Abstract
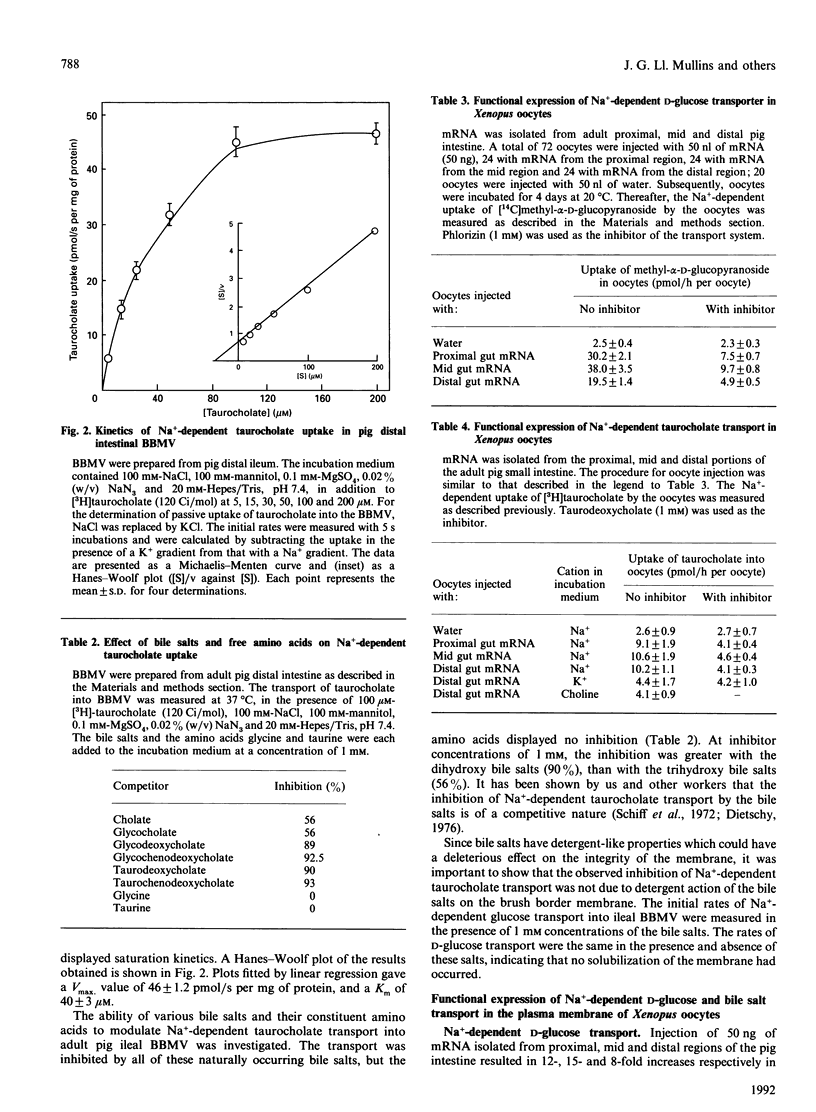
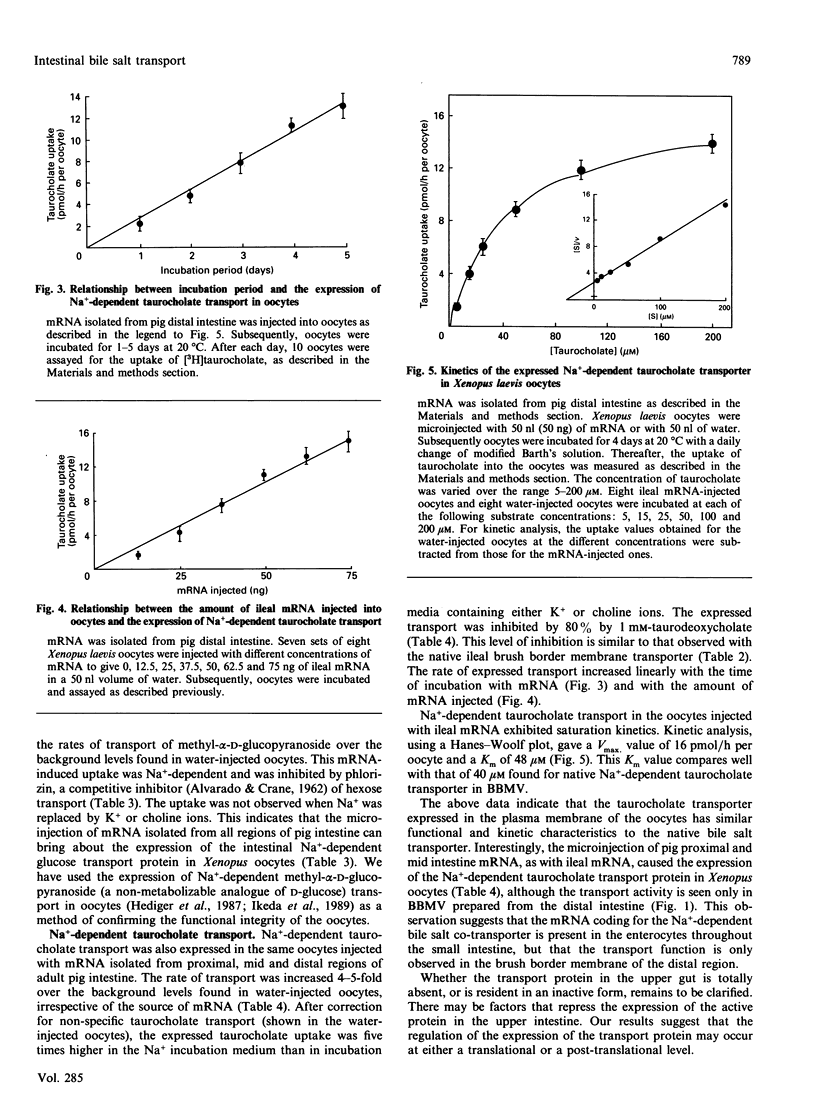
The Na+/bile salt co-transporter of the pig ileal brush border membrane has been expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Injection of pig ileal poly (A)+ RNA into oocytes resulted in the functional expression of an Na(+)-gradient-stimulated taurocholate uptake within 2-5 days. The expressed Na(+)-dependent taurocholate uptake exhibited saturation kinetics (apparent Km of 48 microM), and displayed similar competitive substrate inhibition by taurodeoxycholate as the native brush border Na+/bile salt co-transporter studied in pig ileal brush border membrane vesicles. Interestingly, injection of pig proximal and mid intestinal poly (A)+ RNA into oocytes also resulted in the expression of the Na+/bile salt co-transporter, though the Na(+)-dependent transport of bile salts does not occur in brush border membrane vesicles (BBMV) isolated from pig proximal and mid intestine. This suggests that the mRNA coding for the co-transporter is present in the enterocytes lining the whole length of the small intestine, but that the function is only expressed in the brush border of the distal small intestine. The transport of D-glucose into BBMV, and the transport of methyl-alpha-D-glucopyranoside (a non-metabolizable hexose derivative) into oocytes were used throughout the study as methods of confirming the integrity of vesicles and oocytes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALVARADO F., CRANE R. K. Phlorizin as a competitive inhibitor of the active transport of sugars by hamster small intestine, in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jan 1;56:170–172. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90543-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard J. A., Ghishan F. K. Taurocholate transport by human ileal brush border membrane vesicles. Gastroenterology. 1987 Nov;93(5):925–933. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beesley R. C., Faust R. G. Sodium ion-coupled uptake of taurocholate by intestinal brush-border membrane vesicles. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 15;178(2):299–303. doi: 10.1042/bj1780299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bluett M. K., Abumrad N. N., Arab N., Ghishan F. K. Aboral changes in D-glucose transport by human intestinal brush-border membrane vesicles. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):229–234. doi: 10.1042/bj2370229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRANE R. K. Hypothesis for mechanism of intestinal active transport of sugars. Fed Proc. 1962 Nov-Dec;21:891–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHLQVIST A. METHOD FOR ASSAY OF INTESTINAL DISACCHARIDASES. Anal Biochem. 