Abstract
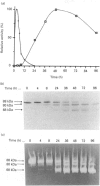
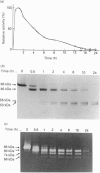
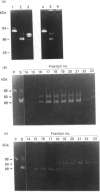
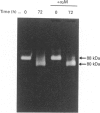
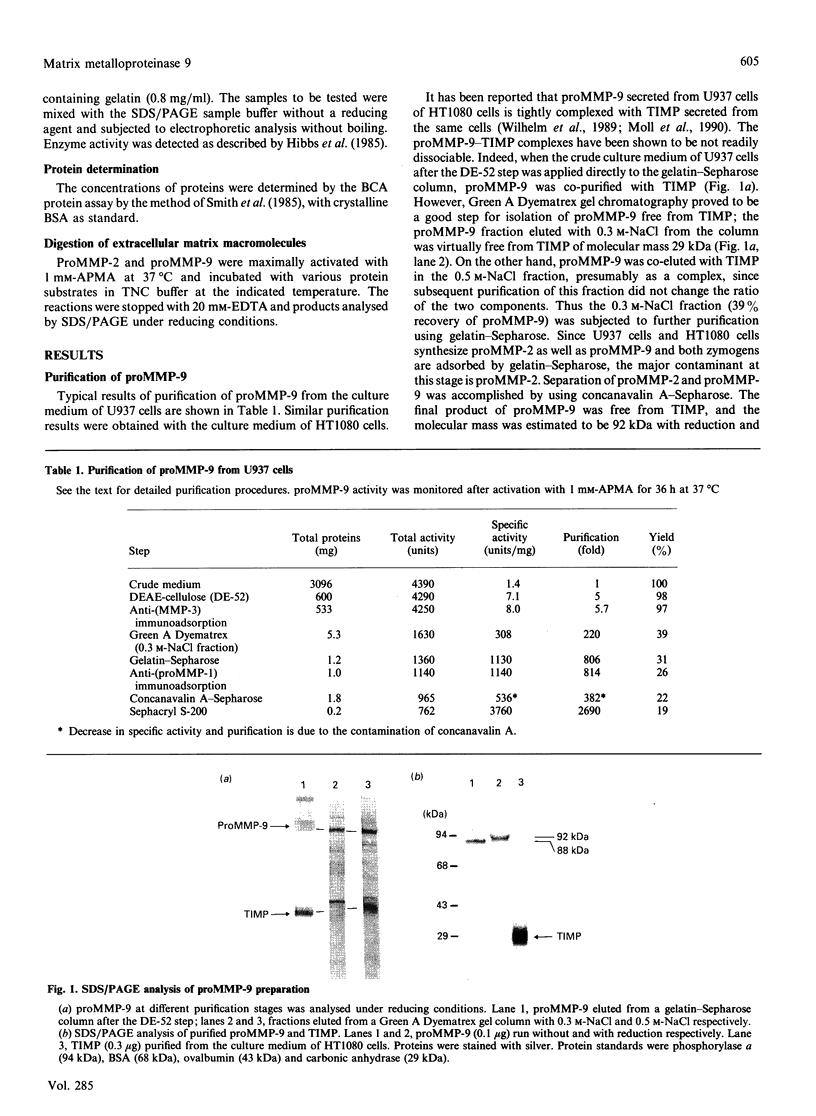
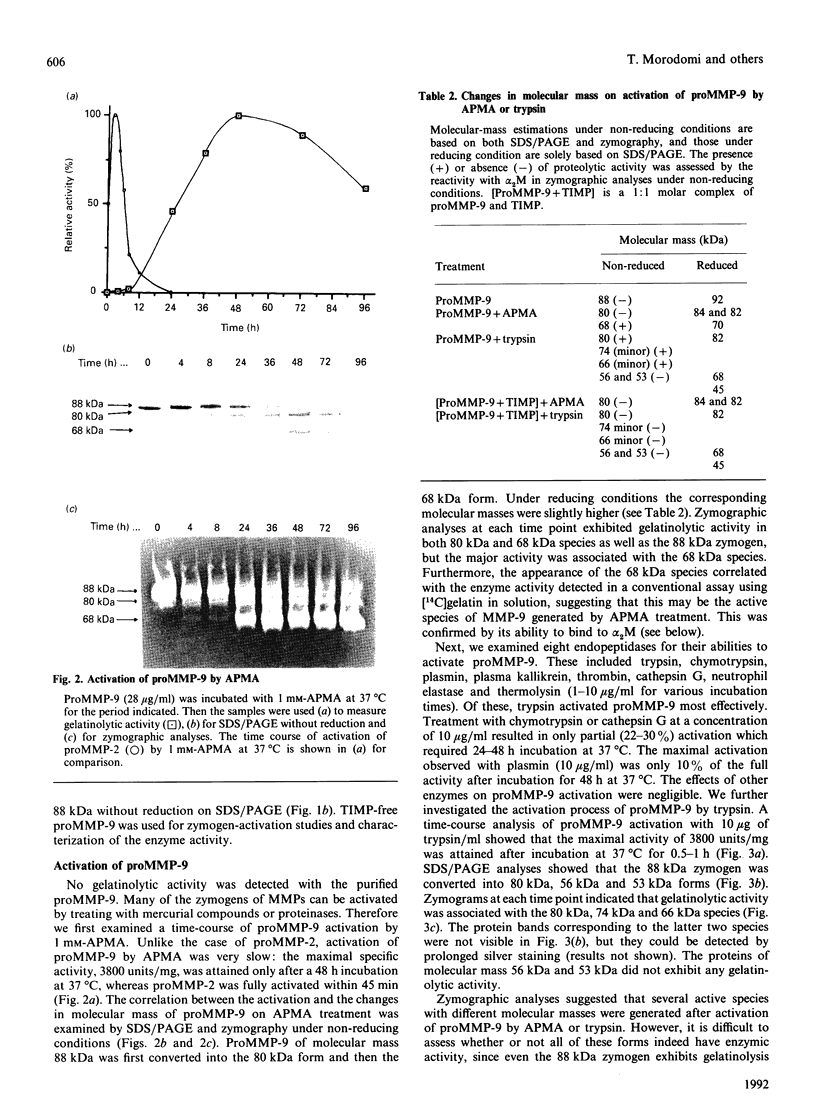
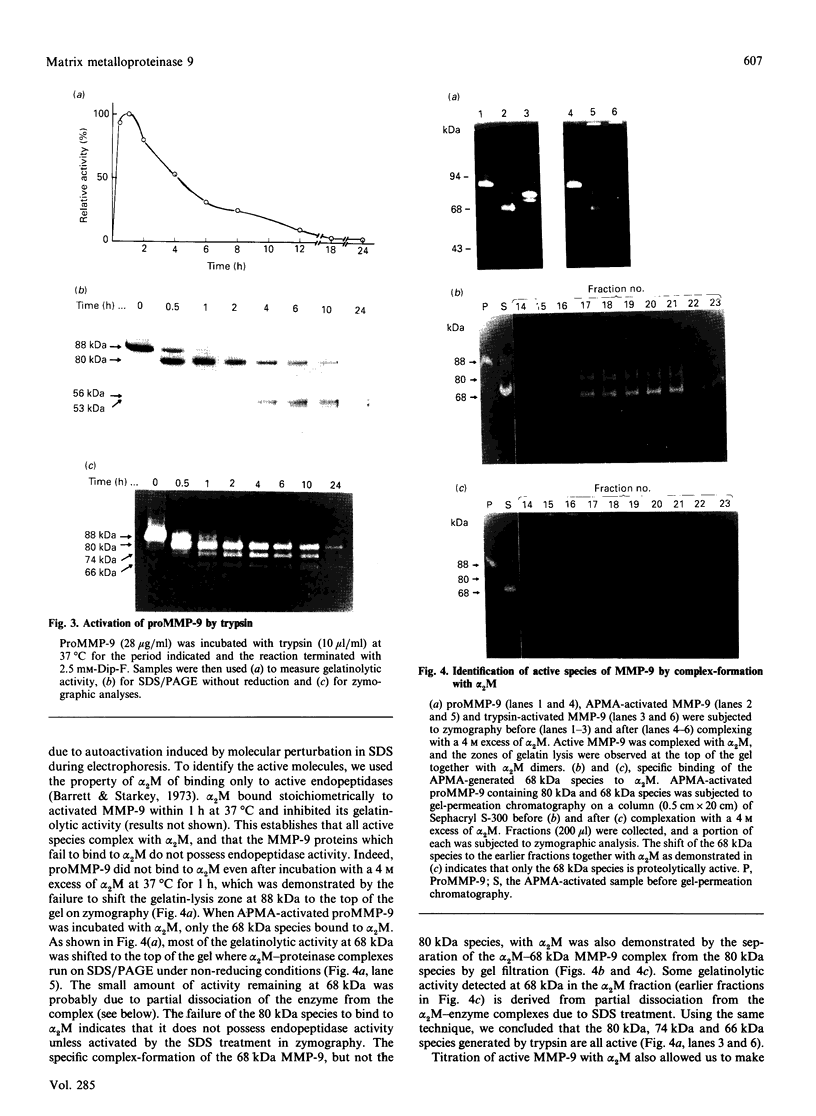
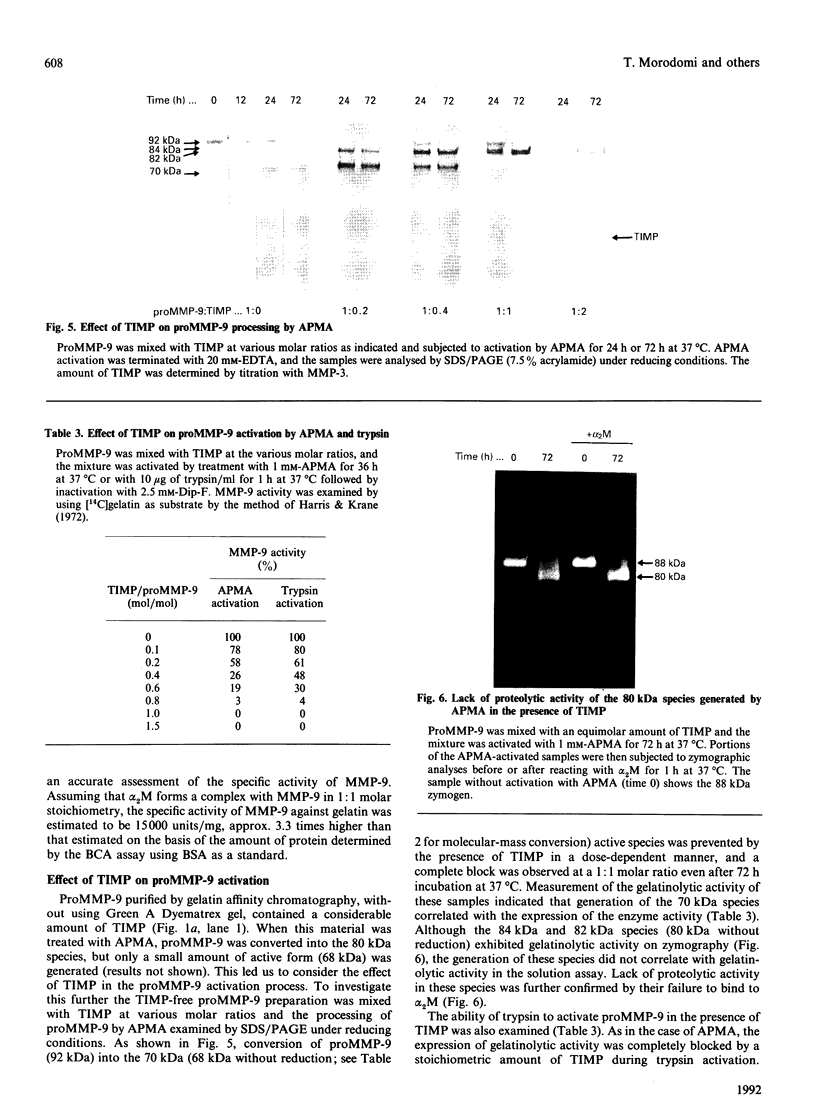
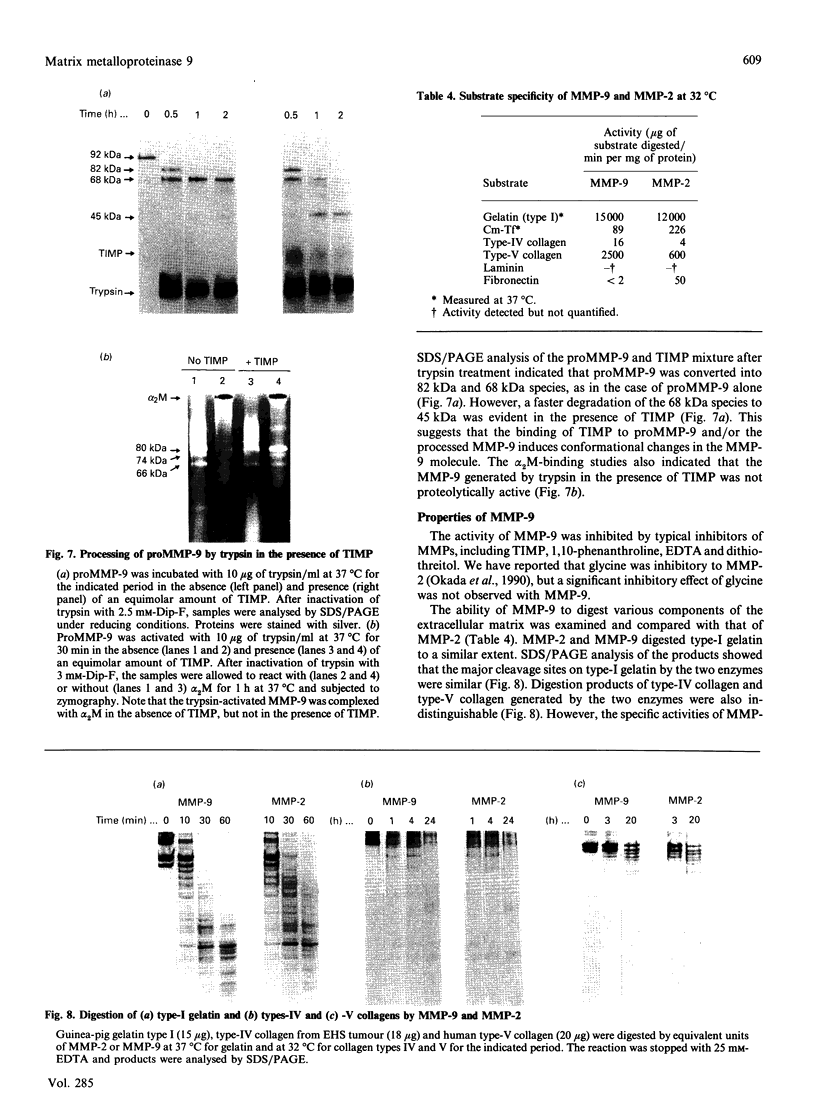
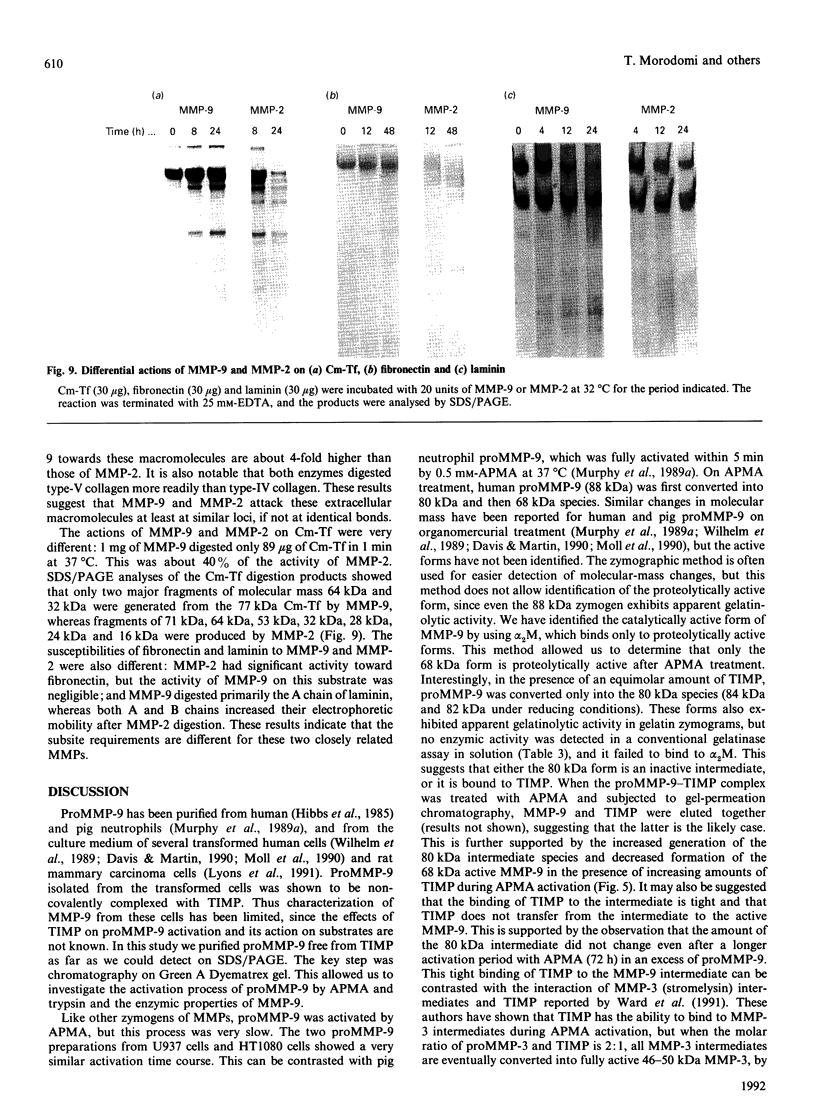
The precursor of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (proMMP-9), also known as '92 kDa progelatinase/type IV procollagenase', was purified from the conditioned medium of U937 monocytic leukaemia and HT1080 fibrosarcoma cell lines stimulated with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. ProMMP-9 in these culture media is non-covalently complexed with the 29 kDa tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP), but free proMMP-9 was separated from the TIMP-proMMP-9 complex by chromatography on Green A Dyematrex gel. The final product was homogeneous on SDS/PAGE, with a molecular mass of 88 kDa without reduction and 92 kDa with reduction. Treatment of proMMP-9 with 4-aminophenylmercuric acetate converted the 88 kDa precursor into 80 kDa and 68 kDa forms. Gelatin-containing zymographic analysis showed zones of lysis associated with all three species. However, only the 68 kDa species was shown to be catalytically active by its ability to bind to alpha 2-macroglobulin. In the presence of an equimolar amount of TIMP, only the 80 kDa species was generated by treatment with 4-aminophenylmercuric acetate, but no enzyme activity was detected. This indicates that TIMP binds to the 80 kDa intermediate and inhibits the generation