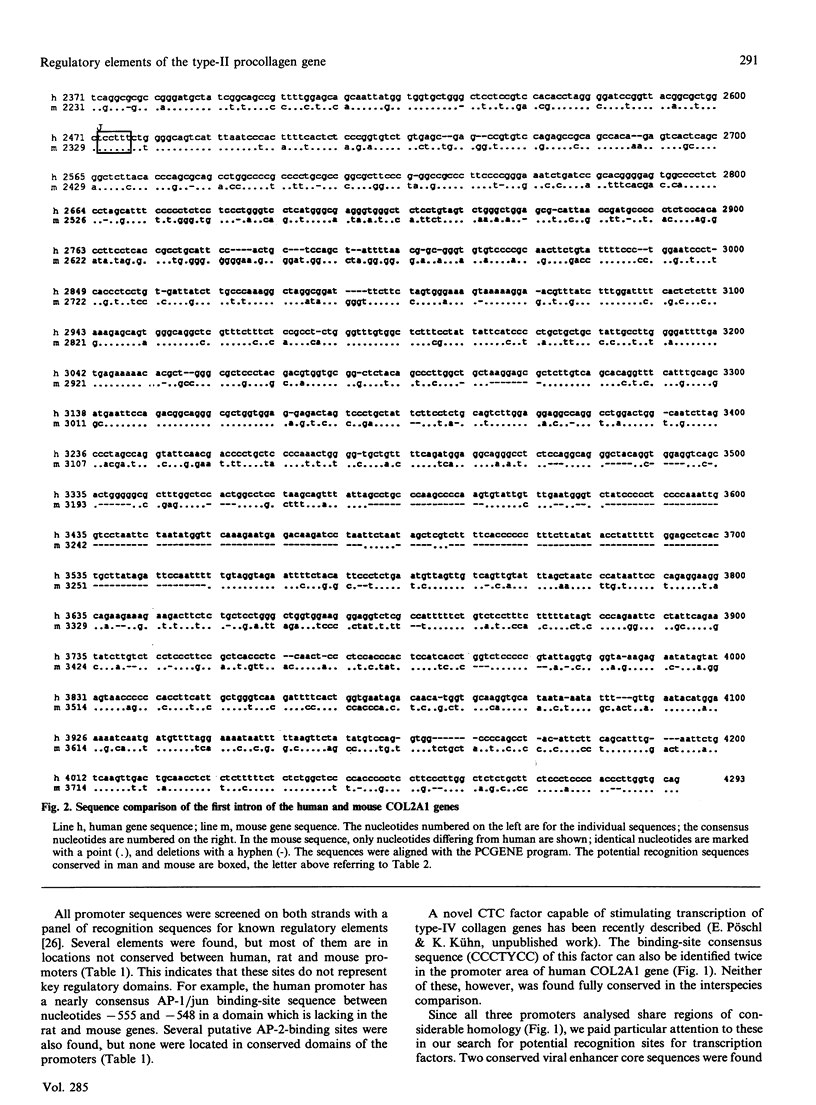
Transcription of the type-II procollagen gene (COL2A1) is very specifically restricted to a limited number of tissues, particularly cartilages. In order to identify transcription-control motifs we have sequenced the promoter region and the first intron of the human and mouse COL2A1 genes. With the assumption that these motifs should be well conserved during evolution, we have searched for potential elements important for the tissue-specific transcription of the COL2A1 gene by aligning the two sequences with each other and with the available rat type-II procollagen sequence for the promoter. With this approach we could identify specific evolutionarily well-conserved motifs in the promoter area. On the other hand, several suggested regulatory elements in the promoter region did not show evolutionary conservation. In the middle of the first intron we found a cluster of well-conserved transcription-control elements and we conclude that these conserved motifs most probably possess a significant function in the control of the tissue-specific transcription of the COL2A1 gene. We also describe locations of additional, highly conserved nucleotide stretches, which are good candidate regions in the search for binding sites of yet-uncharacterized cartilage-specific transcription regulators of the COL2A1 gene.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ala-Kokko L., Baldwin C. T., Moskowitz R. W., Prockop D. J. Single base mutation in the type II procollagen gene (COL2A1) as a cause of primary osteoarthritis associated with a mild chondrodysplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6565–6568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ala-Kokko L., Prockop D. J. Completion of the intron-exon structure of the gene for human type II procollagen (COL2A1): variations in the nucleotide sequences of the alleles from three chromosomes. Genomics. 1990 Nov;8(3):454–460. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90031-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ala-Kokko L., Prockop D. J. Efficient procedure for preparing cosmid libraries from microgram quantities of genomic DNA fragments size fractionated by gel electrophoresis. Matrix. 1990 Oct;10(5):279–284. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8832(11)80182-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., McKay J., Morishima J. K., Devarayalu S., Gelinas R. E. Regulatory elements in the first intron contribute to transcriptional control of the human alpha 1(I) collagen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8869–8873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Sage H. Regulation of collagen gene expression. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1989;37:67–106. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60695-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francomano C. A., Liberfarb R. M., Hirose T., Maumenee I. H., Streeten E. A., Meyers D. A., Pyeritz R. E. The Stickler syndrome: evidence for close linkage to the structural gene for type II collagen. Genomics. 1987 Dec;1(4):293–296. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton W., Miyashita T., Kohno K., Hassell J. R., Yamada Y. Identification of a phenotype-specific enhancer in the first intron of the rat collagen II gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8864–8868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton R. G., Katzenstein P. L., Moskowitz R. W., Weaver E. J., Malemud C. J., Pathria M. N., Jimenez S. A., Prockop D. J. Genetic linkage of a polymorphism in the type II procollagen gene (COL2A1) to primary osteoarthritis associated with mild chondrodysplasia. N Engl J Med. 1990 Feb 22;322(8):526–530. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199002223220807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton R. G., Weaver E. J., Struyk A. F., Knobloch W. H., King R. A., Norris K., Shamban A., Uitto J., Jimenez S. A., Prockop D. J. Genetic linkage analysis of hereditary arthro-ophthalmopathy (Stickler syndrome) and the type II procollagen gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Nov;45(5):681–688. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Vissing H., Ramirez F., Rogers D., Rimoin D. Identification of the molecular defect in a family with spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia. Science. 