Abstract
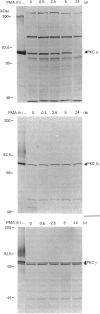
The involvement of protein kinase C (PKC) in the regulation of intestinal ion secretion was studied in polarized monolayers of the HT29cl.19A human colon carcinoma cell line. Carbachol, phorbol esters [PMA (phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate) and PDB (phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate)] and 8-bromo cyclic AMP (8-Br-cAMP) induced Cl secretion, as measured by a rise in the short-circuit current (ISC). The electrical response to carbachol coincided with a transient translocation of PKC alpha from the soluble to the particulate fraction. The carbachol-, PDB- and 8-Br-cAMP-induced ISC responses were inhibited by pretreatment of the cells with PMA (0.5 microM) for 2 h, a time period in which PKC alpha, beta 1 and gamma levels were not changed. As shown by 86Rb+ and 125I- efflux studies, the main targets for this inhibition were basolateral K+ transporters rather than apical Cl- channels. Prolonged exposure to PMA (24 h) led to a 60% recovery of the 8-Br-cAMP response, but not of the carbachol- or PDB-provoked secretion. As shown by immunoblotting with PKC-isoenzyme-specific antisera, the recovery of the 8-Br-cAMP response coincided with the down-regulation of PKC alpha, whereas the levels of PKC beta 1 and gamma were unmodified. These results suggest that PKC alpha, but not PKC beta 1 or gamma, is involved in both acute stimulation and chronic inhibition of ion secretion in the HT29cl.19A colonic cell line.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. P., Gregory R. J., Thompson S., Souza D. W., Paul S., Mulligan R. C., Smith A. E., Welsh M. J. Demonstration that CFTR is a chloride channel by alteration of its anion selectivity. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):202–205. doi: 10.1126/science.1712984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajnath R. B., Augeron C., Laboisse C. L., Bijman J., de Jonge H. R., Groot J. A. Electrophysiological studies of forskolin-induced changes in ion transport in the human colon carcinoma cell line HT-29 cl.19A: lack of evidence for a cAMP-activated basolateral K+ conductance. J Membr Biol. 1991 Jun;122(3):239–250. doi: 10.1007/BF01871424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang E. B., Wang N. S., Rao M. C. Phorbol ester stimulation of active anion secretion in intestine. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 1):C356–C361. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.3.C356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donowitz M., Cheng H. Y., Sharp G. W. Effects of phorbol esters on sodium and chloride transport in rat colon. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):G509–G517. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.4.G509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin C. C., Turner J. T., Kim H. D. Regulation of Na+/K+/Cl- cotransport and [3H]bumetanide binding site density by phorbol esters in HT29 cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6667–6673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho A. K., Thomas T. P., Chik C. L., Anderson W. B., Klein D. C. Protein kinase C: subcellular redistribution by increased Ca2+ influx. Evidence that Ca2+-dependent subcellular redistribution of protein kinase C is involved in potentiation of beta-adrenergic stimulation of pineal cAMP and cGMP by K+ and A23187. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9292–9297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. P., Huang F. L., Nakabayashi H., Yoshida Y. Biochemical characterization of rat brain protein kinase C isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14839–14845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang T. C., Lu L., Zeitlin P. L., Gruenert D. C., Huganir R., Guggino W. B. Cl- channels in CF: lack of activation by protein kinase C and cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1351–1353. doi: 10.1126/science.2472005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isakov N., McMahon P., Altman A. Selective post-transcriptional down-regulation of protein kinase C isoenzymes in leukemic T cells chronically treated with phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2091–2097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kartner N., Hanrahan J. W., Jensen T. J., Naismith A. L., Sun S. Z., Ackerley C. A., Reyes E. F., Tsui L. C., Rommens J. M., Bear C. E. Expression of the cystic fibrosis gene in non-epithelial invertebrate cells produces a regulated anion conductance. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):681–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90498-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., McCann J. D., Anderson M. P., Clancy J. P., Liedtke C. M., Nairn A. C., Greengard P., Welsch M. J. Regulation of chloride channels by protein kinase C in normal and cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1353–1356. doi: 10.1126/science.2472006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marais R. M., Parker P. J. Purification and characterisation of bovine brain protein kinase C isotypes alpha, beta and gamma. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jun 1;182(1):129–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14809.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musch M. W., Nahkla A. M., Chang E. B. Phorbol ester-stimulated secretion in chicken ileum: role of arachidonic acid metabolism. Gastroenterology. 1990 Aug;99(2):393–400. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91021-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Ogita K., Kikkawa U., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. The structure, expression, and properties of additional members of the protein kinase C family. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6927–6932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Ochsner M., Whitebread S., De Gasparo M. Down-regulation of protein kinase C potentiates angiotensin II-stimulated polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in vascular smooth-muscle cells. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 15;262(1):285–291. doi: 10.1042/bj2620285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaap D., Parker P. J. Expression, purification, and characterization of protein kinase C-epsilon. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7301–7307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. S., Warhurst G., Turnberg L. A. Synthesis and degradation of prostaglandin E2 in the epithelial and sub-epithelial layers of the rat intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 13;713(3):684–687. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90331-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly B. C., Tertoolen L. G., Lambrechts A. C., Remorie R., de Laat S. W., Moolenaar W. H. Histamine-H1-receptor-mediated phosphoinositide hydrolysis, Ca2+ signalling and membrane-potential oscillations in human HeLa carcinoma cells. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 15;266(1):235–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2660235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaandrager A. B., Bajnath R., Groot J. A., Bot A. G., De Jonge H. R. Ca2+ and cAMP activate different chloride efflux pathways in HT-29.cl19A colonic epithelial cell line. Am J Physiol. 1991 Dec;261(6 Pt 1):G958–G965. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.261.6.G958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaandrager A. B., van den Berghe N., Bot A. G., de Jonge H. R. Phorbol esters stimulate and inhibit Cl- secretion by different mechanisms in a colonic cell line. Am J Physiol. 1992 Feb;262(2 Pt 1):G249–G256. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.2.G249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venglarik C. J., Bridges R. J., Frizzell R. A. A simple assay for agonist-regulated Cl and K conductances in salt-secreting epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 1):C358–C364. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.2.C358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]