Abstract
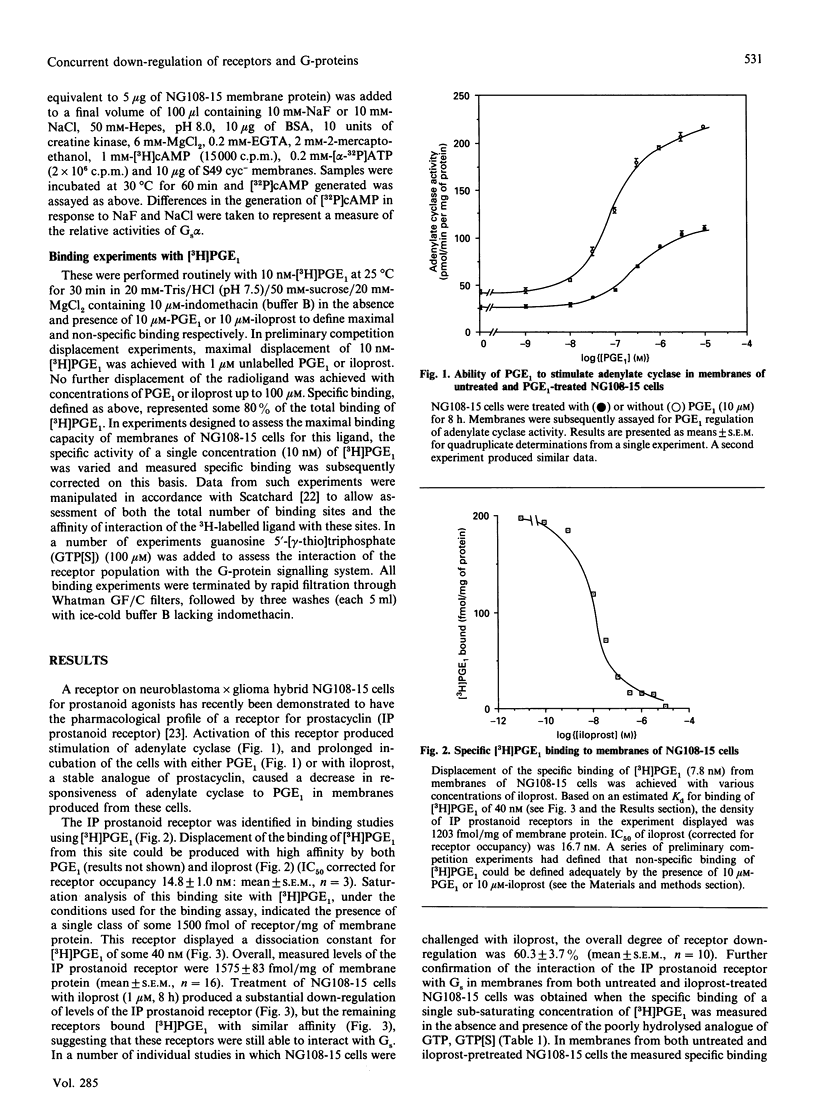
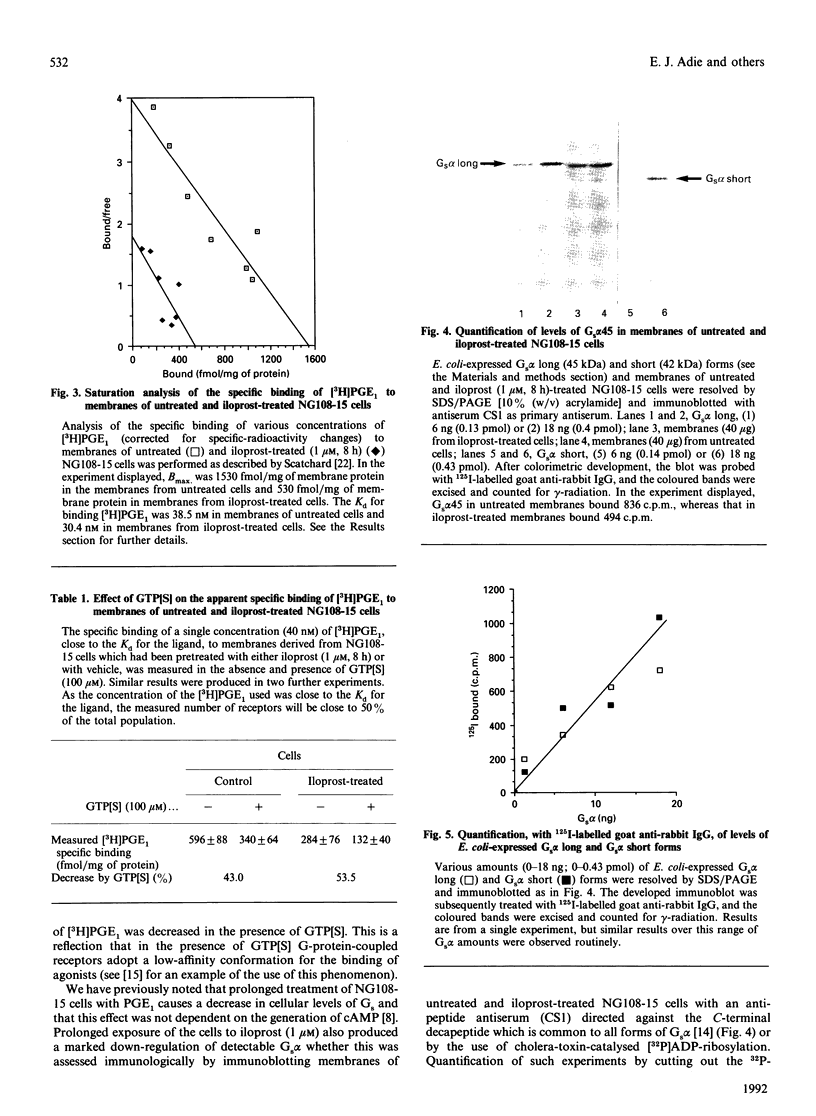
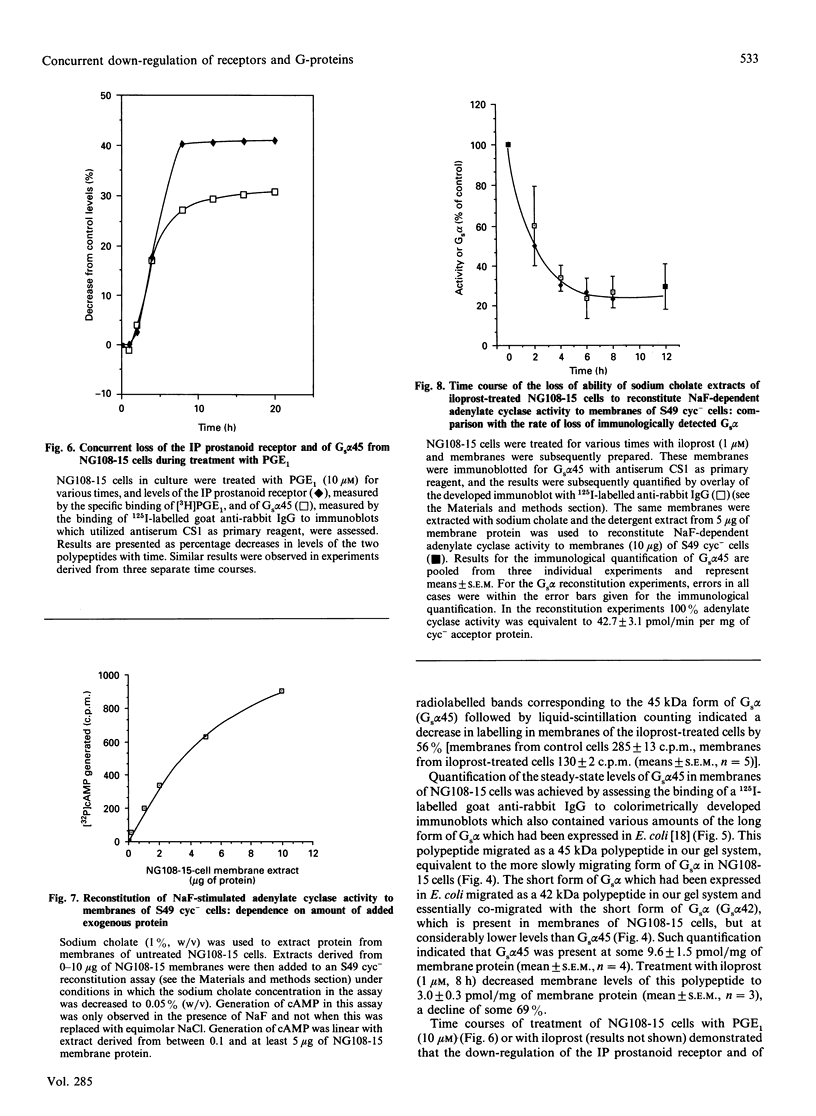
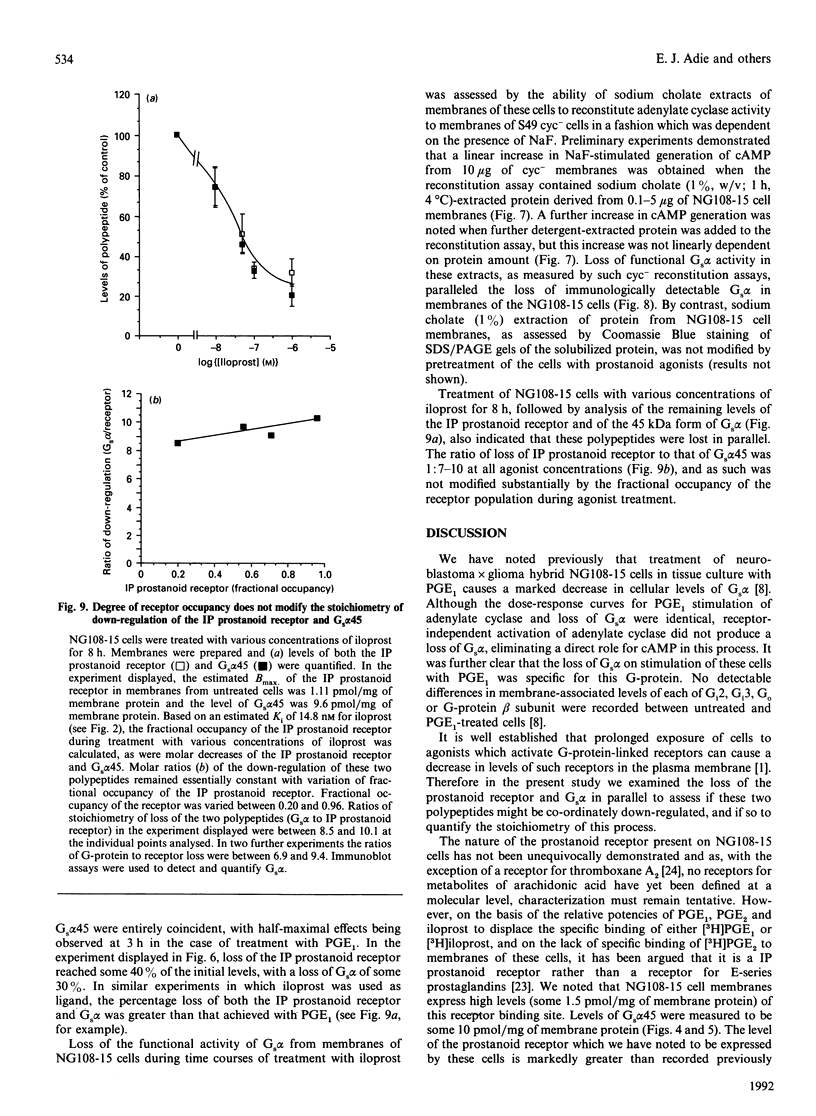
Neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid NG108-15 cells express a high-affinity IP prostanoid receptor. Saturation binding analysis of this receptor, using [3H]prostaglandin E1 ([3H]PGE1) as ligand, indicated that it was present at some 1.5 pmol/mg of membrane protein and displayed a dissociation constant for this ligand of 30-40 nM. Prolonged exposure of these cells either to PGE1 or to iloprost, which is a stable analogue of prostacyclin, caused a 40-70% decrease in levels of the receptor. The remaining receptors were capable of interacting with the stimulatory G-protein (Gs) of the adenylate cyclase cascade, as saturation analysis of the binding of [3H]PGE1 indicated that they had a similar affinity for the 3H-labelled ligand, and because the specific binding of [3H]PGE1 to these receptors was still sensitive to the presence of poorly hydrolysed analogues of GTP. We have recently demonstrated that prolonged exposure of NG108-15 ells to PGE1 causes a cyclic AMP-independent loss of Gs alpha-subunit (Gs alpha) from these cells [McKenzie & Milligan (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265, 17084-17093]. Steady-state concentration of the larger 45 kDa form of Gs alpha (which is the predominant form expressed in these cells) was assessed to be 9.6 pmol/mg of membrane protein, and treatment with iloprost decreased levels of this polypeptide to some 3.0 pmol/mg of protein. Time courses of iloprost-mediated down-regulation of the IP prostanoid receptor, loss of Gs alpha protein as assessed by immunoblotting and loss of Gs alpha activity as assessed by the reconstitution of NaF stimulation of adenylate cyclase activity to membranes of S49 cyc- cells by sodium cholate extracts of NG108-15 cells were identical, suggesting that the loss of the IP prostanoid receptor and G-protein occurred in parallel. Each of these effects was half-maximal between 2 and 3 h of exposure to the agonist. Stoichiometry of loss of Gs alpha and IP prostanoid receptor was unchanged by the percentage receptor occupancy, and quantification indicated the loss of some 7-10 mol