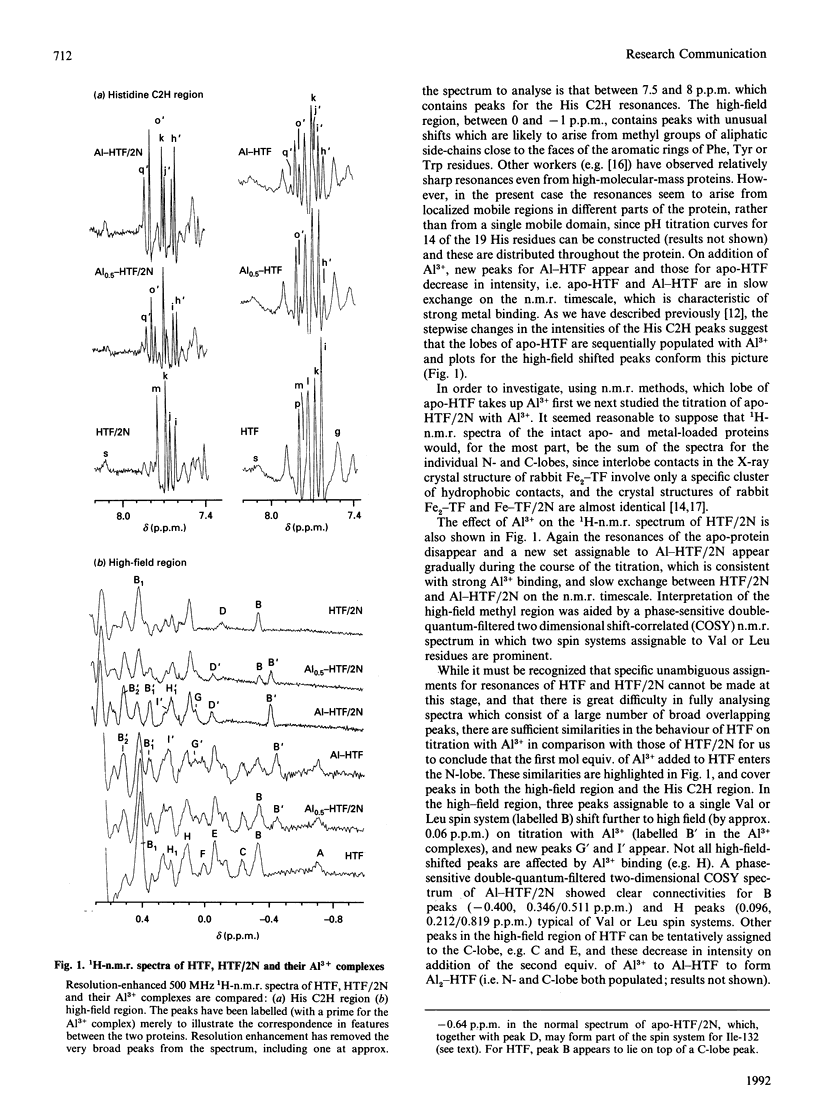
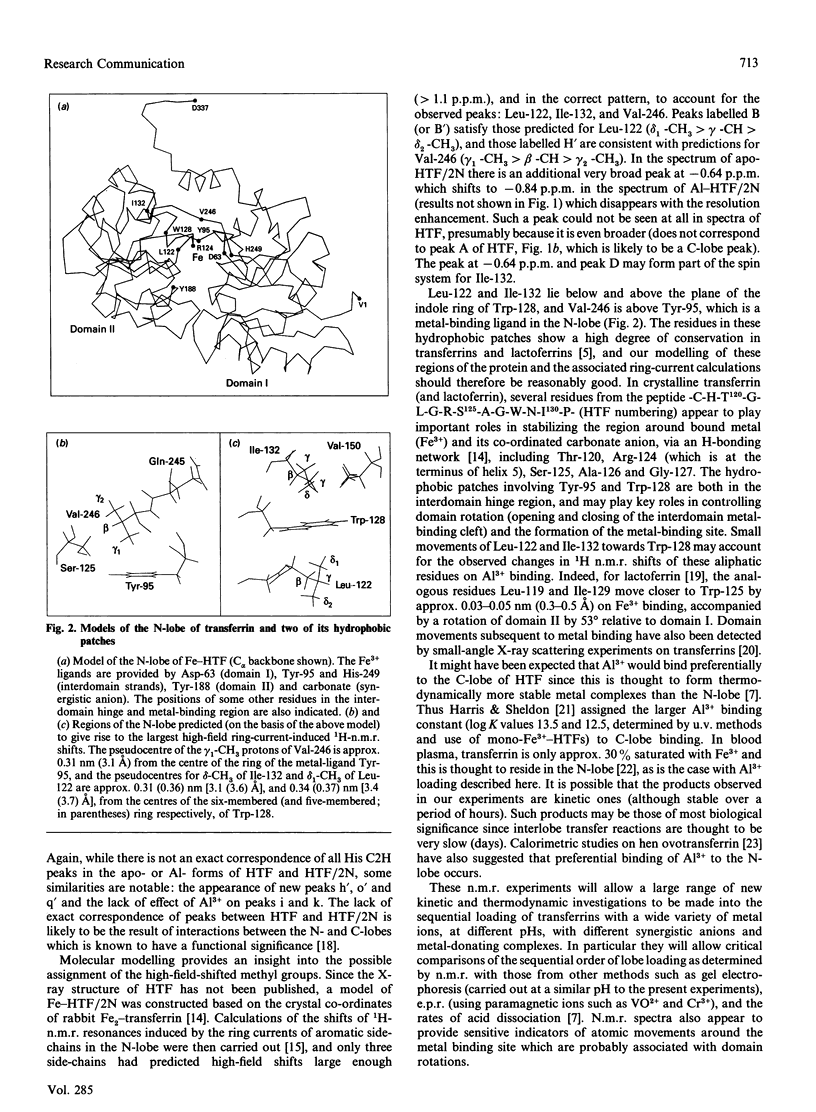
Abstract
We have studied the binding of Al3+ to human serum apotransferrin (80 kDa) and recombinant N-lobe human apotransferrin (40 kDa) in 0.1 M-sodium bicarbonate solution at a pH meter reading in 2H2O (pH*) of 8.8 using 1H n.m.r. spectroscopy. The results show that for the intact protein, preferential binding of Al3+ to the N-lobe occurs. Molecular modelling combined with an analysis of ring-current-induced shifts suggest that n.m.r. spectroscopy can be used to probe hinge bending processes which accompany metal uptake in solution.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson B. F., Baker H. M., Norris G. E., Rumball S. V., Baker E. N. Apolactoferrin structure demonstrates ligand-induced conformational change in transferrins. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):784–787. doi: 10.1038/344784a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey S., Evans R. W., Garratt R. C., Gorinsky B., Hasnain S., Horsburgh C., Jhoti H., Lindley P. F., Mydin A., Sarra R. Molecular structure of serum transferrin at 3.3-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 26;27(15):5804–5812. doi: 10.1021/bi00415a061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown-Mason A., Brown S. A., Butcher N. D., Woodworth R. C. Reversible association of half-molecules of ovotransferrin in solution. Basis of co-operative binding to reticulocytes. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 1;245(1):103–109. doi: 10.1042/bj2450103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crichton R. R. Proteins of iron storage and transport. Adv Protein Chem. 1990;40:281–363. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day J. P., Barker J., Evans L. J., Perks J., Seabright P. J., Ackrill P., Lilley J. S., Drumm P. V., Newton G. W. Aluminum absorption studied by 26Al tracer. Lancet. 1991 Jun 1;337(8753):1345–1345. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)93016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. W., Donovan J. W., Williams J. Calorimetric studies on the binding of iron and aluminium to the amino- and carboxyl-terminal fragments of hen ovotransferrin. FEBS Lett. 1977 Nov 1;83(1):19–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80632-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. W., Williams J. Studies of the binding of different iron donors to human serum transferrin and isolation of iron-binding fragments from the N- and C-terminal regions of the protein. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 1;173(2):543–552. doi: 10.1042/bj1730543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk W. D., MacGillivray R. T., Mason A. B., Brown S. A., Woodworth R. C. Expression of the amino-terminal half-molecule of human serum transferrin in cultured cells and characterization of the recombinant protein. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 13;29(6):1654–1660. doi: 10.1021/bi00458a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris W. R., Stenback J. Z. The bicarbonate-dependence of zinc(II)-transferrin binding. J Inorg Biochem. 1988 Jul;33(3):211–223. doi: 10.1016/0162-0134(88)80050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibman A., Aisen P. Distribution of iron between the binding sites of transferrin in serum: methods and results in normal human subjects. Blood. 1979 Jun;53(6):1058–1065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makey D. G., Seal U. S. The detection of four molecular forms of human transferrin during the iron binding process. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 26;453(1):250–256. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90270-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oswald R. E., Bogusky M. J., Bamberger M., Smith R. A., Dobson C. M. Dynamics of the multidomain fibrinolytic protein urokinase from two-dimensional NMR. Nature. 1989 Feb 9;337(6207):579–582. doi: 10.1038/337579a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