1989 May 26;244(4907):978–980. doi: 10.1126/science.2543071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locker J., Buzard G. A dictionary of transcription control sequences. DNA Seq. 1990;1(1):3–11. doi: 10.3109/10425179009041342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovell-Badge R. H., Bygrave A., Bradley A., Robertson E., Tilly R., Cheah K. S. Tissue-specific expression of the human type II collagen gene in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2803–2807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metsäranta M., Toman D., de Crombrugghe B., Vuorio E. Mouse type II collagen gene. Complete nucleotide sequence, exon structure, and alternative splicing. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16862–16869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Gerster T., Schaffner W. Enhancer sequences and the regulation of gene transcription. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 1;176(3):485–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14306.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunez A. M., Kohno K., Martin G. R., Yamada Y. Promoter region of the human pro-alpha 1(II)-collagen gene. Gene. 1986;44(1):11–16. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palotie A., Väisänen P., Ott J., Ryhänen L., Elima K., Vikkula M., Cheah K., Vuorio E., Peltonen L. Predisposition to familial osteoarthrosis linked to type II collagen gene. Lancet. 1989 Apr 29;1(8644):924–927. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossouw C. M., Vergeer W. P., du Plooy S. J., Bernard M. P., Ramirez F., de Wet W. J. DNA sequences in the first intron of the human pro-alpha 1(I) collagen gene enhance transcription. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15151–15157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. C., Sieraski M., Sandell L. J. The human type II procollagen gene: identification of an additional protein-coding domain and location of potential regulatory sequences in the promoter and first intron. Genomics. 1990 Sep;8(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90224-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg M., Mäkelä J. K., Multimäki P., Vuorio T., Vuorio E. Construction of a human pro alpha 1(III) collagen cDNA clone and localization of type III collagen expression in human fetal tissues. Matrix. 1989 Mar;9(2):82–91. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8832(89)80025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangiorgi F. O., Benson-Chanda V., de Wet W. J., Sobel M. E., Tsipouras P., Ramirez F. Isolation and partial characterization of the entire human pro alpha 1(II) collagen gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2207–2225. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savagner P., Miyashita T., Yamada Y. Two silencers regulate the tissue-specific expression of the collagen II gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6669–6674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood A. L., Bornstein P. Transcriptional control of the alpha 1(I) collagen gene involves orientation- and position-specific intronic sequences. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 1;265(3):895–897. doi: 10.1042/bj2650895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiller G. E., Rimoin D. L., Murray L. W., Cohn D. H. Tandem duplication within a type II collagen gene (COL2A1) exon in an individual with spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3889–3893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vissing H., D'Alessio M., Lee B., Ramirez F., Godfrey M., Hollister D. W. Glycine to serine substitution in the triple helical domain of pro-alpha 1 (II) collagen results in a lethal perinatal form of short-limbed dwarfism. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18265–18267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuorio E., de Crombrugghe B. The family of collagen genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:837–872. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Väisänen P., Elima K., Palotie A., Peltonen L., Vuorio E. Polymorphic restriction sites of type II collagen gene: their location and frequencies in the Finnish population. Hum Hered. 1988;38(2):65–71. doi: 10.1159/000153760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Miyashita T., Savagner P., Horton W., Brown K. S., Abramczuk J., Xie H. X., Kohno K., Bolander M., Bruggeman L. Regulation of the collagen II gene in vitro and in transgenic mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;580:81–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb17920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark K., von der Mark H., Timpl R., Trelstad R. L. Immunofluorescent localization of collagen types I, II, and III in the embryonic chick eye. Dev Biol. 1977 Aug;59(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