of the active 68 kDa species. Eight endopeptidases (trypsin, chymotrypsin, plasmin, plasma kallikrein, thrombin, cathepsin G, neutrophil elastase and thermolysin) were tested for their ability to activate proMMP-9. Of them, trypsin was the most effective activator of proMMP-9. Only partial activation (10-30%) was observed with plasmin, cathepsin G and chymotrypsin. The active forms generated by trypsin were identified as 80 kDa, 74 kDa and 66 kDa by their abilities to bind to alpha 2-macroglobulin. In the presence of an equimolar amount of TIMP, proMMP-9 was also converted into the same molecular-mass species by trypsin, but they were not proteolytically active. This suggests activated MMP-9 is inhibited by TIMP. Activated MMP-9 digested gelatin, type-V collagen, reduced carboxymethylated transferrin and, to a lesser extent, type-IV collagen and laminin A chain. The specific activity against gelatin was estimated to be 15,000 units/mg (1 unit = 1 microgram of gelatin degraded/min at 37 degrees C) by titration with alpha 2-macroglobulin. Comparative studies on digestion of gelatin and collagen types IV and V by MMP-9 and MMP-2 indicated that both enzymes degrade these substrates into similar fragments. However, the susceptibilities of laminin, fibronectin and reduced carboxymethylated transferrin to these two MMPs were sufficiently different to indicate differences in substrate specificities between these two closely related proteinases.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett A. J., Starkey P. M. The interaction of alpha 2-macroglobulin with proteinases. Characteristics and specificity of the reaction, and a hypothesis concerning its molecular mechanism. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;133(4):709–724. doi: 10.1042/bj1330709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier I. E., Wilhelm S. M., Eisen A. Z., Marmer B. L., Grant G. A., Seltzer J. L., Kronberger A., He C. S., Bauer E. A., Goldberg G. I. H-ras oncogene-transformed human bronchial epithelial cells (TBE-1) secrete a single metalloprotease capable of degrading basement membrane collagen. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6579–6587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. E., Martin B. M. A latent Mr 94,000 gelatin-degrading metalloprotease induced during differentiation of HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells: a member of the collagenase family of enzymes. Cancer Res. 1990 Feb 15;50(4):1113–1120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr, Krane S. M. An endopeptidase from rheumatoid synovial tissue culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;258(2):566–576. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs M. S., Hasty K. A., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H., Mainardi C. L. Biochemical and immunological characterization of the secreted forms of human neutrophil gelatinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2493–2500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs M. S., Hoidal J. R., Kang A. H. Expression of a metalloproteinase that degrades native type V collagen and denatured collagens by cultured human alveolar macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1644–1650. doi: 10.1172/JCI113253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons J. G., Birkedal-Hansen B., Moore W. G., O'Grady R. L., Birkedal-Hansen H. Characteristics of a 95-kDa matrix metalloproteinase produced by mammary carcinoma cells. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 12;30(6):1449–1456. doi: 10.1021/bi00220a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainardi C. L., Hibbs M. S., Hasty K. A., Seyer J. M. Purification of a type V collagen degrading metalloproteinase from rabbit alveolar macrophages. Coll Relat Res. 1984 Dec;4(6):479–492. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(84)80014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M. Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in matrix remodeling. Trends Genet. 1990 Apr;6(4):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90126-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll U. M., Youngleib G. L., Rosinski K. B., Quigley J. P. Tumor promoter-stimulated Mr 92,000 gelatinase secreted by normal and malignant human cells: isolation and characterization of the enzyme from HT1080 tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1990 Oct 1;50(19):6162–6170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Cockett M. I., Ward R. V., Docherty A. J. Matrix metalloproteinase degradation of elastin, type IV collagen and proteoglycan. A quantitative comparison of the activities of 95 kDa and 72 kDa gelatinases, stromelysins-1 and -2 and punctuated metalloproteinase (PUMP). Biochem J. 1991 Jul 1;277(Pt 1):277–279. doi: 10.1042/bj2770277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Hembry R. M., McGarrity A. M., Reynolds J. J., Henderson B. Gelatinase (type IV collagenase) immunolocalization in cells and tissues: use of an antiserum to rabbit bone gelatinase that identifies high and low Mr forms. J Cell Sci. 1989 Mar;92(Pt 3):487–495. doi: 10.1242/jcs.92.3.