1964 Jan;7:18–25. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher K., Mauskopf J., Walker J. T., Lack L. Ionic requirements for the active ileal bile salt transport system. J Lipid Res. 1976 Nov;17(6):572–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hediger M. A., Coady M. J., Ikeda T. S., Wright E. M. Expression cloning and cDNA sequencing of the Na+/glucose co-transporter. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):379–381. doi: 10.1038/330379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F., Poley J. R. Role of bile acid malabsorption in pathogenesis of diarrhea and steatorrhea in patients with ileal resection. I. Response to cholestyramine or replacement of dietary long chain triglyceride by medium chain triglyceride. Gastroenterology. 1972 May;62(5):918–934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F. The syndrome of ileal disease and the broken enterohepatic circulation: cholerheic enteropathy. Gastroenterology. 1967 Apr;52(4):752–757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda T. S., Hwang E. S., Coady M. J., Hirayama B. A., Hediger M. A., Wright E. M. Characterization of a Na+/glucose cotransporter cloned from rabbit small intestine. J Membr Biol. 1989 Aug;110(1):87–95. doi: 10.1007/BF01870995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lack L., Weiner I. M. Intestinal bile salt transport: structure-activity relationships and other properties. Am J Physiol. 1966 May;210(5):1142–1152. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.5.1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. M., Lester R. Ontogenesis of intestinal bile salt absorption in the neonatal rat. Am J Physiol. 1980 Oct;239(4):G319–G323. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1980.239.4.G319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lücke H., Stange G., Kinne R., Murer H. Taurocholate--sodium co-transport by brush-border membrane vesicles isolated from rat ileum. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 15;174(3):951–958. doi: 10.1042/bj1740951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meihoff W. E., Kern F., Jr Bile salt malabsorption in regional ileitis, ileal resection and mannitol-induced diarrhea. J Clin Invest. 1968 Feb;47(2):261–267. doi: 10.1172/JCI105722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekjian H. S., Phillips S. F., Hofmann A. F. Colonic secretion of water and electrolytes induced by bile acids: perfusion studies in man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1569–1577. doi: 10.1172/JCI106644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer M. S., Heubi J. E., Goodrich A. L., Balistreri W. F., Suchy F. J. Ontogeny of bile acid transport in brush border membrane vesicles from rat ileum. Gastroenterology. 