Abstract
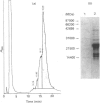
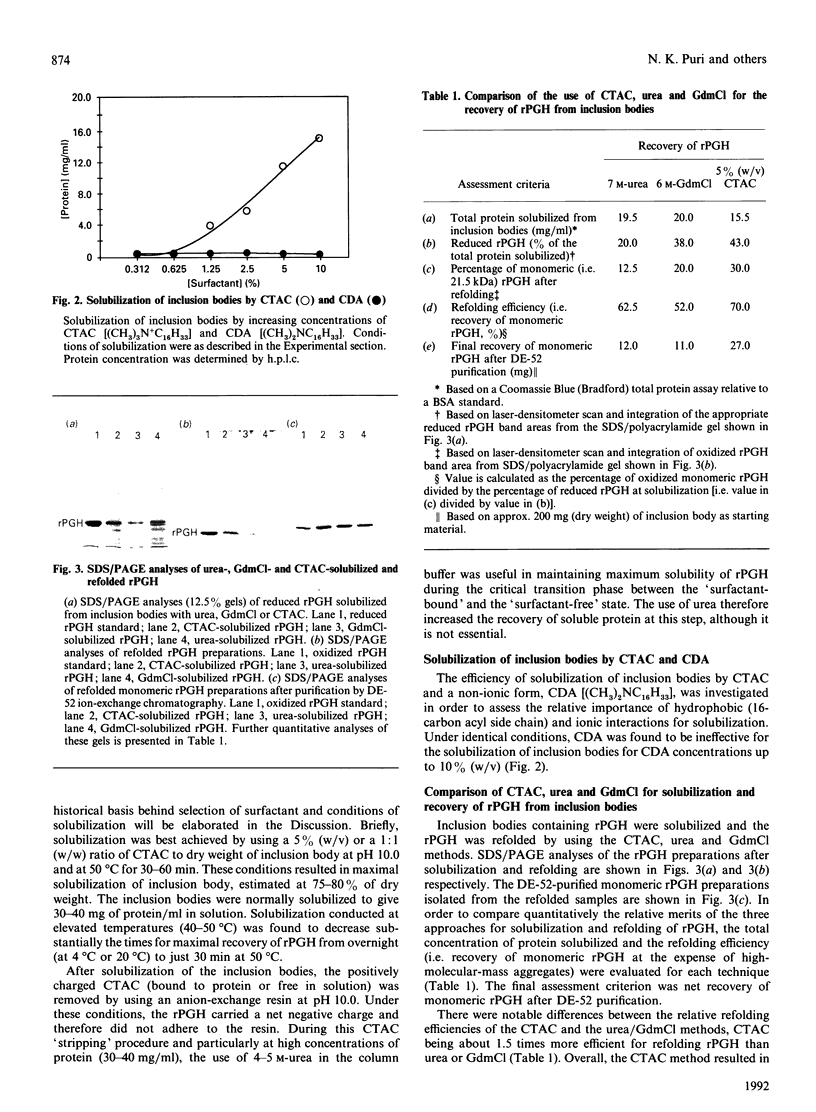
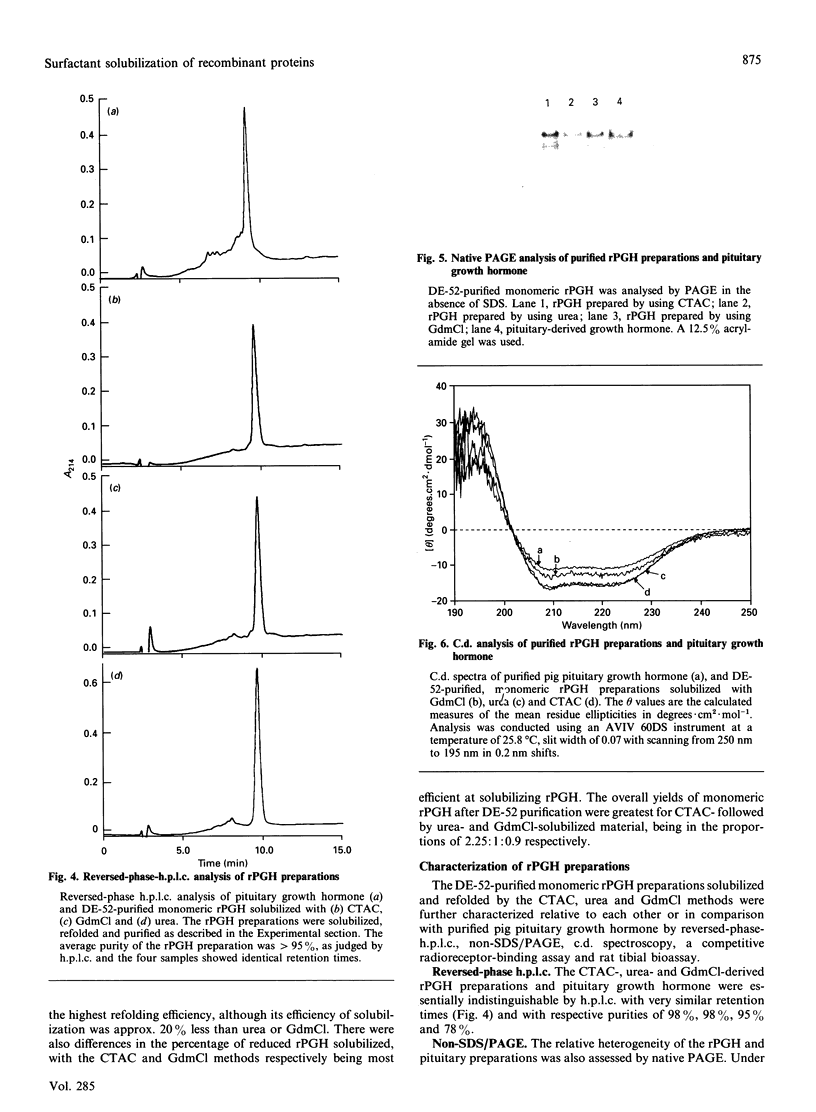
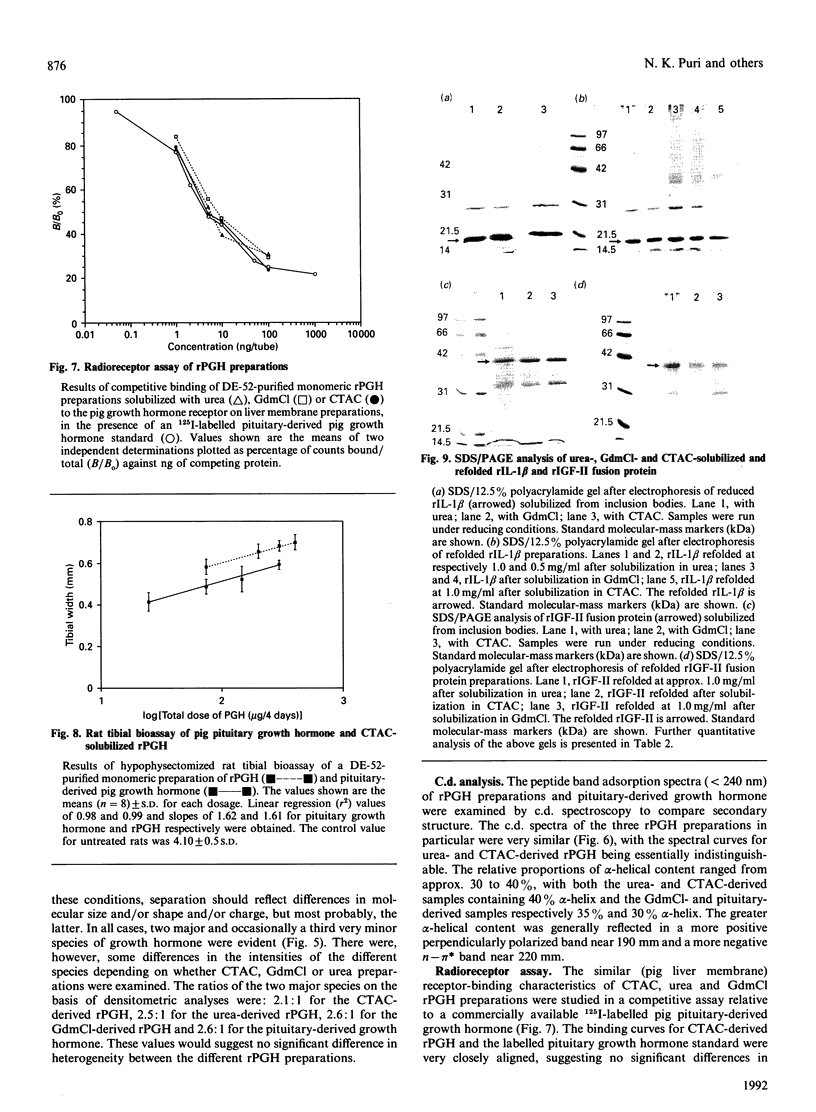
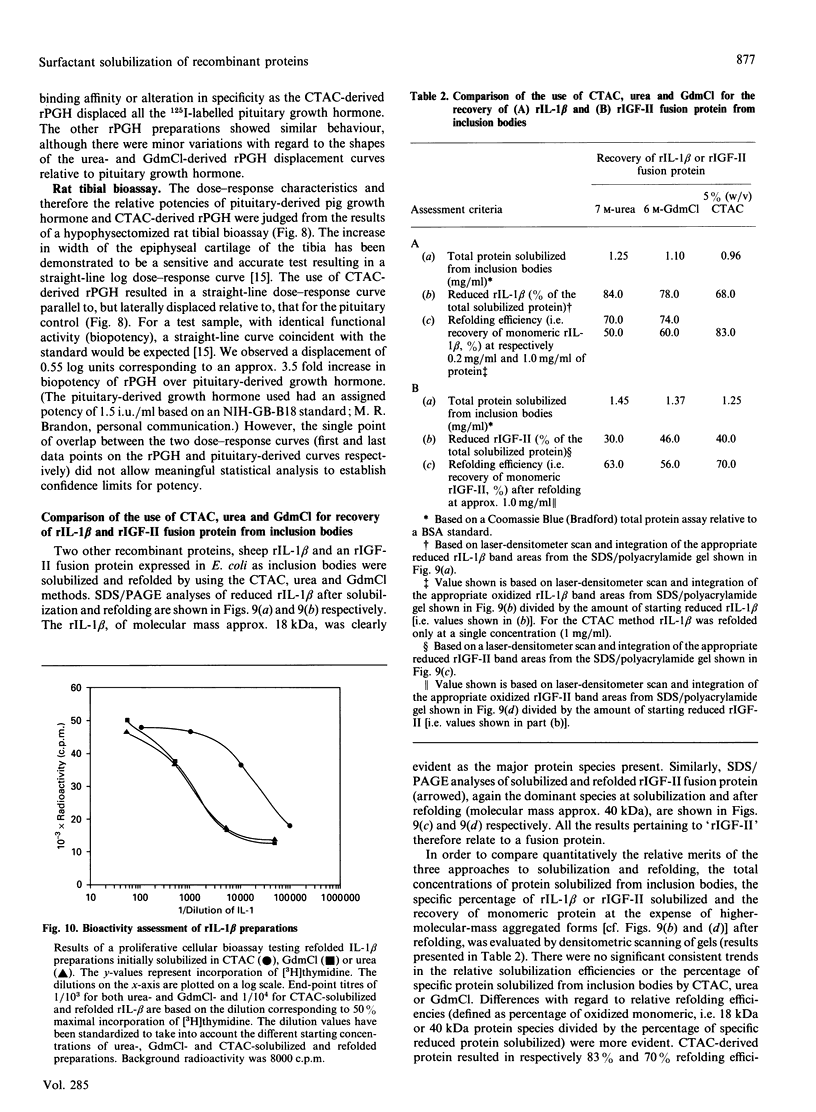
Recombinant pig growth hormone (rPGH) was solubilized from inclusion bodies by using the cationic surfactant cetyltrimethylammonium chloride (CTAC). The solubilizing action of CTAC appeared to be dependent on the presence of a positively charged head group, as a non-charged variant was inactive. Relatively low concentrations of CTAC were required for rapid solubilization, and protein-bound CTAC was easily removed by ion-exchange chromatography. Compared with solubilization and recovery of rPGH from inclusion bodies with 7.5 M-urea and 6 M-guanidinium chloride, the relative efficiency of solubilization was lower with CTAC. However, superior refolding efficiency resulted in final yields of purified rPGH being in the order of CTAC greater than urea greater than or equal to guanidinium chloride. Detailed comparison of the different rPGH preparations as well as pituitary-derived growth hormone by h.p.l.c., native PAGE, c.d. spectral analysis and radioreceptor-binding assay showed that the CTAC-derived rPGH was essentially indistinguishable from the urea and guanidinium chloride preparations. The CTAC-derived rPGH was of greater biopotency than pituitary-derived growth hormone. The advantages of CTAC over urea and guanidinium chloride for