of Gs alpha/mol of receptor. This is the first report to demonstrate the temporal concurrence of loss of Gs alpha and of a receptor which interacts with this G-protein. Chronic activation of the IP prostanoid receptor on these cells results in the development of a heterologous form of desensitization to agents which function to activate adenylate cyclase [Kelly, Keen, Nobbs & MacDermot (1990) Br. J. Pharmacol. 99, 306-316]. Agonist regulation of Gs alpha levels in these cells may contribute to this process.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brandt D. R., Ross E. M. Catecholamine-stimulated GTPase cycle. Multiple sites of regulation by beta-adrenergic receptor and Mg2+ studied in reconstituted receptor-Gs vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1656–1664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray P., Carter A., Simons C., Guo V., Puckett C., Kamholz J., Spiegel A., Nirenberg M. Human cDNA clones for four species of G alpha s signal transduction protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8893–8897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freissmuth M., Gilman A. G. Mutations of GS alpha designed to alter the reactivity of the protein with bacterial toxins. Substitutions at ARG187 result in loss of GTPase activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21907–21914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossen D., Tastenoy M., Robberecht P., Christophe J. Secretin receptors in the neuroglioma hybrid cell line NG108-15. Characterization and regulation of their expression. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Oct 5;193(1):149–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. Adenosine receptor down-regulation and insulin resistance following prolonged incubation of adipocytes with an A1 adenosine receptor agonist. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15702–15707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A., Johnson J. L., Milligan G. Down-regulation of Gi sub-types by prolonged incubation of adipocytes with an A1 adenosine receptor agonist. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5206–5210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A., Milligan G., Dobias S. B. Gi down-regulation as a mechanism for heterologous desensitization in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3223–3229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata M., Hayashi Y., Ushikubi F., Yokota Y., Kageyama R., Nakanishi S., Narumiya S. Cloning and expression of cDNA for a human thromboxane A2 receptor. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):617–620. doi: 10.1038/349617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen M., Kelly E., MacDermot J. Guanine nucleotide sensitivity of [3H]iloprost binding to prostacyclin receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun 19;207(2):111–117. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(91)90085-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen M., Kelly E., Nobbs P., MacDermot J. A selective binding site for 3H-NECA that is not an adenosine A2 receptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Nov 1;38(21):3827–3833. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90592-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly E., Keen M., Nobbs P., MacDermot J. Segregation of discrete GS alpha-mediated responses that accompany homologous or heterologous desensitization in two related somatic hybrids. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;99(2):309–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14700.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenimer J. G., Nirenberg M. Desensitization of adenylate cyclase to prostaglandin E1 or 2-chloroadenosine. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;20(3):585–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macleod K. G., Milligan G. Biphasic regulation of adenylate cyclase by cholera toxin in neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells is due to the activation and subsequent loss of the alpha subunit of the stimulatory GTP binding protein (GS). Cell Signal. 1990;2(2):139–151. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(90)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie F. R., Adie E. J., Milligan G. Prostanoid-mediated downregulation of Gs in NG108-15 cells. Biochem Soc Trans. 