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., McAlpine C. G., Poll C. T., Reynolds J. J. Purification and characterization of a bone metalloproteinase that degrades gelatin and types IV and V collagen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 20;831(1):49–58. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Ward R., Hembry R. M., Reynolds J. J., Kühn K., Tryggvason K. Characterization of gelatinase from pig polymorphonuclear leucocytes. A metalloproteinase resembling tumour type IV collagenase. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 1;258(2):463–472. doi: 10.1042/bj2580463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagase H., Barrett A. J. Human plasma kallikrein. A rapid purification method with high yield. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 1;193(1):187–192. doi: 10.1042/bj1930187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagase H., Enghild J. J., Suzuki K., Salvesen G. Stepwise activation mechanisms of the precursor of matrix metalloproteinase 3 (stromelysin) by proteinases and (4-aminophenyl)mercuric acetate. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 19;29(24):5783–5789. doi: 10.1021/bi00476a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Harris E. D., Jr, Nagase H. The precursor of a metalloendopeptidase from human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Purification and mechanisms of activation by endopeptidases and 4-aminophenylmercuric acetate. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 15;254(3):731–741. doi: 10.1042/bj2540731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Morodomi T., Enghild J. J., Suzuki K., Yasui A., Nakanishi I., Salvesen G., Nagase H. Matrix metalloproteinase 2 from human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Purification and activation of the precursor and enzymic properties. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Dec 27;194(3):721–730. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19462.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Nagase H., Harris E. D., Jr A metalloproteinase from human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts that digests connective tissue matrix components. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14245–14255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Watanabe S., Nakanishi I., Kishi J., Hayakawa T., Watorek W., Travis J., Nagase H. Inactivation of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases by neutrophil elastase and other serine proteinases. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 29;229(1):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80817-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Engvall E. Immunochemical and collagen-binding properties of fibronectin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 20;312:178–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb16802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R. M., Griffin G. L., Fliszar C. J., Shapiro S. D., Goldberg G. I., Welgus H. G. Human 92- and 72-kilodalton type IV collagenases are elastases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7870–7875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sopata I., Dancewicz A. M. Presence of a gelatin-specific proteinase and its latent form in human leucocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 29;370(2):510–523. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90112-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Brown P. D., Onisto M., Levy A. T., Liotta L. A. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2) mRNA expression in tumor cell lines and human tumor tissues. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13933–13938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Enghild J. J., Morodomi T., Salvesen G., Nagase H. Mechanisms of activation of tissue procollagenase by matrix metalloproteinase 3 (stromelysin). Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 6;29(44):10261–10270. doi: 10.1021/bi00496a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. V., Hembry R. M., Reynolds J. J., Murphy G. The purification of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 from its 72 kDa progelatinase complex. Demonstration of the biochemical similarities of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 15;278(Pt 1):179–187. doi: 10.1042/bj2780179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm S. M., Collier I. E., Marmer B. L., Eisen A. Z., Grant G. A., Goldberg G. I. SV40-transformed human lung fibroblasts secrete a 92-kDa type IV collagenase which is identical to that secreted by normal human macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17213–17221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner J. F., Jr Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in connective tissue remodeling. FASEB J. 1991 May;5(8):2145–2154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]