increasing recovery of monomeric rPGH by minimizing aggregation during refolding in vitro were also found with recombinant sheep interleukin-I beta and a sheep insulin-like growth factor II fusion protein. In addition, the bioactivity of the CTAC-derived recombinant interleukin-1 beta was approximately ten-fold greater than that of an equivalent amount obtained from urea and guanidinium chloride preparations. It is concluded that CTAC represents, in general, an excellent additional approach or a superior alternative to urea and in particular guanidinium chloride for solubilization and recovery of bioactive recombinant proteins from inclusion bodies.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akin D. T., Shapira R., Kinkade J. M., Jr The determination of molecular weights of biologically active proteins by cetyltrimethylammonium bromide-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1985 Feb 15;145(1):170–176. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90343-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews A. E., Barcham G. J., Brandon M. R., Nash A. D. Molecular cloning and characterization of ovine IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta. Immunology. 1991 Nov;74(3):453–460. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Zaltsman Z., Turtle J. R. Rat growth hormone (GH) but not prolactin (PRL) induces both GH and PRL receptors in female rat liver. Endocrinology. 1984 May;114(5):1893–1901. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-5-1893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J. S., Robertson H. A., Friesen H. G. Distribution of binding sites for ovine placental lactogen in the sheep. Endocrinology. 1978 Feb;102(2):632–640. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-2-632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing A. J., Bird C. R., Bristow A., Poole S., Thorpe R. A simple sensitive bioassay for interleukin-1 which is unresponsive to 10(3) U/ml of interleukin-2. J Immunol Methods. 1987 May 4;99(1):7–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley D. L., Kane J. F. Properties of inclusion bodies from recombinant Escherichia coli. Biochem Soc Trans. 1988 Apr;16(2):101–102. doi: 10.1042/bst0160101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. N., Skinner H. A., Tipping E., Wilkinson A. The interaction between ribonuclease A and surfactants. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;135(1):231–236. doi: 10.1042/bj1350231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marston F. A. The purification of eukaryotic polypeptides synthesized in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):1–12. doi: 10.1042/bj2400001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki Y., Reynolds J. A., Tanford C. The interaction of a cationic detergent with bovine serum albumin and other proteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4452–4459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahoney J. V., Adams T. E. Nucleotide sequence of an ovine insulin-like growth factor-II cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5392–5392. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace C. N. Determination and analysis of urea and guanidine hydrochloride denaturation curves. Methods Enzymol. 1986;131:266–280. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)31045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri N. K. Refolding of recombinant porcine growth hormone in a reducing environment limits in vitro aggregate formation. FEBS Lett. 1991 Nov 4;292(1-2):187–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80864-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein C. H. Solubility as a function of protein structure and solvent components. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 Apr;8(4):308–317. doi: 10.1038/nbt0490-308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian M., Sheshadri B. S., Venkatappa M. P. Interaction of cationic detergents, cetyl- and dodecyl-trimethylammonium bromides, with lysozyme. J Biochem. 1984 Feb;95(2):413–421. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarranton G. T., Wright E., Robinson M. K., Humphreys G. O. Dual-origin plasmid vectors whose origin of replication is controlled by the coliphage lambda promoter pL. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90146-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]