1991 Apr;19(2):81S–81S. doi: 10.1042/bst019081s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie F. R., Kelly E. C., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M., Milligan G. Antibodies which recognize the C-terminus of the inhibitory guanine-nucleotide-binding protein (Gi) demonstrate that opioid peptides and foetal-calf serum stimulate the high-affinity GTPase activity of two separate pertussis-toxin substrates. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 1;249(3):653–659. doi: 10.1042/bj2490653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie F. R., Milligan G. Delta-opioid-receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase is transduced specifically by the guanine-nucleotide-binding protein Gi2. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 15;267(2):391–398. doi: 10.1042/bj2670391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie F. R., Milligan G. Prostaglandin E1-mediated, cyclic AMP-independent, down-regulation of Gs alpha in neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17084–17093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G. Foetal-calf serum stimulates a pertussis-toxin-sensitive high-affinity GTPase activity in rat glioma C6 BU1 cells. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):501–505. doi: 10.1042/bj2450501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Green A. Agonist control of G-protein levels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Jun;12(6):207–209. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90551-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G. Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins and cellular control. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;1(2):196–200. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90086-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Klee W. A. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding protein (Ni) purified from bovine brain is a high affinity GTPase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2057–2063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Streaty R. A., Gierschik P., Spiegel A. M., Klee W. A. Development of opiate receptors and GTP-binding regulatory proteins in neonatal rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8626–8630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Unson C. G. Persistent activation of the alpha subunit of Gs promotes its removal from the plasma membrane. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 15;260(3):837–841. doi: 10.1042/bj2600837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell F. M., Griffiths S. L., Saggerson E. D., Houslay M. D., Knowler J. T., Milligan G. Guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins expressed in rat white adipose tissue. Identification of both mRNAs and proteins corresponding to Gi1, Gi2 and Gi3. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):403–408. doi: 10.1042/bj2620403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochly-Rosen D., Chang F. H., Cheever L., Kim M., Diamond I., Gordon A. S. Chronic ethanol causes heterologous desensitization of receptors by reducing alpha s messenger RNA. Nature. 1988 Jun 30;333(6176):848–850. doi: 10.1038/333848a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy L. E., Diamond I., Casso D. J., Franklin C., Gordon A. S. Ethanol increases extracellular adenosine by inhibiting adenosine uptake via the nucleoside transporter. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):1946–1951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olate J., Mattera R., Codina J., Birnbaumer L. Reticulocyte lysates synthesize an active alpha subunit of the stimulatory G protein Gs. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10394–10400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robishaw J. D., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. Molecular basis for two forms of the G protein that stimulates adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9587–9590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Lefkowitz R. J. Molecular mechanisms of receptor desensitization using the beta-adrenergic receptor-coupled adenylate cyclase system as a model. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):124–129. doi: 10.1038/317124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walseth T. F., Zhang H. J., Olson L. K., Schroeder W. A., Robertson R. P. Increase in Gs and cyclic AMP generation in HIT cells. Evidence that the 45-kDa alpha-subunit of Gs has greater functional activity than the 52-kDa alpha-subunit. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21106–21111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]