1986 May;90(5 Pt 1):1188–1196. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90384-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENNINGTON R. J. Biochemistry of dystrophic muscle. Mitochondrial succinate-tetrazolium reductase and adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80:649–654. doi: 10.1042/bj0800649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T. J. Analytical subcellular fractionation of jejunal biopsy specimens: methodology and characterization of the organelles in normal tissue. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Dec;51(6):557–574. doi: 10.1042/cs0510557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff E. R., Small N. C., Dietschy J. M. Characterization of the kinetics of the passive and active transport mechanisms for bile acid absorption in the small intestine and colon of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1351–1362. doi: 10.1172/JCI106931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz S. M., Watkins J. B., Ling S. C. Taurocholate transport by brush-border membrane vesicles from the developing rabbit ileum: structure/function relationships. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1990 May;10(4):482–489. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199005000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirazi-Beechey S. P., Gorvel J. P., Beechey R. B. Phosphate transport in intestinal brush-border membrane. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1988 Apr;20(2):273–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00768399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirazi-Beechey S. P., Hirayama B. A., Wang Y., Scott D., Smith M. W., Wright E. M. Ontogenic development of lamb intestinal sodium-glucose co-transporter is regulated by diet. J Physiol. 1991 Jun;437:699–708. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirazi S. P., Beechey R. B., Butterworth P. J. The use of potent inhibitors of alkaline phosphatase to investigate the role of the enzyme in intestinal transport of inorganic phosphate. Biochem J. 1981 Mar 15;194(3):803–809. doi: 10.1042/bj1940803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulsiani D. R., Opheim D. J., Touster O. Purification and characterization of alpha-D-mannosidase from rat liver golgi membranes. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3227–3233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson F. A. Intestinal transport of bile acids. Am J Physiol. 1981 Aug;241(2):G83–G92. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1981.241.2.G83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



